Siddharth Gandhi
Ministral 3
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:We introduce the Ministral 3 series, a family of parameter-efficient dense language models designed for compute and memory constrained applications, available in three model sizes: 3B, 8B, and 14B parameters. For each model size, we release three variants: a pretrained base model for general-purpose use, an instruction finetuned, and a reasoning model for complex problem-solving. In addition, we present our recipe to derive the Ministral 3 models through Cascade Distillation, an iterative pruning and continued training with distillation technique. Each model comes with image understanding capabilities, all under the Apache 2.0 license.
Voxtral
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:We present Voxtral Mini and Voxtral Small, two multimodal audio chat models. Voxtral is trained to comprehend both spoken audio and text documents, achieving state-of-the-art performance across a diverse range of audio benchmarks, while preserving strong text capabilities. Voxtral Small outperforms a number of closed-source models, while being small enough to run locally. A 32K context window enables the model to handle audio files up to 40 minutes in duration and long multi-turn conversations. We also contribute three benchmarks for evaluating speech understanding models on knowledge and trivia. Both Voxtral models are released under Apache 2.0 license.
Magistral
Jun 12, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Magistral, Mistral's first reasoning model and our own scalable reinforcement learning (RL) pipeline. Instead of relying on existing implementations and RL traces distilled from prior models, we follow a ground up approach, relying solely on our own models and infrastructure. Notably, we demonstrate a stack that enabled us to explore the limits of pure RL training of LLMs, present a simple method to force the reasoning language of the model, and show that RL on text data alone maintains most of the initial checkpoint's capabilities. We find that RL on text maintains or improves multimodal understanding, instruction following and function calling. We present Magistral Medium, trained for reasoning on top of Mistral Medium 3 with RL alone, and we open-source Magistral Small (Apache 2.0) which further includes cold-start data from Magistral Medium.
Unified Multimodal Discrete Diffusion
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Multimodal generative models that can understand and generate across multiple modalities are dominated by autoregressive (AR) approaches, which process tokens sequentially from left to right, or top to bottom. These models jointly handle images, text, video, and audio for various tasks such as image captioning, question answering, and image generation. In this work, we explore discrete diffusion models as a unified generative formulation in the joint text and image domain, building upon their recent success in text generation. Discrete diffusion models offer several advantages over AR models, including improved control over quality versus diversity of generated samples, the ability to perform joint multimodal inpainting (across both text and image domains), and greater controllability in generation through guidance. Leveraging these benefits, we present the first Unified Multimodal Discrete Diffusion (UniDisc) model which is capable of jointly understanding and generating text and images for a variety of downstream tasks. We compare UniDisc to multimodal AR models, performing a scaling analysis and demonstrating that UniDisc outperforms them in terms of both performance and inference-time compute, enhanced controllability, editability, inpainting, and flexible trade-off between inference time and generation quality. Code and additional visualizations are available at https://unidisc.github.io.
Repository-level Code Search with Neural Retrieval Methods
Feb 10, 2025
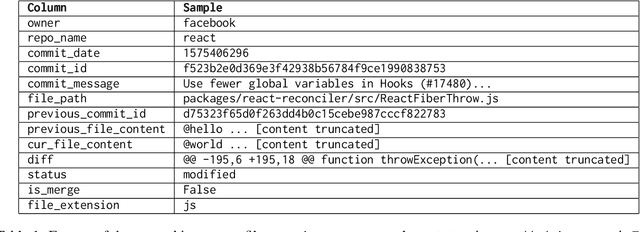
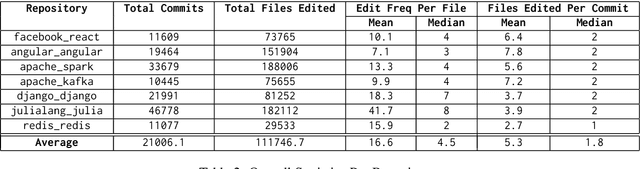

Abstract:This paper presents a multi-stage reranking system for repository-level code search, which leverages the vastly available commit histories of large open-source repositories to aid in bug fixing. We define the task of repository-level code search as retrieving the set of files from the current state of a code repository that are most relevant to addressing a user's question or bug. The proposed approach combines BM25-based retrieval over commit messages with neural reranking using CodeBERT to identify the most pertinent files. By learning patterns from diverse repositories and their commit histories, the system can surface relevant files for the task at hand. The system leverages both commit messages and source code for relevance matching, and is evaluated in both normal and oracle settings. Experiments on a new dataset created from 7 popular open-source repositories demonstrate substantial improvements of up to 80% in MAP, MRR and P@1 over the BM25 baseline, across a diverse set of queries, demonstrating the effectiveness this approach. We hope this work aids LLM agents as a tool for better code search and understanding. Our code and results obtained are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge