Siau-Cheng Khoo
Expediting Neural Network Verification via Network Reduction
Aug 14, 2023Abstract:A wide range of verification methods have been proposed to verify the safety properties of deep neural networks ensuring that the networks function correctly in critical applications. However, many well-known verification tools still struggle with complicated network architectures and large network sizes. In this work, we propose a network reduction technique as a pre-processing method prior to verification. The proposed method reduces neural networks via eliminating stable ReLU neurons, and transforming them into a sequential neural network consisting of ReLU and Affine layers which can be handled by the most verification tools. We instantiate the reduction technique on the state-of-the-art complete and incomplete verification tools, including alpha-beta-crown, VeriNet and PRIMA. Our experiments on a large set of benchmarks indicate that the proposed technique can significantly reduce neural networks and speed up existing verification tools. Furthermore, the experiment results also show that network reduction can improve the availability of existing verification tools on many networks by reducing them into sequential neural networks.
Scalable and Modular Robustness Analysis of Deep Neural Networks
Aug 31, 2021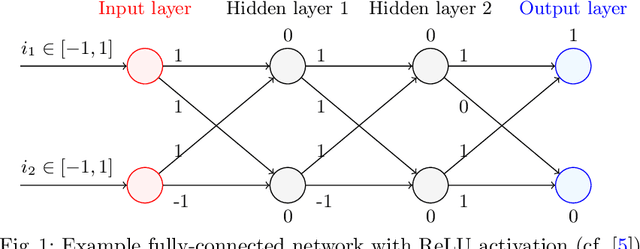

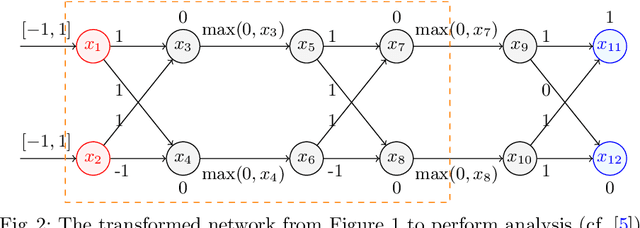
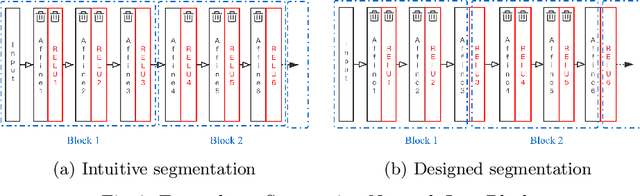
Abstract:As neural networks are trained to be deeper and larger, the scalability of neural network analyzers is urgently required. The main technical insight of our method is modularly analyzing neural networks by segmenting a network into blocks and conduct the analysis for each block. In particular, we propose the network block summarization technique to capture the behaviors within a network block using a block summary and leverage the summary to speed up the analysis process. We instantiate our method in the context of a CPU-version of the state-of-the-art analyzer DeepPoly and name our system as Bounded-Block Poly (BBPoly). We evaluate BBPoly extensively on various experiment settings. The experimental result indicates that our method yields comparable precision as DeepPoly but runs faster and requires less computational resources. For example, BBPoly can analyze really large neural networks like SkipNet or ResNet which contain up to one million neurons in less than around 1 hour per input image, while DeepPoly needs to spend even 40 hours to analyze one image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge