Aditya Jyoti Paul
Local and Global Context-Based Pairwise Models for Sentence Ordering
Oct 08, 2021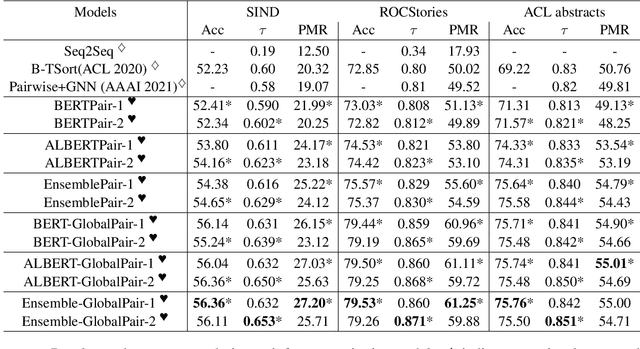
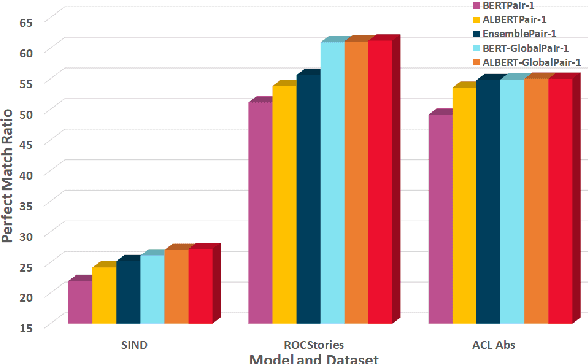
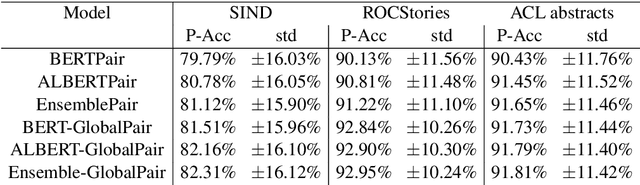
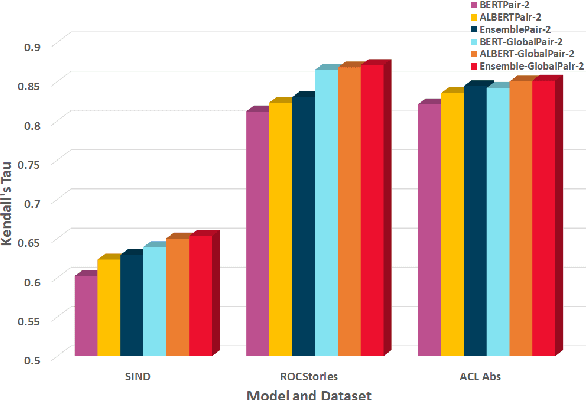
Abstract:Sentence Ordering refers to the task of rearranging a set of sentences into the appropriate coherent order. For this task, most previous approaches have explored global context-based end-to-end methods using Sequence Generation techniques. In this paper, we put forward a set of robust local and global context-based pairwise ordering strategies, leveraging which our prediction strategies outperform all previous works in this domain. Our proposed encoding method utilizes the paragraph's rich global contextual information to predict the pairwise order using novel transformer architectures. Analysis of the two proposed decoding strategies helps better explain error propagation in pairwise models. This approach is the most accurate pure pairwise model and our encoding strategy also significantly improves the performance of other recent approaches that use pairwise models, including the previous state-of-the-art, demonstrating the research novelty and generalizability of this work. Additionally, we show how the pre-training task for ALBERT helps it to significantly outperform BERT, despite having considerably lesser parameters. The extensive experimental results, architectural analysis and ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed models compared to the previous state-of-the-art, besides providing a much better understanding of the functioning of pairwise models.
Machine Learning Advances aiding Recognition and Classification of Indian Monuments and Landmarks
Jul 29, 2021


Abstract:Tourism in India plays a quintessential role in the country's economy with an estimated 9.2% GDP share for the year 2018. With a yearly growth rate of 6.2%, the industry holds a huge potential for being the primary driver of the economy as observed in the nations of the Middle East like the United Arab Emirates. The historical and cultural diversity exhibited throughout the geography of the nation is a unique spectacle for people around the world and therefore serves to attract tourists in tens of millions in number every year. Traditionally, tour guides or academic professionals who study these heritage monuments were responsible for providing information to the visitors regarding their architectural and historical significance. However, unfortunately this system has several caveats when considered on a large scale such as unavailability of sufficient trained people, lack of accurate information, failure to convey the richness of details in an attractive format etc. Recently, machine learning approaches revolving around the usage of monument pictures have been shown to be useful for rudimentary analysis of heritage sights. This paper serves as a survey of the research endeavors undertaken in this direction which would eventually provide insights for building an automated decision system that could be utilized to make the experience of tourism in India more modernized for visitors.
The Need and Status of Sea Turtle Conservation and Survey of Associated Computer Vision Advances
Jul 29, 2021



Abstract:For over hundreds of millions of years, sea turtles and their ancestors have swum in the vast expanses of the ocean. They have undergone a number of evolutionary changes, leading to speciation and sub-speciation. However, in the past few decades, some of the most notable forces driving the genetic variance and population decline have been global warming and anthropogenic impact ranging from large-scale poaching, collecting turtle eggs for food, besides dumping trash including plastic waste into the ocean. This leads to severe detrimental effects in the sea turtle population, driving them to extinction. This research focusses on the forces causing the decline in sea turtle population, the necessity for the global conservation efforts along with its successes and failures, followed by an in-depth analysis of the modern advances in detection and recognition of sea turtles, involving Machine Learning and Computer Vision systems, aiding the conservation efforts.
Advances in Classifying the Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy Using Convolutional Neural Networks in Low Memory Edge Devices
Jun 03, 2021



Abstract:Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a severe complication that may lead to retinal vascular damage and is one of the leading causes of vision impairment and blindness. DR broadly is classified into two stages - non-proliferative (NPDR), where there are almost no symptoms, except a few microaneurysms, and proliferative (PDR) involving a huge number of microaneurysms and hemorrhages, soft and hard exudates, neo-vascularization, macular ischemia or a combination of these, making it easier to detect. More specifically, DR is usually classified into five levels, labeled 0-4, from 0 indicating no DR to 4 which is most severe. This paper firstly presents a discussion on the risk factors of the disease, then surveys the recent literature on the topic followed by examining certain techniques which were found to be highly effective in improving the prognosis accuracy. Finally, a convolutional neural network model is proposed to detect all the stages of DR on a low-memory edge microcontroller. The model has a size of just 5.9 MB, accuracy and F1 score both of 94% and an inference speed of about 20 frames per second.
A Tiny CNN Architecture for Medical Face Mask Detection for Resource-Constrained Endpoints
Dec 22, 2020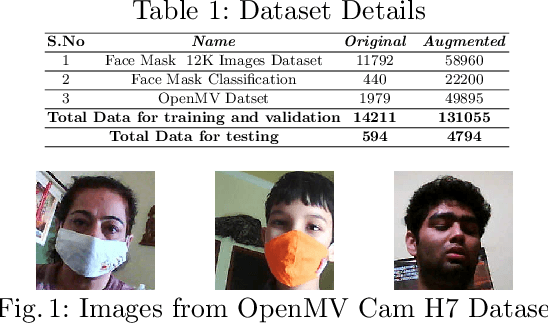

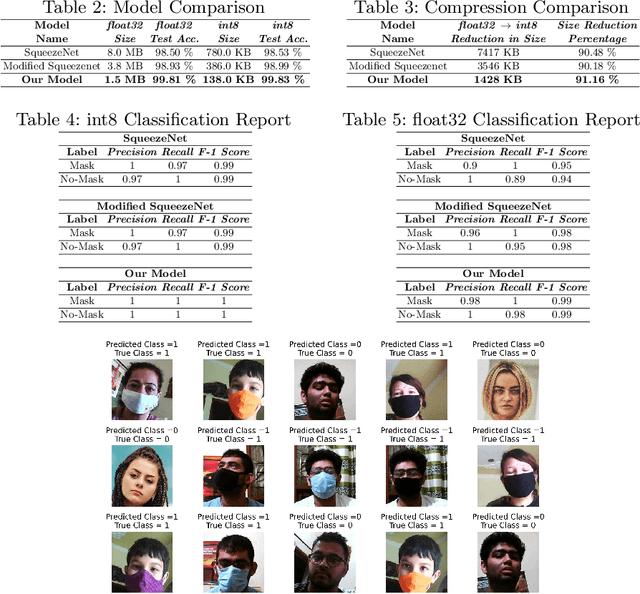

Abstract:The world is going through one of the most dangerous pandemics of all time with the rapid spread of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19). According to the World Health Organisation, the most effective way to thwart the transmission of coronavirus is to wear medical face masks. Monitoring the use of face masks in public places has been a challenge because manual monitoring could be unsafe. This paper proposes an architecture for detecting medical face masks for deployment on resource-constrained endpoints having extremely low memory footprints. A small development board with an ARM Cortex-M7 microcontroller clocked at 480 Mhz and having just 496 KB of framebuffer RAM, has been used for the deployment of the model. Using the TensorFlow Lite framework, the model is quantized to further reduce its size. The proposed model is 138 KB post quantization and runs at the inference speed of 30 FPS.
Rethinking Generalization in American Sign Language Prediction for Edge Devices with Extremely Low Memory Footprint
Nov 27, 2020



Abstract:Due to the boom in technical compute in the last few years, the world has seen massive advances in artificially intelligent systems solving diverse real-world problems. But a major roadblock in the ubiquitous acceptance of these models is their enormous computational complexity and memory footprint. Hence efficient architectures and training techniques are required for deployment on extremely low resource inference endpoints. This paper proposes an architecture for detection of alphabets in American Sign Language on an ARM Cortex-M7 microcontroller having just 496 KB of framebuffer RAM. Leveraging parameter quantization is a common technique that might cause varying drops in test accuracy. This paper proposes using interpolation as augmentation amongst other techniques as an efficient method of reducing this drop, which also helps the model generalize well to previously unseen noisy data. The proposed model is about 185 KB post-quantization and inference speed is 20 frames per second.
Randomized fast no-loss expert system to play tic tac toe like a human
Sep 23, 2020
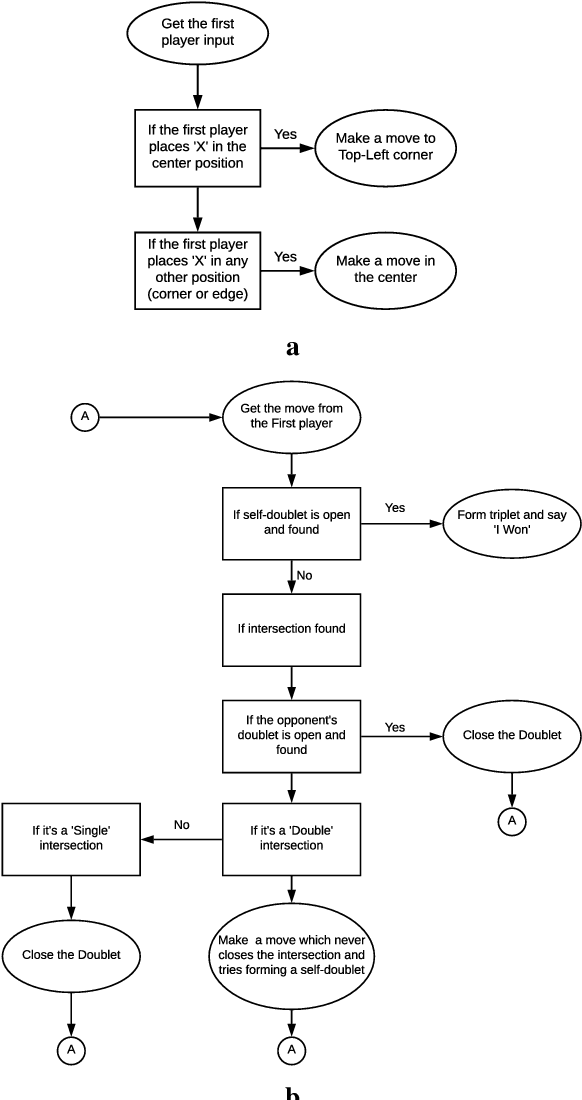

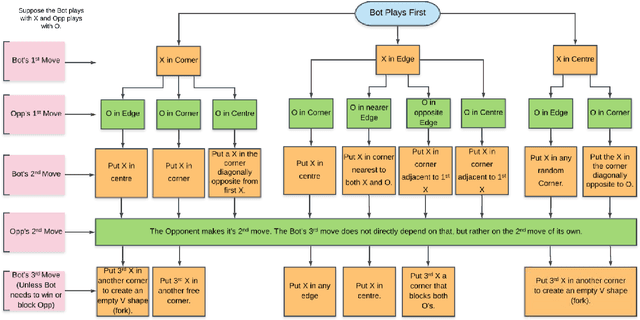
Abstract:This paper introduces a blazingly fast, no-loss expert system for Tic Tac Toe using Decision Trees called T3DT, that tries to emulate human gameplay as closely as possible. It does not make use of any brute force, minimax or evolutionary techniques, but is still always unbeatable. In order to make the gameplay more human-like, randomization is prioritized and T3DT randomly chooses one of the multiple optimal moves at each step. Since it does not need to analyse the complete game tree at any point, T3DT is exceptionally faster than any brute force or minimax algorithm, this has been shown theoretically as well as empirically from clock-time analyses in this paper. T3DT also doesn't need the data sets or the time to train an evolutionary model, making it a practical no-loss approach to play Tic Tac Toe.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge