Shuzhe Shi
Physics-Driven Learning for Inverse Problems in Quantum Chromodynamics
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:The integration of deep learning techniques and physics-driven designs is reforming the way we address inverse problems, in which accurate physical properties are extracted from complex data sets. This is particularly relevant for quantum chromodynamics (QCD), the theory of strong interactions, with its inherent limitations in observational data and demanding computational approaches. This perspective highlights advances and potential of physics-driven learning methods, focusing on predictions of physical quantities towards QCD physics, and drawing connections to machine learning(ML). It is shown that the fusion of ML and physics can lead to more efficient and reliable problem-solving strategies. Key ideas of ML, methodology of embedding physics priors, and generative models as inverse modelling of physical probability distributions are introduced. Specific applications cover first-principle lattice calculations, and QCD physics of hadrons, neutron stars, and heavy-ion collisions. These examples provide a structured and concise overview of how incorporating prior knowledge such as symmetry, continuity and equations into deep learning designs can address diverse inverse problems across different physical sciences.
* 14 pages, 5 figures, submitted version to Nat Rev Phys
Reconstructing spectral functions via automatic differentiation
Jan 01, 2022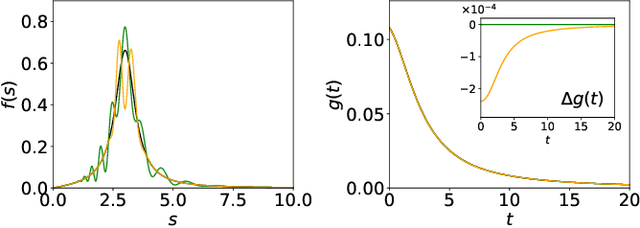
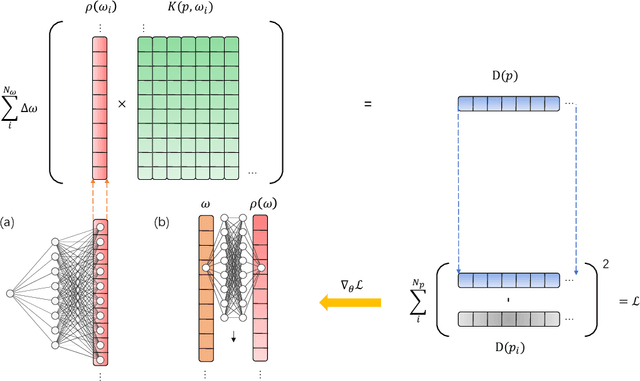
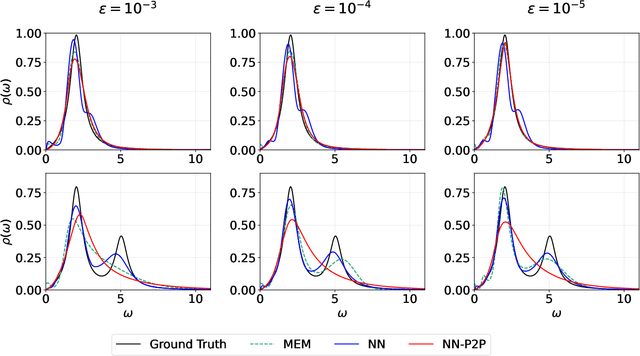
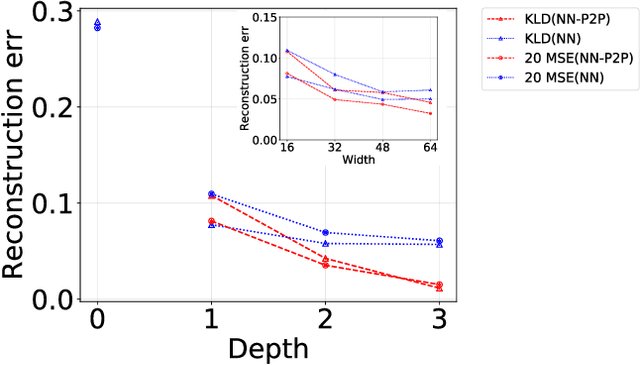
Abstract:Reconstructing spectral functions from Euclidean Green's functions is an important inverse problem in many-body physics. However, the inversion is proved to be ill-posed in the realistic systems with noisy Green's functions. In this Letter, we propose an automatic differentiation(AD) framework as a generic tool for the spectral reconstruction from propagator observable. Exploiting the neural networks' regularization as a non-local smoothness regulator of the spectral function, we represent spectral functions by neural networks and use the propagator's reconstruction error to optimize the network parameters unsupervisedly. In the training process, except for the positive-definite form for the spectral function, there are no other explicit physical priors embedded into the neural networks. The reconstruction performance is assessed through relative entropy and mean square error for two different network representations. Compared to the maximum entropy method, the AD framework achieves better performance in the large-noise situation. It is noted that the freedom of introducing non-local regularization is an inherent advantage of the present framework and may lead to substantial improvements in solving inverse problems.
Automatic differentiation approach for reconstructing spectral functions with neural networks
Dec 12, 2021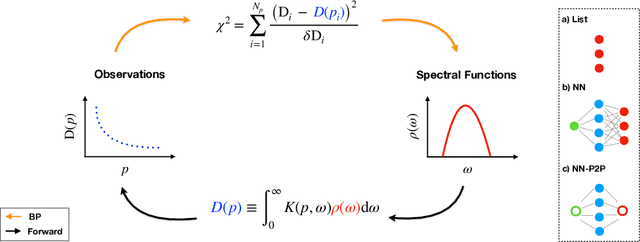
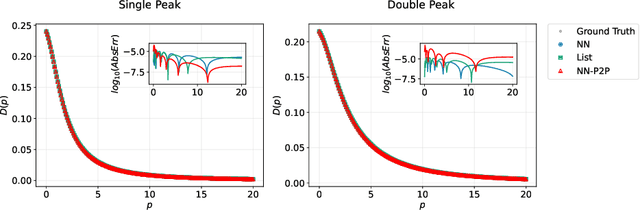
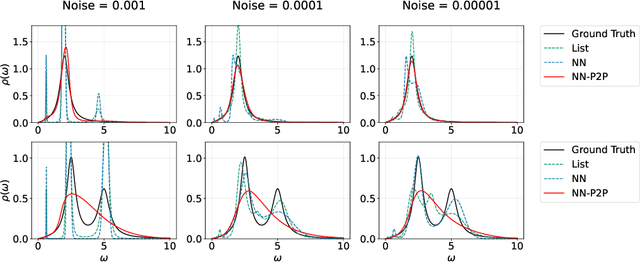
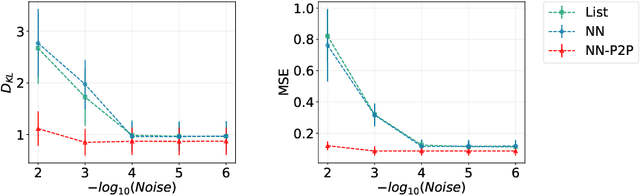
Abstract:Reconstructing spectral functions from Euclidean Green's functions is an important inverse problem in physics. The prior knowledge for specific physical systems routinely offers essential regularization schemes for solving the ill-posed problem approximately. Aiming at this point, we propose an automatic differentiation framework as a generic tool for the reconstruction from observable data. We represent the spectra by neural networks and set chi-square as loss function to optimize the parameters with backward automatic differentiation unsupervisedly. In the training process, there is no explicit physical prior embedding into neural networks except the positive-definite form. The reconstruction accuracy is assessed through Kullback-Leibler(KL) divergence and mean square error(MSE) at multiple noise levels. It should be noted that the automatic differential framework and the freedom of introducing regularization are inherent advantages of the present approach and may lead to improvements of solving inverse problem in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge