Shuangxun Ma
Tensor-based Intrinsic Subspace Representation Learning for Multi-view Clustering
Nov 12, 2020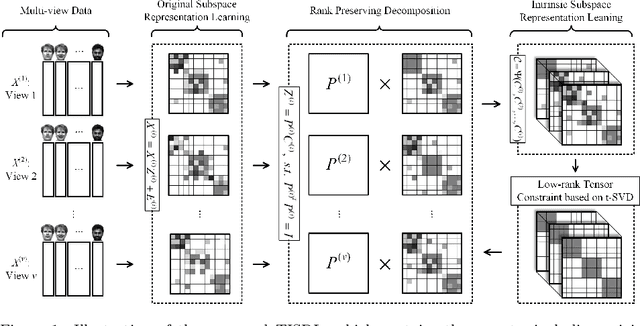
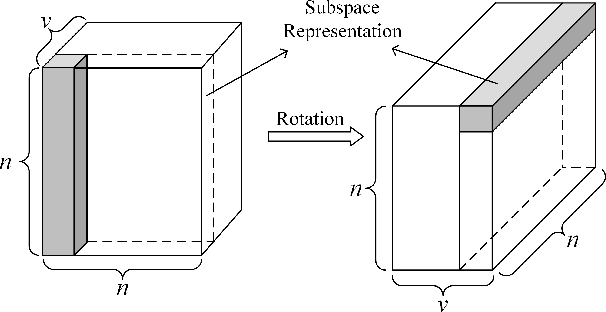
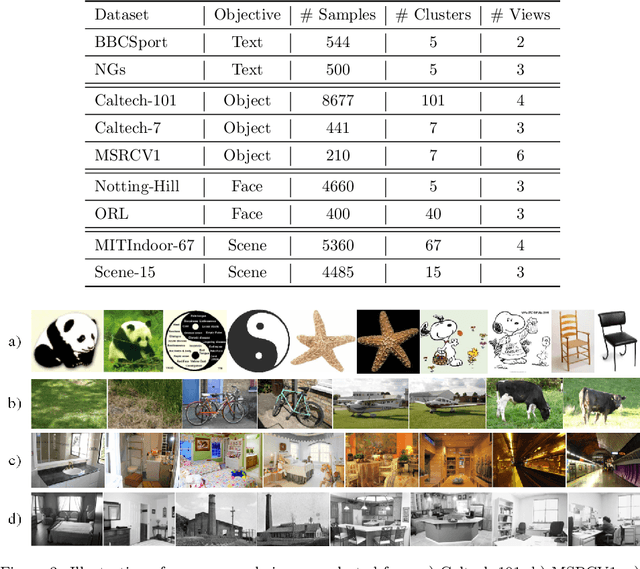
Abstract:As a hot research topic, many multi-view clustering approaches are proposed over the past few years. Nevertheless, most existing algorithms merely take the consensus information among different views into consideration for clustering. Actually, it may hinder the multi-view clustering performance in real-life applications, since different views usually contain diverse statistic properties. To address this problem, we propose a novel Tensor-based Intrinsic Subspace Representation Learning (TISRL) for multi-view clustering in this paper. Concretely, the rank preserving decomposition is proposed firstly to effectively deal with the diverse statistic information contained in different views. Then, to achieve the intrinsic subspace representation, the tensor-singular value decomposition based low-rank tensor constraint is also utilized in our method. It can be seen that specific information contained in different views is fully investigated by the rank preserving decomposition, and the high-order correlations of multi-view data are also mined by the low-rank tensor constraint. The objective function can be optimized by an augmented Lagrangian multiplier based alternating direction minimization algorithm. Experimental results on nine common used real-world multi-view datasets illustrate the superiority of TISRL.
Multi-view Hierarchical Clustering
Oct 15, 2020



Abstract:This paper focuses on the multi-view clustering, which aims to promote clustering results with multi-view data. Usually, most existing works suffer from the issues of parameter selection and high computational complexity. To overcome these limitations, we propose a Multi-view Hierarchical Clustering (MHC), which partitions multi-view data recursively at multiple levels of granularity. Specifically, MHC consists of two important components: the cosine distance integration (CDI) and the nearest neighbor agglomeration (NNA). The CDI can explore the underlying complementary information of multi-view data so as to learn an essential distance matrix, which is utilized in NNA to obtain the clustering results. Significantly, the proposed MHC can be easily and effectively employed in real-world applications without parameter selection. Experiments on nine benchmark datasets illustrate the superiority of our method comparing to several state-of-the-art multi-view clustering methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge