Shravan Vasishth
Deconstructing sentence disambiguation by joint latent modeling of reading paradigms: LLM surprisal is not enough
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Using temporarily ambiguous garden-path sentences ("While the team trained the striker wondered ...") as a test case, we present a latent-process mixture model of human reading behavior across four different reading paradigms (eye tracking, uni- and bidirectional self-paced reading, Maze). The model distinguishes between garden-path probability, garden-path cost, and reanalysis cost, and yields more realistic processing cost estimates by taking into account trials with inattentive reading. We show that the model is able to reproduce empirical patterns with regard to rereading behavior, comprehension question responses, and grammaticality judgments. Cross-validation reveals that the mixture model also has better predictive fit to human reading patterns and end-of-trial task data than a mixture-free model based on GPT-2-derived surprisal values. We discuss implications for future work.
SEAM: An Integrated Activation-Coupled Model of Sentence Processing and Eye Movements in Reading
Mar 09, 2023



Abstract:Models of eye-movement control during reading, developed largely within psychology, usually focus on visual, attentional, and motor processes but neglect post-lexical language processing; by contrast, models of sentence comprehension processes, developed largely within psycholinguistics, generally focus only on post-lexical language processes. We present a model that combines these two research threads, by integrating eye-movement control and sentence processing. Developing such an integrated model is extremely challenging and computationally demanding, but such an integration is an important step toward complete mathematical models of natural language comprehension in reading. We combine the SWIFT model of eye-movement control (Engbert et al., Psychological Review, 112, 2005, pp. 777-813) with key components of the Lewis and Vasishth sentence processing model (Lewis and Vasishth, Cognitive Science, 29, 2005, pp. 375-419). This integration becomes possible, for the first time, due in part to recent advances in successful parameter identification in dynamical models, which allows us to investigate profile log-likelihoods for individual model parameters. We present a fully implemented proof-of-concept model demonstrating how such an integrated model can be achieved; our approach includes Bayesian model inference with Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling as a key computational tool. The integrated model, SEAM, can successfully reproduce eye movement patterns that arise due to similarity-based interference in reading. To our knowledge, this is the first-ever integration of a complete process model of eye-movement control with linguistic dependency completion processes in sentence comprehension. In future work, this proof of concept model will need to be evaluated using a comprehensive set of benchmark data.
Feature overwriting as a finite mixture process: Evidence from comprehension data
Jan 20, 2018


Abstract:The ungrammatical sentence "The key to the cabinets are on the table" is known to lead to an illusion of grammaticality. As discussed in the meta-analysis by Jaeger et al., 2017, faster reading times are observed at the verb are in the agreement-attraction sentence above compared to the equally ungrammatical sentence "The key to the cabinet are on the table". One explanation for this facilitation effect is the feature percolation account: the plural feature on cabinets percolates up to the head noun key, leading to the illusion. An alternative account is in terms of cue-based retrieval (Lewis & Vasishth, 2005), which assumes that the non-subject noun cabinets is misretrieved due to a partial feature-match when a dependency completion process at the auxiliary initiates a memory access for a subject with plural marking. We present evidence for yet another explanation for the observed facilitation. Because the second sentence has two nouns with identical number, it is possible that these are, in some proportion of trials, more difficult to keep distinct, leading to slower reading times at the verb in the first sentence above; this is the feature overwriting account of Nairne, 1990. We show that the feature overwriting proposal can be implemented as a finite mixture process. We reanalysed ten published data-sets, fitting hierarchical Bayesian mixture models to these data assuming a two-mixture distribution. We show that in nine out of the ten studies, a mixture distribution corresponding to feature overwriting furnishes a superior fit over both the feature percolation and the cue-based retrieval accounts.
Models of retrieval in sentence comprehension: A computational evaluation using Bayesian hierarchical modeling
Aug 24, 2017



Abstract:Research on interference has provided evidence that the formation of dependencies between non-adjacent words relies on a cue-based retrieval mechanism. Two different models can account for one of the main predictions of interference, i.e., a slowdown at a retrieval site, when several items share a feature associated with a retrieval cue: Lewis and Vasishth's (2005) activation-based model and McElree's (2000) direct access model. Even though these two models have been used almost interchangeably, they are based on different assumptions and predict differences in the relationship between reading times and response accuracy. The activation-based model follows the assumptions of ACT-R, and its retrieval process behaves as a lognormal race between accumulators of evidence with a single variance. Under this model, accuracy of the retrieval is determined by the winner of the race and retrieval time by its rate of accumulation. In contrast, the direct access model assumes a model of memory where only the probability of retrieval varies between items; in this model, differences in latencies are a by-product of the possibility and repairing incorrect retrievals. We implemented both models in a Bayesian hierarchical framework in order to evaluate them and compare them. We show that some aspects of the data are better fit under the direct access model than under the activation-based model. We suggest that this finding does not rule out the possibility that retrieval may be behaving as a race model with assumptions that follow less closely the ones from the ACT-R framework. We show that by introducing a modification of the activation model, i.e, by assuming that the accumulation of evidence for retrieval of incorrect items is not only slower but noisier (i.e., different variances for the correct and incorrect items), the model can provide a fit as good as the one of the direct access model.
A computational investigation of sources of variability in sentence comprehension difficulty in aphasia
May 31, 2017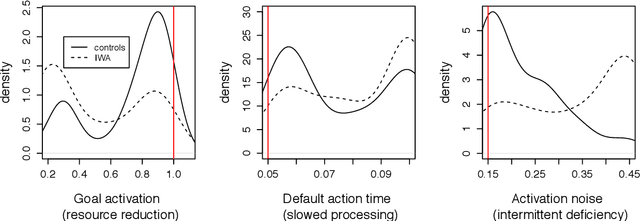
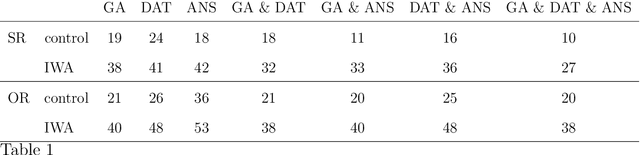
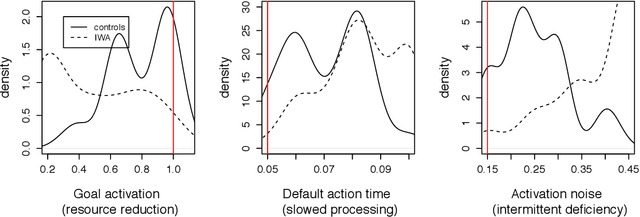
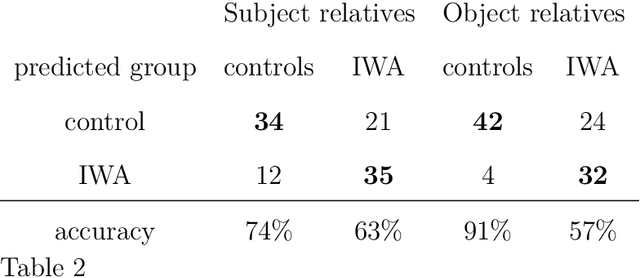
Abstract:We present a computational evaluation of three hypotheses about sources of deficit in sentence comprehension in aphasia: slowed processing, intermittent deficiency, and resource reduction. The ACT-R based Lewis and Vasishth (2005) model is used to implement these three proposals. Slowed processing is implemented as slowed default production-rule firing time; intermittent deficiency as increased random noise in activation of chunks in memory; and resource reduction as reduced goal activation. As data, we considered subject vs. object rela- tives whose matrix clause contained either an NP or a reflexive, presented in a self-paced listening modality to 56 individuals with aphasia (IWA) and 46 matched controls. The participants heard the sentences and carried out a picture verification task to decide on an interpretation of the sentence. These response accuracies are used to identify the best parameters (for each participant) that correspond to the three hypotheses mentioned above. We show that controls have more tightly clustered (less variable) parameter values than IWA; specifically, compared to controls, among IWA there are more individuals with low goal activations, high noise, and slow default action times. This suggests that (i) individual patients show differential amounts of deficit along the three dimensions of slowed processing, intermittent deficient, and resource reduction, (ii) overall, there is evidence for all three sources of deficit playing a role, and (iii) IWA have a more variable range of parameter values than controls. In sum, this study contributes a proof of concept of a quantitative implementation of, and evidence for, these three accounts of comprehension deficits in aphasia.
Modelling dependency completion in sentence comprehension as a Bayesian hierarchical mixture process: A case study involving Chinese relative clauses
May 05, 2017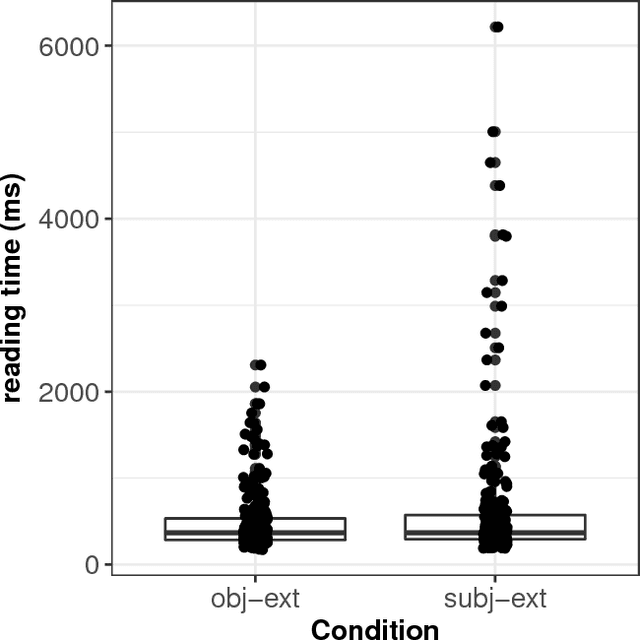
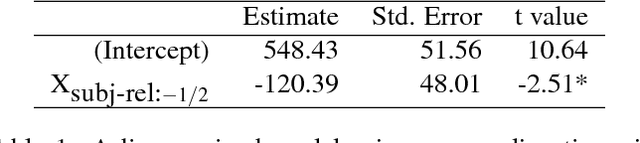
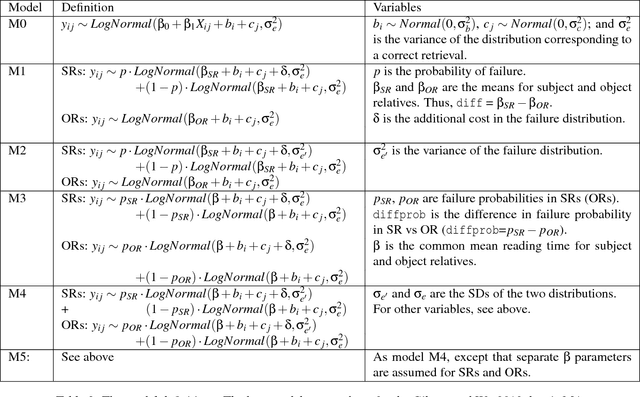
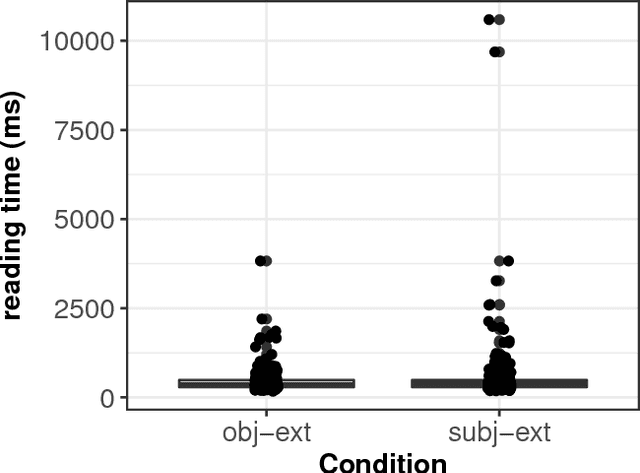
Abstract:We present a case-study demonstrating the usefulness of Bayesian hierarchical mixture modelling for investigating cognitive processes. In sentence comprehension, it is widely assumed that the distance between linguistic co-dependents affects the latency of dependency resolution: the longer the distance, the longer the retrieval time (the distance-based account). An alternative theory, direct-access, assumes that retrieval times are a mixture of two distributions: one distribution represents successful retrievals (these are independent of dependency distance) and the other represents an initial failure to retrieve the correct dependent, followed by a reanalysis that leads to successful retrieval. We implement both models as Bayesian hierarchical models and show that the direct-access model explains Chinese relative clause reading time data better than the distance account.
Introduction: Cognitive Issues in Natural Language Processing
Oct 24, 2016Abstract:This special issue is dedicated to get a better picture of the relationships between computational linguistics and cognitive science. It specifically raises two questions: "what is the potential contribution of computational language modeling to cognitive science?" and conversely: "what is the influence of cognitive science in contemporary computational linguistics?"
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge