Shrey Aggarwal
Rapid Likelihood Free Inference of Compact Binary Coalescences using Accelerated Hardware
Jul 26, 2024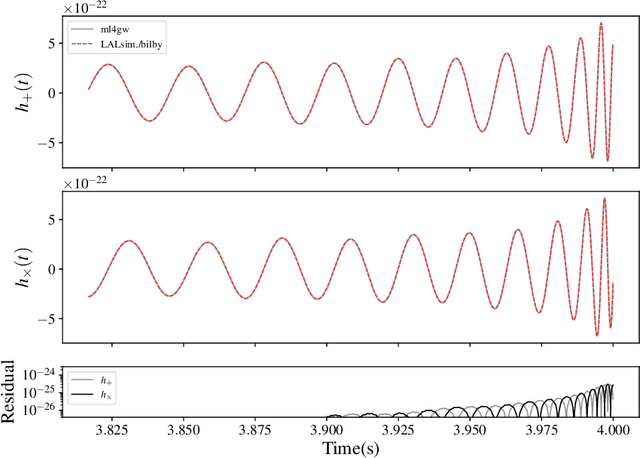
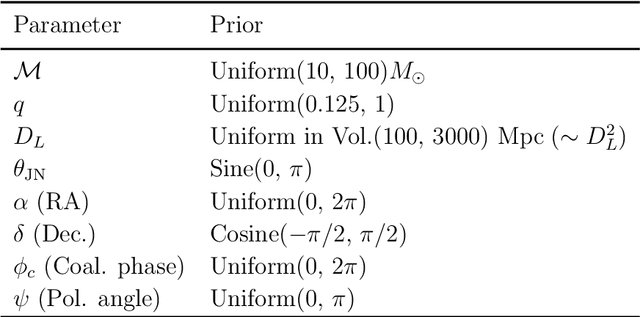
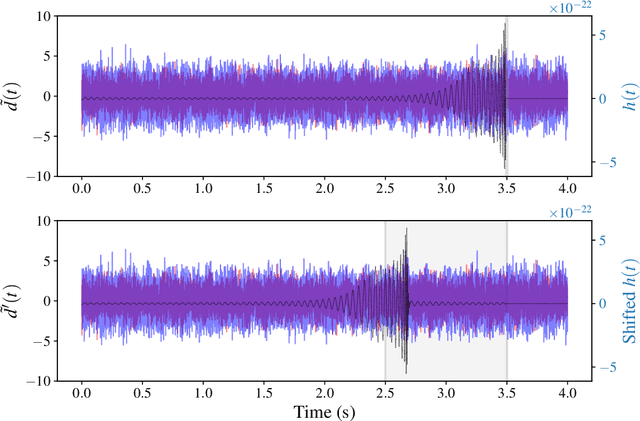
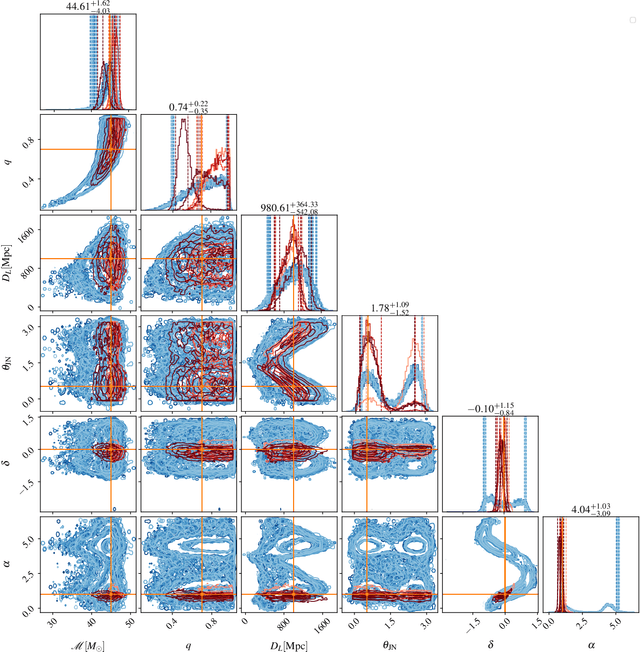
Abstract:We report a gravitational-wave parameter estimation algorithm, AMPLFI, based on likelihood-free inference using normalizing flows. The focus of AMPLFI is to perform real-time parameter estimation for candidates detected by machine-learning based compact binary coalescence search, Aframe. We present details of our algorithm and optimizations done related to data-loading and pre-processing on accelerated hardware. We train our model using binary black-hole (BBH) simulations on real LIGO-Virgo detector noise. Our model has $\sim 6$ million trainable parameters with training times $\lesssim 24$ hours. Based on online deployment on a mock data stream of LIGO-Virgo data, Aframe + AMPLFI is able to pick up BBH candidates and infer parameters for real-time alerts from data acquisition with a net latency of $\sim 6$s.
Mimetic Muscle Rehabilitation Analysis Using Clustering of Low Dimensional 3D Kinect Data
Feb 15, 2023Abstract:Facial nerve paresis is a severe complication that arises post-head and neck surgery; This results in articulation problems, facial asymmetry, and severe problems in non-verbal communication. To overcome the side effects of post-surgery facial paralysis, rehabilitation requires which last for several weeks. This paper discusses an unsupervised approach to rehabilitating patients who have temporary facial paralysis due to damage in mimetic muscles. The work aims to make the rehabilitation process objective compared to the current subjective approach, such as House-Brackmann (HB) scale. Also, the approach will assist clinicians by reducing their workload in assessing the improvement during rehabilitation. This paper focuses on the clustering approach to monitor the rehabilitation process. We compare the results obtained from different clustering algorithms on various forms of the same data set, namely dynamic form, data expressed as functional data using B-spline basis expansion, and by finding the functional principal components of the functional data. The study contains data set of 85 distinct patients with 120 measurements obtained using a Kinect stereo-vision camera. The method distinguish effectively between patients with the least and greatest degree of facial paralysis, however patients with adjacent degrees of paralysis provide some challenges. In addition, we compared the cluster results to the HB scale outputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge