Sher Badshah
TALE: A Tool-Augmented Framework for Reference-Free Evaluation of Large Language Models
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly integrated into real-world, autonomous applications, relying on static, pre-annotated references for evaluation poses significant challenges in cost, scalability, and completeness. We propose Tool-Augmented LLM Evaluation (TALE), a framework to assess LLM outputs without predetermined ground-truth answers. Unlike conventional metrics that compare to fixed references or depend solely on LLM-as-a-judge knowledge, TALE employs an agent with tool-access capabilities that actively retrieves and synthesizes external evidence. It iteratively generates web queries, collects information, summarizes findings, and refines subsequent searches through reflection. By shifting away from static references, TALE aligns with free-form question-answering tasks common in real-world scenarios. Experimental results on multiple free-form QA benchmarks show that TALE not only outperforms standard reference-based metrics for measuring response accuracy but also achieves substantial to near-perfect agreement with human evaluations. TALE enhances the reliability of LLM evaluations in real-world, dynamic scenarios without relying on static references.
DAFE: LLM-Based Evaluation Through Dynamic Arbitration for Free-Form Question-Answering
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) free-form generated responses remains a challenge due to their diverse and open-ended nature. Traditional supervised signal-based automatic metrics fail to capture semantic equivalence or handle the variability of open-ended responses, while human evaluation, though reliable, is resource-intensive. Leveraging LLMs as evaluators offers a promising alternative due to their strong language understanding and instruction-following capabilities. Taking advantage of these capabilities, we propose the Dynamic Arbitration Framework for Evaluation (DAFE), which employs two primary LLM-as-judges and engages a third arbitrator only in cases of disagreements. This selective arbitration prioritizes evaluation reliability while reducing unnecessary computational demands compared to conventional majority voting. DAFE utilizes task-specific reference answers with dynamic arbitration to enhance judgment accuracy, resulting in significant improvements in evaluation metrics such as Macro F1 and Cohen's Kappa. Through experiments, including a comprehensive human evaluation, we demonstrate DAFE's ability to provide consistent, scalable, and resource-efficient assessments, establishing it as a robust framework for evaluating free-form model outputs.
Reference-Guided Verdict: LLMs-as-Judges in Automatic Evaluation of Free-Form Text
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) as chat assistants capable of generating human-like conversations has amplified the need for robust evaluation methods, particularly for open-ended tasks. Conventional metrics like BLEU and ROUGE, while useful, are increasingly inadequate for capturing the subtle semantics and contextual richness of such generative outputs. We propose a reference-guided verdict method that automates the evaluation process by leveraging multiple LLMs-as-judges. Through experiments on three open-ended question-answering tasks, we demonstrate that combining multiple LLMs-as-judges significantly improves the reliability and accuracy of evaluations, particularly in complex tasks where a single model might struggle. Our findings reveal a strong correlation with human evaluations, establishing our method as a viable and effective alternative to traditional metrics and human judgments, particularly in the context of LLM-based chat assistants where the complexity and diversity of responses challenge existing benchmarks.
Quantifying the Capabilities of LLMs across Scale and Precision
May 08, 2024



Abstract:Scale is often attributed as one of the factors that cause an increase in the performance of LLMs, resulting in models with billion and trillion parameters. One of the limitations of such large models is the high computational requirements that limit their usage, deployment, and debugging in resource-constrained scenarios. Two commonly used alternatives to bypass these limitations are to use the smaller versions of LLMs (e.g. Llama 7B instead of Llama 70B) and lower the memory requirements by using quantization. While these approaches effectively address the limitation of resources, their impact on model performance needs thorough examination. In this study, we perform a comprehensive evaluation to investigate the effect of model scale and quantization on the performance. We experiment with two major families of open-source instruct models ranging from 7 billion to 70 billion parameters. Our extensive zero-shot experiments across various tasks including natural language understanding, reasoning, misinformation detection, and hallucination reveal that larger models generally outperform their smaller counterparts, suggesting that scale remains an important factor in enhancing performance. We found that larger models show exceptional resilience to precision reduction and can maintain high accuracy even at 4-bit quantization for numerous tasks and they serve as a better solution than using smaller models at high precision under similar memory requirements.
Ethics of AI: A Systematic Literature Review of Principles and Challenges
Sep 12, 2021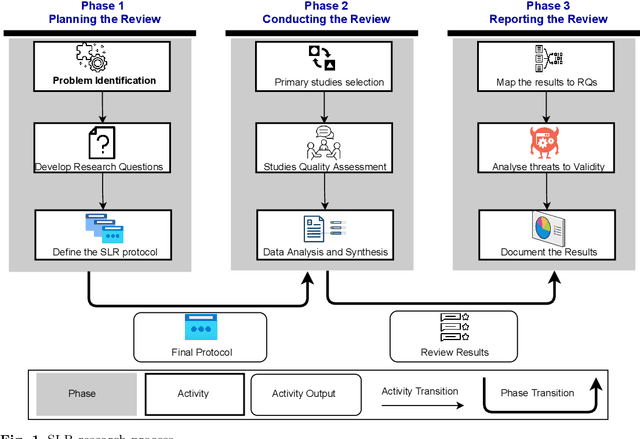

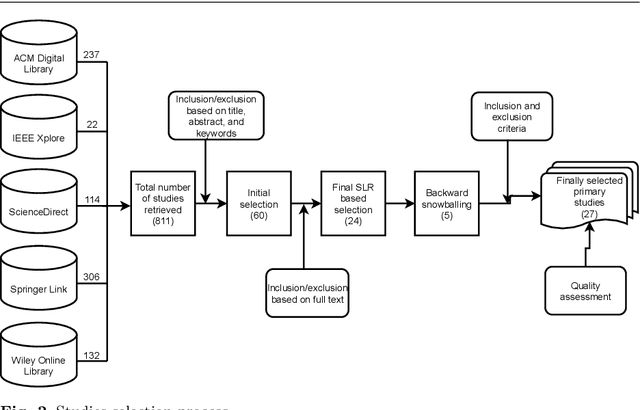

Abstract:Ethics in AI becomes a global topic of interest for both policymakers and academic researchers. In the last few years, various research organizations, lawyers, think tankers and regulatory bodies get involved in developing AI ethics guidelines and principles. However, there is still debate about the implications of these principles. We conducted a systematic literature review (SLR) study to investigate the agreement on the significance of AI principles and identify the challenging factors that could negatively impact the adoption of AI ethics principles. The results reveal that the global convergence set consists of 22 ethical principles and 15 challenges. Transparency, privacy, accountability and fairness are identified as the most common AI ethics principles. Similarly, lack of ethical knowledge and vague principles are reported as the significant challenges for considering ethics in AI. The findings of this study are the preliminary inputs for proposing a maturity model that assess the ethical capabilities of AI systems and provide best practices for further improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge