Shaun Canavan
FlowCon: Out-of-Distribution Detection using Flow-Based Contrastive Learning
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:Identifying Out-of-distribution (OOD) data is becoming increasingly critical as the real-world applications of deep learning methods expand. Post-hoc methods modify softmax scores fine-tuned on outlier data or leverage intermediate feature layers to identify distinctive patterns between In-Distribution (ID) and OOD samples. Other methods focus on employing diverse OOD samples to learn discrepancies between ID and OOD. These techniques, however, are typically dependent on the quality of the outlier samples assumed. Density-based methods explicitly model class-conditioned distributions but this requires long training time or retraining the classifier. To tackle these issues, we introduce \textit{FlowCon}, a new density-based OOD detection technique. Our main innovation lies in efficiently combining the properties of normalizing flow with supervised contrastive learning, ensuring robust representation learning with tractable density estimation. Empirical evaluation shows the enhanced performance of our method across common vision datasets such as CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 pretrained on ResNet18 and WideResNet classifiers. We also perform quantitative analysis using likelihood plots and qualitative visualization using UMAP embeddings and demonstrate the robustness of the proposed method under various OOD contexts. Code will be open-sourced post decision.
Random Forest Regression for continuous affect using Facial Action Units
Mar 29, 2022
Abstract:In this paper we describe our approach to the arousal and valence track of the 3rd Workshop and Competition on Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-wild (ABAW). We extracted facial features using OpenFace and used them to train a multiple output random forest regressor. Our approach performed comparable to the baseline approach.
Quantified Facial Expressiveness for Affective Behavior Analytics
Oct 07, 2021Abstract:The quantified measurement of facial expressiveness is crucial to analyze human affective behavior at scale. Unfortunately, methods for expressiveness quantification at the video frame-level are largely unexplored, unlike the study of discrete expression. In this work, we propose an algorithm that quantifies facial expressiveness using a bounded, continuous expressiveness score using multimodal facial features, such as action units (AUs), landmarks, head pose, and gaze. The proposed algorithm more heavily weights AUs with high intensities and large temporal changes. The proposed algorithm can compute the expressiveness in terms of discrete expression, and can be used to perform tasks including facial behavior tracking and subjectivity quantification in context. Our results on benchmark datasets show the proposed algorithm is effective in terms of capturing temporal changes and expressiveness, measuring subjective differences in context, and extracting useful insight.
Accounting for Affect in Pain Level Recognition
Nov 15, 2020



Abstract:In this work, we address the importance of affect in automated pain assessment and the implications in real-world settings. To achieve this, we curate a new physiological dataset by merging the publicly available bioVid pain and emotion datasets. We then investigate pain level recognition on this dataset simulating participants' naturalistic affective behaviors. Our findings demonstrate that acknowledging affect in pain assessment is essential. We observe degradation in recognition performance when simulating the existence of affect to validate pain assessment models that do not account for it. Conversely, we observe a performance boost in recognition when we account for affect.
Quantified Facial Temporal-Expressiveness Dynamics for Affect Analysis
Oct 28, 2020



Abstract:The quantification of visual affect data (e.g. face images) is essential to build and monitor automated affect modeling systems efficiently. Considering this, this work proposes quantified facial Temporal-expressiveness Dynamics (TED) to quantify the expressiveness of human faces. The proposed algorithm leverages multimodal facial features by incorporating static and dynamic information to enable accurate measurements of facial expressiveness. We show that TED can be used for high-level tasks such as summarization of unstructured visual data, and expectation from and interpretation of automated affect recognition models. To evaluate the positive impact of using TED, a case study was conducted on spontaneous pain using the UNBC-McMaster spontaneous shoulder pain dataset. Experimental results show the efficacy of using TED for quantified affect analysis.
Impact of Action Unit Occurrence Patterns on Detection
Oct 15, 2020



Abstract:Detecting action units is an important task in face analysis, especially in facial expression recognition. This is due, in part, to the idea that expressions can be decomposed into multiple action units. In this paper we investigate the impact of action unit occurrence patterns on detection of action units. To facilitate this investigation, we review state of the art literature, for AU detection, on 2 state-of-the-art face databases that are commonly used for this task, namely DISFA, and BP4D. Our findings, from this literature review, suggest that action unit occurrence patterns strongly impact evaluation metrics (e.g. F1-binary). Along with the literature review, we also conduct multi and single action unit detection, as well as propose a new approach to explicitly train deep neural networks using the occurrence patterns to boost the accuracy of action unit detection. These experiments validate that action unit patterns directly impact the evaluation metrics.
Detecting Forged Facial Videos using convolutional neural network
May 17, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose to detect forged videos, of faces, in online videos. To facilitate this detection, we propose to use smaller (fewer parameters to learn) convolutional neural networks (CNN), for a data-driven approach to forged video detection. To validate our approach, we investigate the FaceForensics public dataset detailing both frame-based and video-based results. The proposed method is shown to outperform current state of the art. We also perform an ablation study, analyzing the impact of batch size, number of filters, and number of network layers on the accuracy of detecting forged videos.
Facial Action Unit Detection using 3D Facial Landmarks
May 17, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we propose to detect facial action units (AU) using 3D facial landmarks. Specifically, we train a 2D convolutional neural network (CNN) on 3D facial landmarks, tracked using a shape index-based statistical shape model, for binary and multi-class AU detection. We show that the proposed approach is able to accurately model AU occurrences, as the movement of the facial landmarks corresponds directly to the movement of the AUs. By training a CNN on 3D landmarks, we can achieve accurate AU detection on two state-of-the-art emotion datasets, namely BP4D and BP4D+. Using the proposed method, we detect multiple AUs on over 330,000 frames, reporting improved results over state-of-the-art methods.
Impact of multiple modalities on emotion recognition: investigation into 3d facial landmarks, action units, and physiological data
May 17, 2020
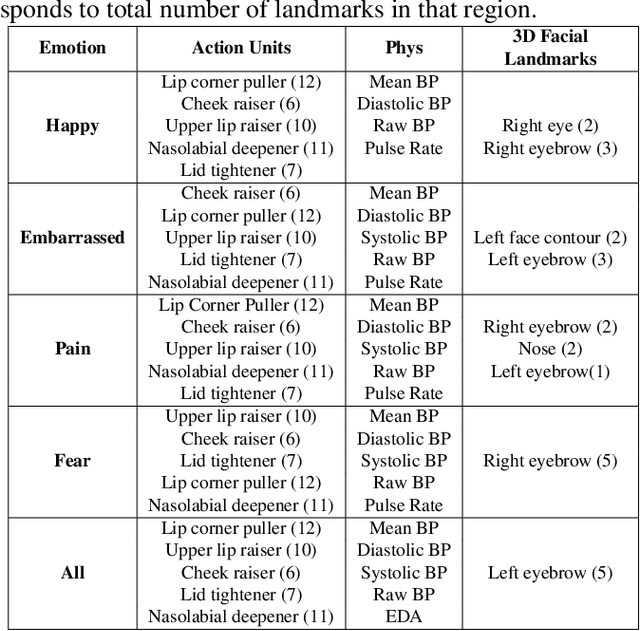

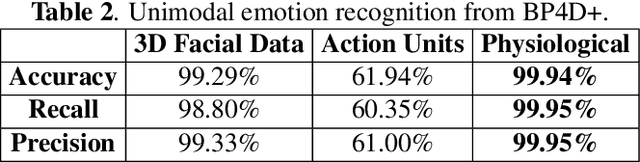
Abstract:To fully understand the complexities of human emotion, the integration of multiple physical features from different modalities can be advantageous. Considering this, we present an analysis of 3D facial data, action units, and physiological data as it relates to their impact on emotion recognition. We analyze each modality independently, as well as the fusion of each for recognizing human emotion. This analysis includes which features are most important for specific emotions (e.g. happy). Our analysis indicates that both 3D facial landmarks and physiological data are encouraging for expression/emotion recognition. On the other hand, while action units can positively impact emotion recognition when fused with other modalities, the results suggest it is difficult to detect emotion using them in a unimodal fashion.
Subject Identification Across Large Expression Variations Using 3D Facial Landmarks
May 17, 2020
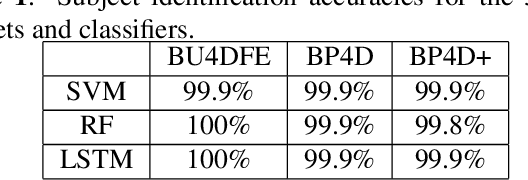

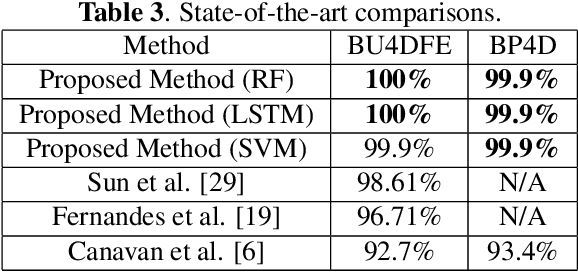
Abstract:Landmark localization is an important first step towards geometric based vision research including subject identification. Considering this, we propose to use 3D facial landmarks for the task of subject identification, over a range of expressed emotion. Landmarks are detected, using a Temporal Deformable Shape Model and used to train a Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), and Long Short-term Memory (LSTM) neural network for subject identification. As we are interested in subject identification with large variations in expression, we conducted experiments on 3 emotion-based databases, namely the BU-4DFE, BP4D, and BP4D+ 3D/4D face databases. We show that our proposed method outperforms current state of the art methods for subject identification on BU-4DFE and BP4D. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to investigate subject identification on the BP4D+, resulting in a baseline for the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge