Shreyas Kapur
Evidence of Learned Look-Ahead in a Chess-Playing Neural Network
Jun 02, 2024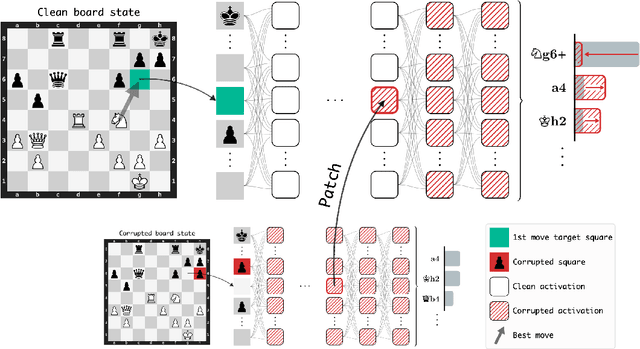
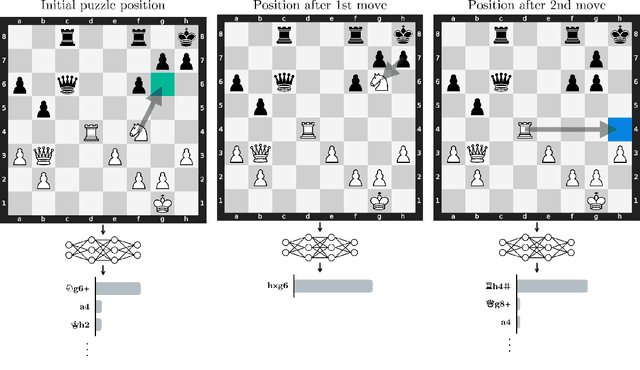
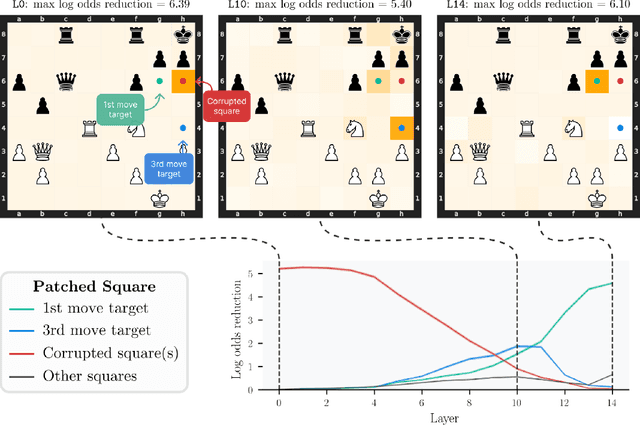
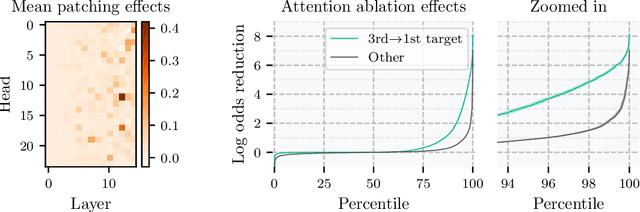
Abstract:Do neural networks learn to implement algorithms such as look-ahead or search "in the wild"? Or do they rely purely on collections of simple heuristics? We present evidence of learned look-ahead in the policy network of Leela Chess Zero, the currently strongest neural chess engine. We find that Leela internally represents future optimal moves and that these representations are crucial for its final output in certain board states. Concretely, we exploit the fact that Leela is a transformer that treats every chessboard square like a token in language models, and give three lines of evidence (1) activations on certain squares of future moves are unusually important causally; (2) we find attention heads that move important information "forward and backward in time," e.g., from squares of future moves to squares of earlier ones; and (3) we train a simple probe that can predict the optimal move 2 turns ahead with 92% accuracy (in board states where Leela finds a single best line). These findings are an existence proof of learned look-ahead in neural networks and might be a step towards a better understanding of their capabilities.
Diffusion On Syntax Trees For Program Synthesis
May 30, 2024Abstract:Large language models generate code one token at a time. Their autoregressive generation process lacks the feedback of observing the program's output. Training LLMs to suggest edits directly can be challenging due to the scarcity of rich edit data. To address these problems, we propose neural diffusion models that operate on syntax trees of any context-free grammar. Similar to image diffusion models, our method also inverts ``noise'' applied to syntax trees. Rather than generating code sequentially, we iteratively edit it while preserving syntactic validity, which makes it easy to combine this neural model with search. We apply our approach to inverse graphics tasks, where our model learns to convert images into programs that produce those images. Combined with search, our model is able to write graphics programs, see the execution result, and debug them to meet the required specifications. We additionally show how our system can write graphics programs for hand-drawn sketches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge