Shivam Pal
Federated Learning with Uncertainty and Personalization via Efficient Second-order Optimization
Nov 27, 2024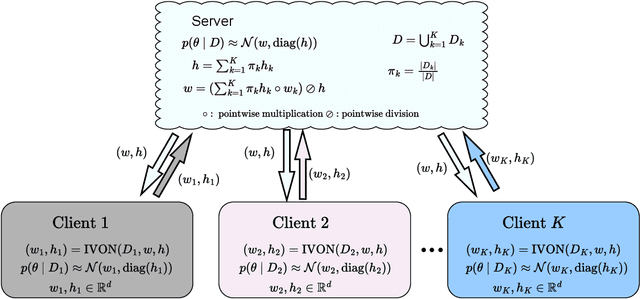
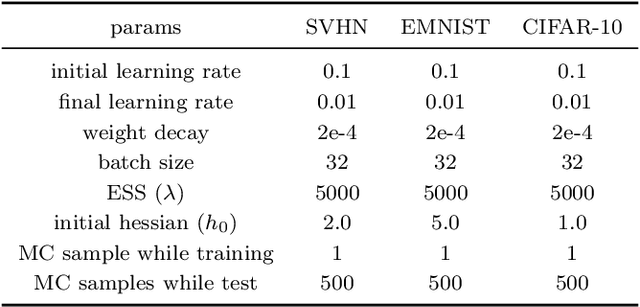
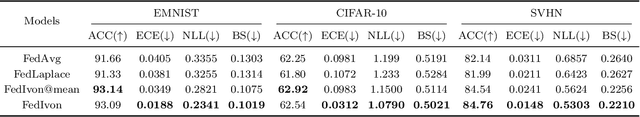

Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a promising method to collaboratively learn from decentralized and heterogeneous data available at different clients without the requirement of data ever leaving the clients. Recent works on FL have advocated taking a Bayesian approach to FL as it offers a principled way to account for the model and predictive uncertainty by learning a posterior distribution for the client and/or server models. Moreover, Bayesian FL also naturally enables personalization in FL to handle data heterogeneity across the different clients by having each client learn its own distinct personalized model. In particular, the hierarchical Bayesian approach enables all the clients to learn their personalized models while also taking into account the commonalities via a prior distribution provided by the server. However, despite their promise, Bayesian approaches for FL can be computationally expensive and can have high communication costs as well because of the requirement of computing and sending the posterior distributions. We present a novel Bayesian FL method using an efficient second-order optimization approach, with a computational cost that is similar to first-order optimization methods like Adam, but also provides the various benefits of the Bayesian approach for FL (e.g., uncertainty, personalization), while also being significantly more efficient and accurate than SOTA Bayesian FL methods (both for standard as well as personalized FL settings). Our method achieves improved predictive accuracies as well as better uncertainty estimates as compared to the baselines which include both optimization based as well as Bayesian FL methods.
Machine Learning Advances aiding Recognition and Classification of Indian Monuments and Landmarks
Jul 29, 2021
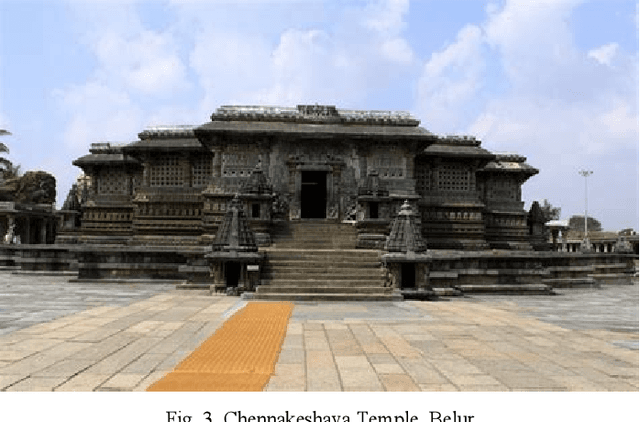
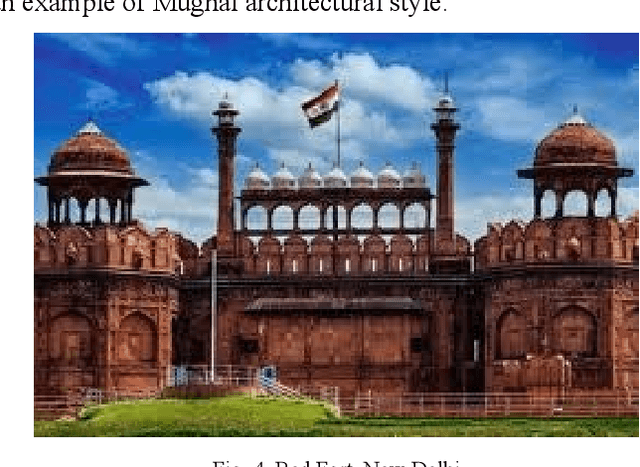


Abstract:Tourism in India plays a quintessential role in the country's economy with an estimated 9.2% GDP share for the year 2018. With a yearly growth rate of 6.2%, the industry holds a huge potential for being the primary driver of the economy as observed in the nations of the Middle East like the United Arab Emirates. The historical and cultural diversity exhibited throughout the geography of the nation is a unique spectacle for people around the world and therefore serves to attract tourists in tens of millions in number every year. Traditionally, tour guides or academic professionals who study these heritage monuments were responsible for providing information to the visitors regarding their architectural and historical significance. However, unfortunately this system has several caveats when considered on a large scale such as unavailability of sufficient trained people, lack of accurate information, failure to convey the richness of details in an attractive format etc. Recently, machine learning approaches revolving around the usage of monument pictures have been shown to be useful for rudimentary analysis of heritage sights. This paper serves as a survey of the research endeavors undertaken in this direction which would eventually provide insights for building an automated decision system that could be utilized to make the experience of tourism in India more modernized for visitors.
Finding Prerequisite Relations between Concepts using Textbook
Nov 20, 2020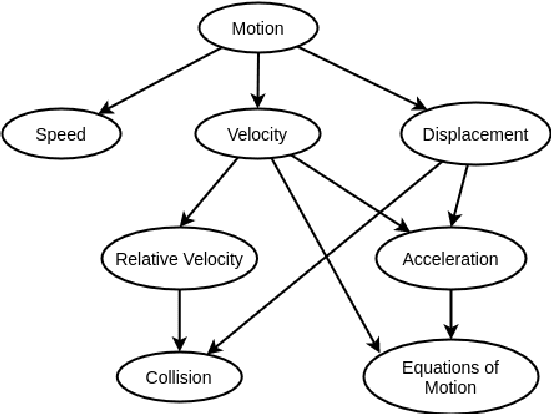
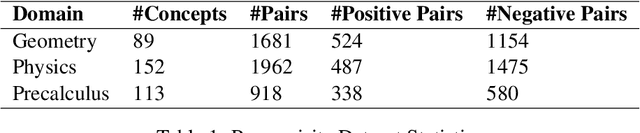
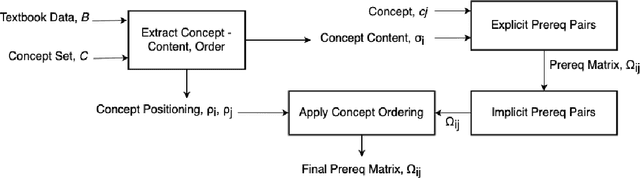
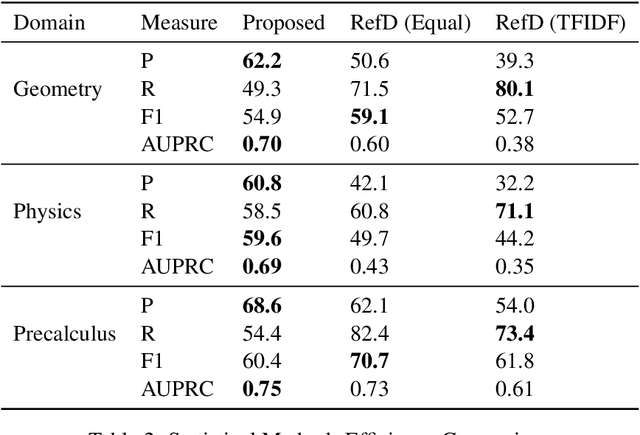
Abstract:A prerequisite is anything that you need to know or understand first before attempting to learn or understand something new. In the current work, we present a method of finding prerequisite relations between concepts using related textbooks. Previous researchers have focused on finding these relations using Wikipedia link structure through unsupervised and supervised learning approaches. In the current work, we have proposed two methods, one is statistical method and another is learning-based method. We mine the rich and structured knowledge available in the textbooks to find the content for those concepts and the order in which they are discussed. Using this information, proposed statistical method estimates explicit as well as implicit prerequisite relations between concepts. During experiments, we have found performance of proposed statistical method is better than the popular RefD method, which uses Wikipedia link structure. And proposed learning-based method has shown a significant increase in the efficiency of supervised learning method when compared with graph and text-based learning-based approaches.
Estimating the Cheeger constant using machine learning
May 12, 2020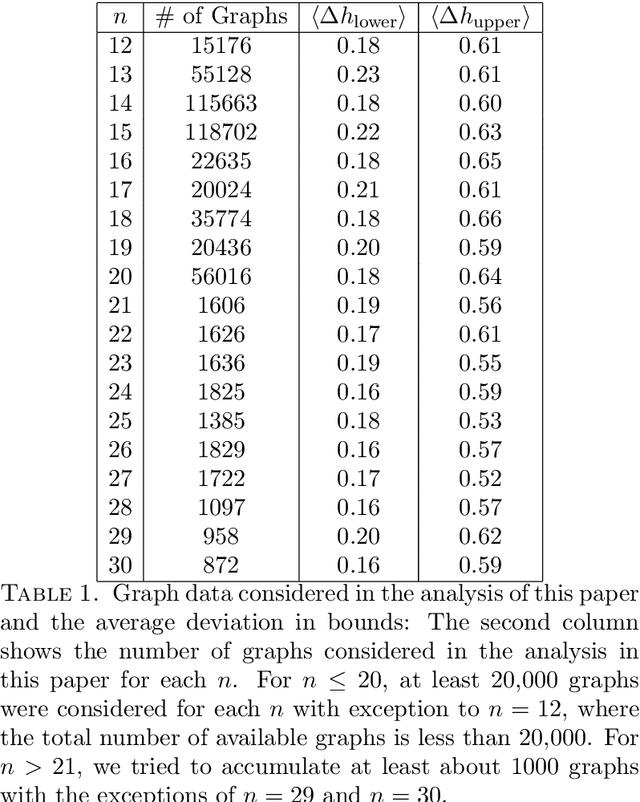
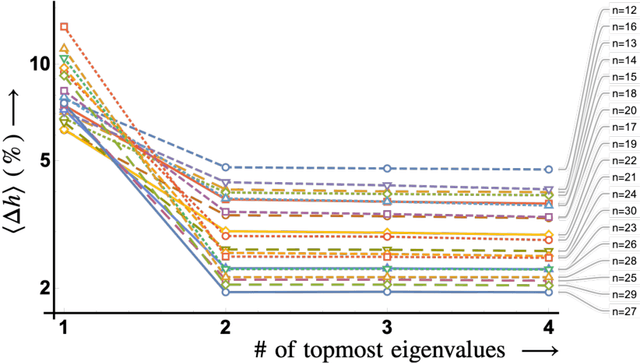
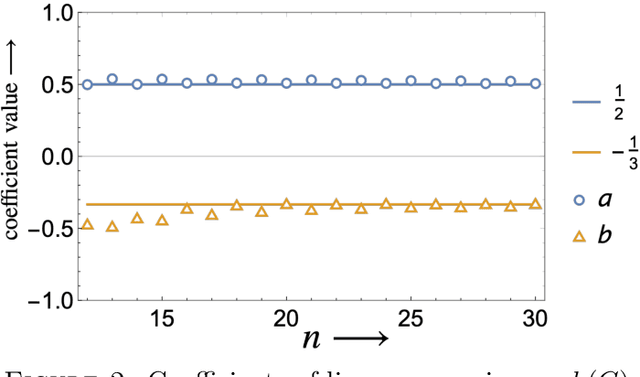
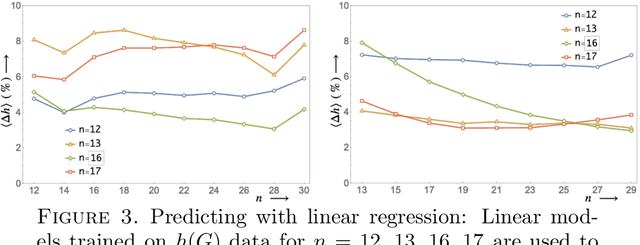
Abstract:In this paper, we use machine learning to show that the Cheeger constant of a connected regular graph has a predominant linear dependence on the largest two eigenvalues of the graph spectrum. We also show that a trained deep neural network on graphs of smaller sizes can be used as an effective estimator in estimating the Cheeger constant of larger graphs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge