Shashank Kedia
Generating Rich Product Descriptions for Conversational E-commerce Systems
Nov 30, 2021



Abstract:Through recent advancements in speech technologies and introduction of smart assistants, such as Amazon Alexa, Apple Siri and Google Home, increasing number of users are interacting with various applications through voice commands. E-commerce companies typically display short product titles on their webpages, either human-curated or algorithmically generated, when brevity is required. However, these titles are dissimilar from natural spoken language. For example, "Lucky Charms Gluten Free Break-fast Cereal, 20.5 oz a box Lucky Charms Gluten Free" is acceptable to display on a webpage, while a similar title cannot be used in a voice based text-to-speech application. In such conversational systems, an easy to comprehend sentence, such as "a 20.5 ounce box of lucky charms gluten free cereal" is preferred. Compared to display devices, where images and detailed product information can be presented to users, short titles for products which convey the most important information, are necessary when interfacing with voice assistants. We propose eBERT, a sequence-to-sequence approach by further pre-training the BERT embeddings on an e-commerce product description corpus, and then fine-tuning the resulting model to generate short, natural, spoken language titles from input web titles. Our extensive experiments on a real-world industry dataset, as well as human evaluation of model output, demonstrate that eBERT summarization outperforms comparable baseline models. Owing to the efficacy of the model, a version of this model has been deployed in real-world setting.
* 8 pages, 1 figure. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2007.11768
A Real-Time Whole Page Personalization Framework for E-Commerce
Dec 08, 2020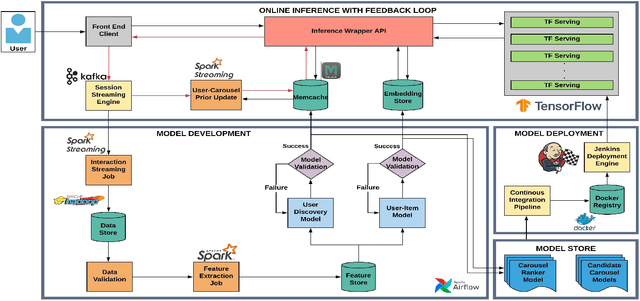
Abstract:E-commerce platforms consistently aim to provide personalized recommendations to drive user engagement, enhance overall user experience, and improve business metrics. Most e-commerce platforms contain multiple carousels on their homepage, each attempting to capture different facets of the shopping experience. Given varied user preferences, optimizing the placement of these carousels is critical for improved user satisfaction. Furthermore, items within a carousel may change dynamically based on sequential user actions, thus necessitating online ranking of carousels. In this work, we present a scalable end-to-end production system to optimally rank item-carousels in real-time on the Walmart online grocery homepage. The proposed system utilizes a novel model that captures the user's affinity for different carousels and their likelihood to interact with previously unseen items. Our system is flexible in design and is easily extendable to settings where page components need to be ranked. We provide the system architecture consisting of a model development phase and an online inference framework. To ensure low-latency, various optimizations across these stages are implemented. We conducted extensive online evaluations to benchmark against the prior experience. In production, our system resulted in an improvement in item discovery, an increase in online engagement, and a significant lift on add-to-carts (ATCs) per visitor on the homepage.
Product Title Generation for Conversational Systems using BERT
Jul 23, 2020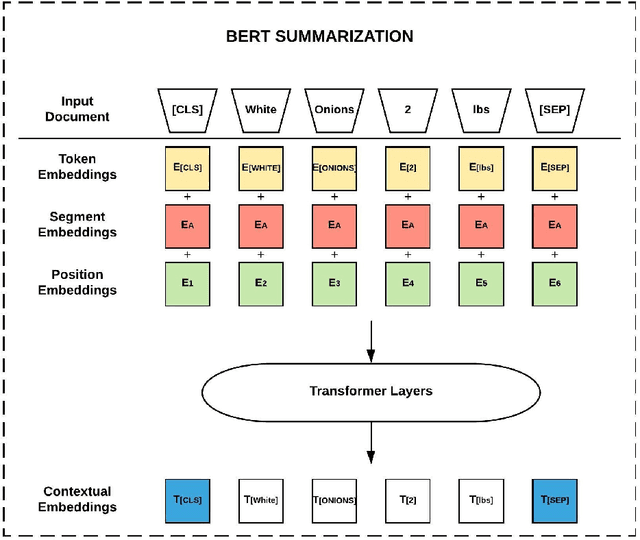



Abstract:Through recent advancements in speech technology and introduction of smart devices, such as Amazon Alexa and Google Home, increasing number of users are interacting with applications through voice. E-commerce companies typically display short product titles on their webpages, either human-curated or algorithmically generated, when brevity is required, but these titles are dissimilar from natural spoken language. For example, "Lucky Charms Gluten Free Break-fast Cereal, 20.5 oz a box Lucky Charms Gluten Free" is acceptable to display on a webpage, but "a 20.5 ounce box of lucky charms gluten free cereal" is easier to comprehend over a conversational system. As compared to display devices, where images and detailed product information can be presented to users, short titles for products are necessary when interfacing with voice assistants. We propose a sequence-to-sequence approach using BERT to generate short, natural, spoken language titles from input web titles. Our extensive experiments on a real-world industry dataset and human evaluation of model outputs, demonstrate that BERT summarization outperforms comparable baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge