Shyamali Mitra
An ensemble framework approach of hybrid Quantum convolutional neural networks for classification of breast cancer images
Sep 24, 2024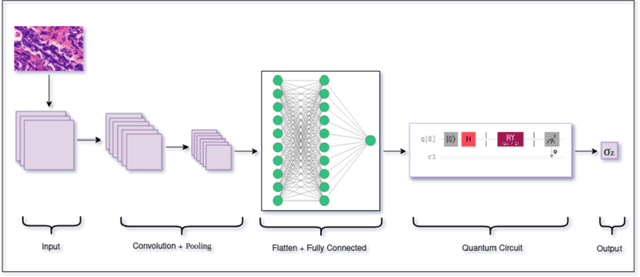
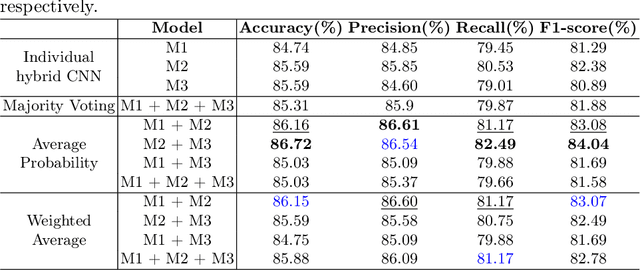

Abstract:Quantum neural networks are deemed suitable to replace classical neural networks in their ability to learn and scale up network models using quantum-exclusive phenomena like superposition and entanglement. However, in the noisy intermediate scale quantum (NISQ) era, the trainability and expressibility of quantum models are yet under investigation. Medical image classification on the other hand, pertains well to applications in deep learning, particularly, convolutional neural networks. In this paper, we carry out a study of three hybrid classical-quantum neural network architectures and combine them using standard ensembling techniques on a breast cancer histopathological dataset. The best accuracy percentage obtained by an individual model is 85.59. Whereas, on performing ensemble, we have obtained accuracy as high as 86.72%, an improvement over the individual hybrid network as well as classical neural network counterparts of the hybrid network models.
Cytology Image Analysis Techniques Towards Automation: Systematically Revisited
Mar 17, 2020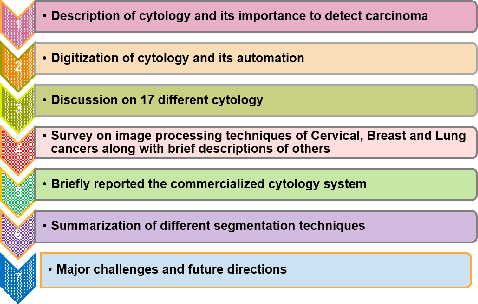
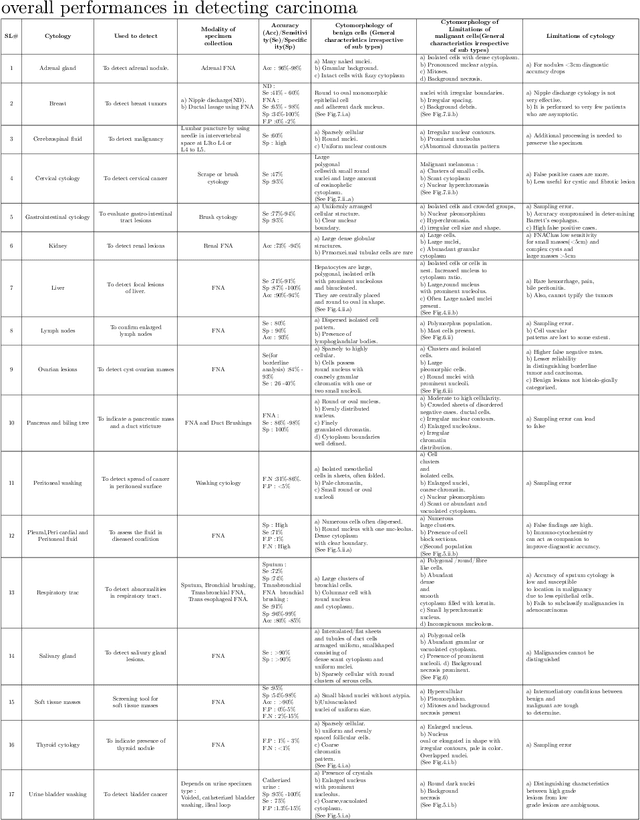
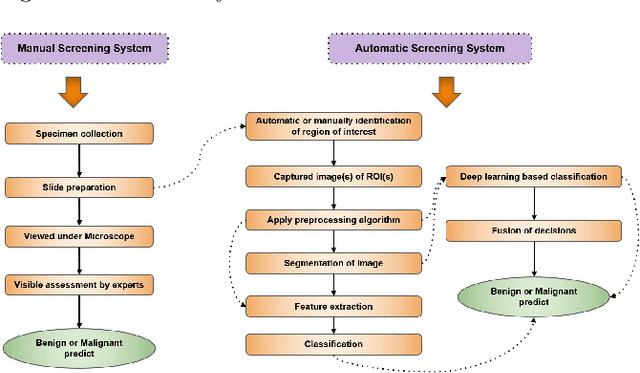
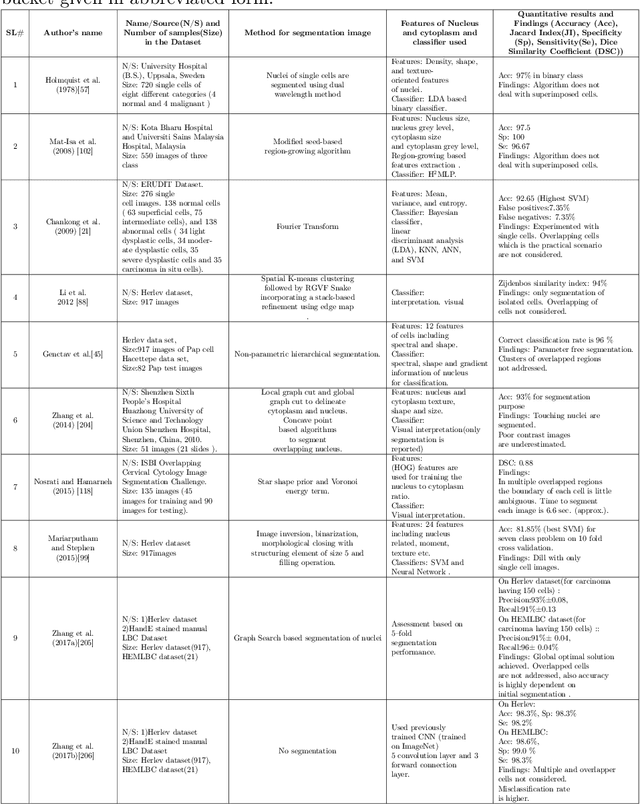
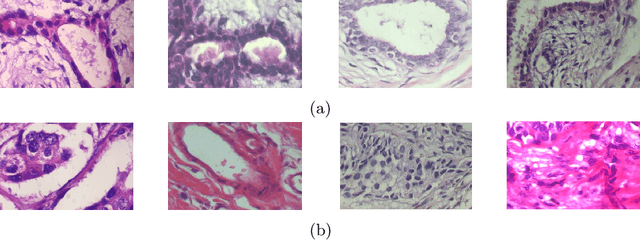
Abstract:Cytology is the branch of pathology which deals with the microscopic examination of cells for diagnosis of carcinoma or inflammatory conditions. Automation in cytology started in the early 1950s with the aim to reduce manual efforts in diagnosis of cancer. The inflush of intelligent technological units with high computational power and improved specimen collection techniques helped to achieve its technological heights. In the present survey, we focus on such image processing techniques which put steps forward towards the automation of cytology. We take a short tour to 17 types of cytology and explore various segmentation and/or classification techniques which evolved during last three decades boosting the concept of automation in cytology. It is observed, that most of the works are aligned towards three types of cytology: Cervical, Breast and Lung, which are discussed elaborately in this paper. The user-end systems developed during that period are summarized to comprehend the overall growth in the respective domains. To be precise, we discuss the diversity of the state-of-the-art methodologies, their challenges to provide prolific and competent future research directions inbringing the cytology-based commercial systems into the mainstream.
SynCGAN: Using learnable class specific priors to generate synthetic data for improving classifier performance on cytological images
Mar 12, 2020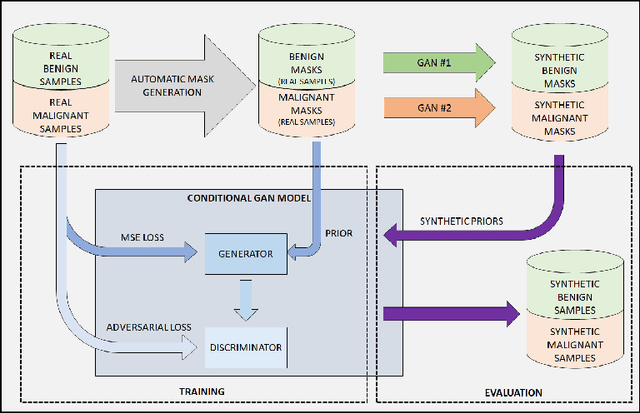

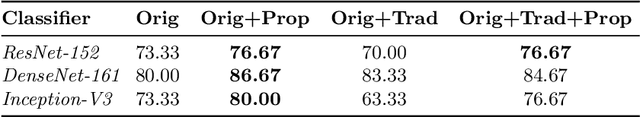
Abstract:One of the most challenging aspects of medical image analysis is the lack of a high quantity of annotated data. This makes it difficult for deep learning algorithms to perform well due to a lack of variations in the input space. While generative adversarial networks have shown promise in the field of synthetic data generation, but without a carefully designed prior the generation procedure can not be performed well. In the proposed approach we have demonstrated the use of automatically generated segmentation masks as learnable class-specific priors to guide a conditional GAN for the generation of patho-realistic samples for cytology image. We have observed that augmentation of data using the proposed pipeline called "SynCGAN" improves the performance of state of the art classifiers such as ResNet-152, DenseNet-161, Inception-V3 significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge