Shahnewaz Siddique
QuXAI: Explainers for Hybrid Quantum Machine Learning Models
May 15, 2025Abstract:The emergence of hybrid quantum-classical machine learning (HQML) models opens new horizons of computational intelligence but their fundamental complexity frequently leads to black box behavior that undermines transparency and reliability in their application. Although XAI for quantum systems still in its infancy, a major research gap is evident in robust global and local explainability approaches that are designed for HQML architectures that employ quantized feature encoding followed by classical learning. The gap is the focus of this work, which introduces QuXAI, an framework based upon Q-MEDLEY, an explainer for explaining feature importance in these hybrid systems. Our model entails the creation of HQML models incorporating quantum feature maps, the use of Q-MEDLEY, which combines feature based inferences, preserving the quantum transformation stage and visualizing the resulting attributions. Our result shows that Q-MEDLEY delineates influential classical aspects in HQML models, as well as separates their noise, and competes well against established XAI techniques in classical validation settings. Ablation studies more significantly expose the virtues of the composite structure used in Q-MEDLEY. The implications of this work are critically important, as it provides a route to improve the interpretability and reliability of HQML models, thus promoting greater confidence and being able to engage in safer and more responsible use of quantum-enhanced AI technology.
Real-time Bangla Sign Language Translator
Dec 21, 2024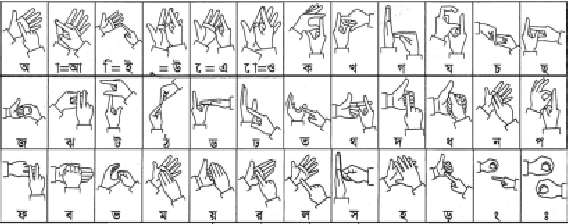
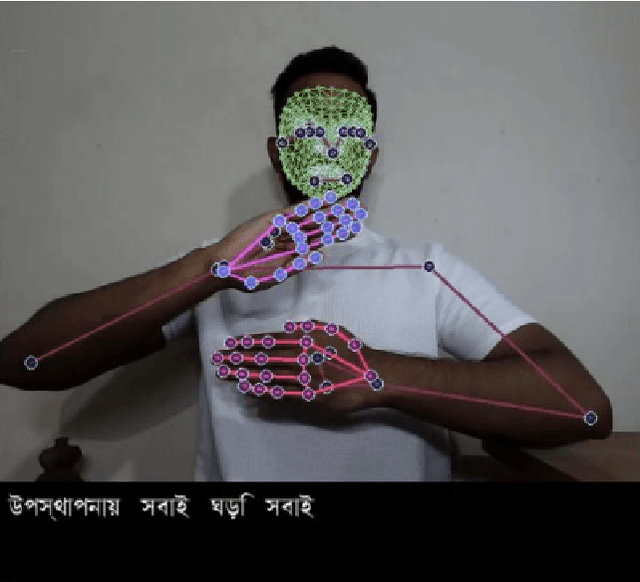

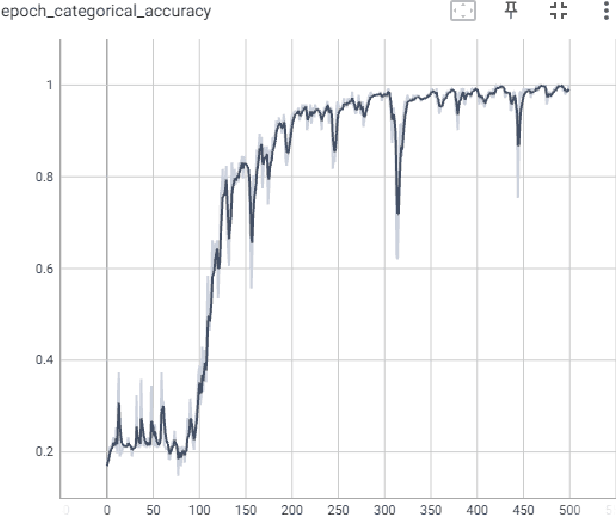
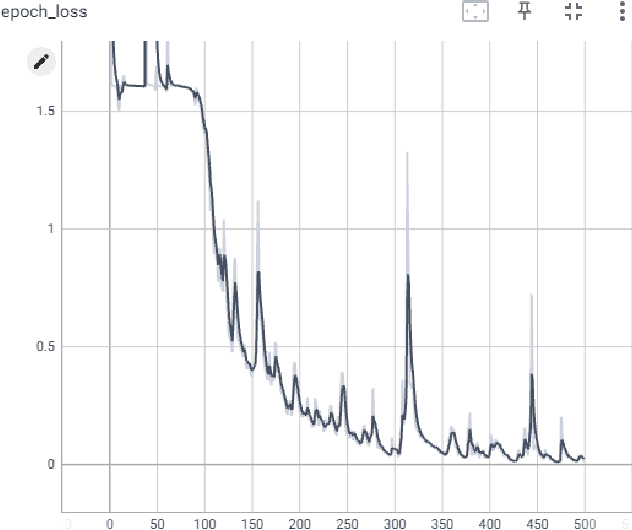
Abstract:The human body communicates through various meaningful gestures, with sign language using hands being a prominent example. Bangla Sign Language Translation (BSLT) aims to bridge communication gaps for the deaf and mute community. Our approach involves using Mediapipe Holistic to gather key points, LSTM architecture for data training, and Computer Vision for realtime sign language detection with an accuracy of 94%. Keywords=Recurrent Neural Network, LSTM, Computer Vision, Bangla font.
A Memory Efficient Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach For Snake Game Autonomous Agents
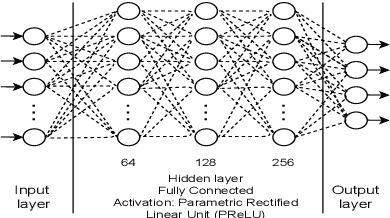
Jan 27, 2023Abstract:To perform well, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) methods require significant memory resources and computational time. Also, sometimes these systems need additional environment information to achieve a good reward. However, it is more important for many applications and devices to reduce memory usage and computational times than to achieve the maximum reward. This paper presents a modified DRL method that performs reasonably well with compressed imagery data without requiring additional environment information and also uses less memory and time. We have designed a lightweight Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with a variant of the Q-network that efficiently takes preprocessed image data as input and uses less memory. Furthermore, we use a simple reward mechanism and small experience replay memory so as to provide only the minimum necessary information. Our modified DRL method enables our autonomous agent to play Snake, a classical control game. The results show our model can achieve similar performance as other DRL methods.
* AICT 2022
Investigation of Minerals Using Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery in Bangladesh
Dec 08, 2022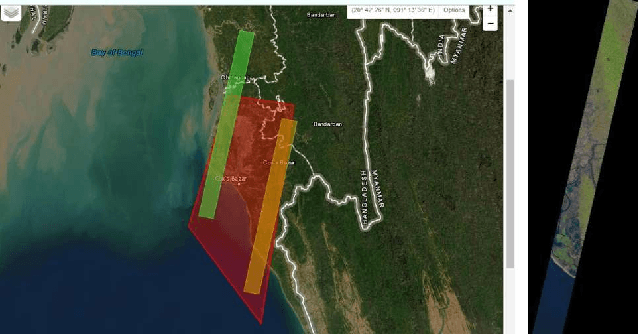
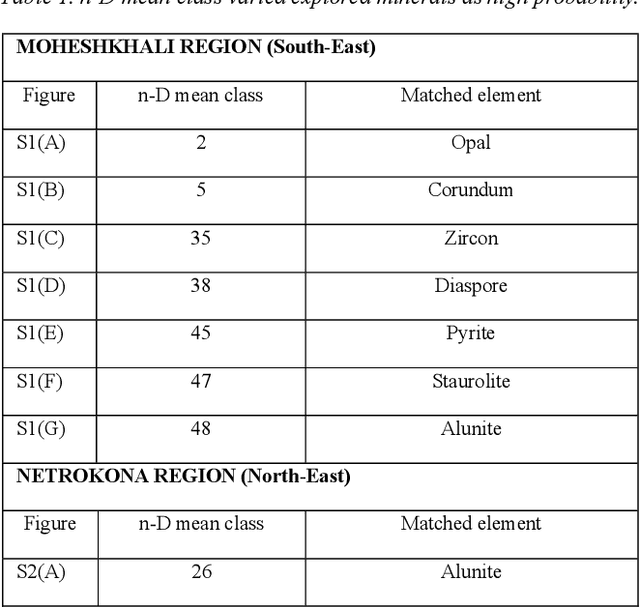

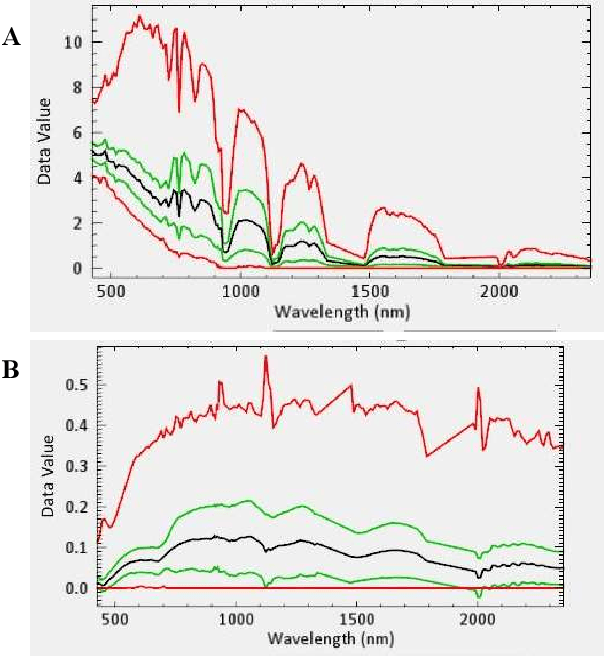
Abstract:Mineral identification using remote sensing technologies is becoming more dominant in this field since it saves time by demonstrating a more effective way for land resources survey. In such remote sensing technologies, hyperspectral remote sensing (HSRS) technology has increased gradually for its efficient manner. This technology is usually used from an airborne platform, i.e., satellite. Hence, satellite imagery remote sensing technology is now more capable of providing accuracy in mineral identification, and mapping. Hyperspectral satellite imagery can identify minerals more accurately compared to traditional technologies in remote sensing by constructing a complete reflectance of the spectrum from each pixel with its advanced imaging sensor. Bangladesh is a developing country with an area of 1,50,000 square kilometers located in Southeast Asia. Though it is a small country, it is enriched with several mineral resources through rivers, forests, hills, and the Bay of Bengal. In this study, hyperspectral imaging technology is employed on some major identical areas (Maheshkhali, Netrokona, Panchagarh, and Patuakhali) of Bangladesh to identify minerals there. As there are no studies done in Bangladesh using hyperspectral imaging yet, it is a good opportunity to explore the potentiality of HS imagery in this field. In this study, the FLAASH (Fast Line-of-sight Atmospheric Analysis) module with necessary parameter settings is used to filter the data, and finally, mineral identification is done by the spectral matched filtering method. Our investigation resulted in finding some potential minerals in those areas including Stariolite, Diasphore, Zircon, Alunite, Quartz, and so on. This indicates that there still is enormous potential for further exploration of minerals in Bangladesh by Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery.
Autonomous Warehouse Robot using Deep Q-Learning
Feb 21, 2022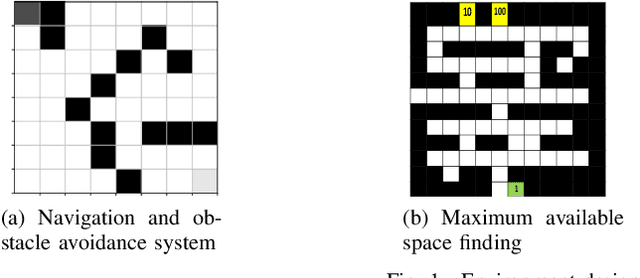
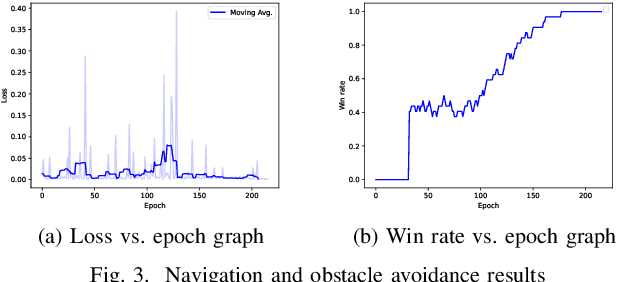
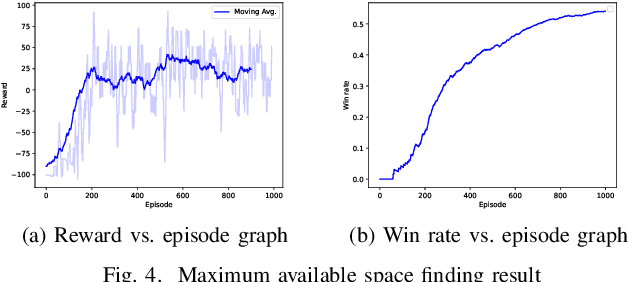
Abstract:In warehouses, specialized agents need to navigate, avoid obstacles and maximize the use of space in the warehouse environment. Due to the unpredictability of these environments, reinforcement learning approaches can be applied to complete these tasks. In this paper, we propose using Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) to address the robot navigation and obstacle avoidance problem and traditional Q-learning with minor variations to maximize the use of space for product placement. We first investigate the problem for the single robot case. Next, based on the single robot model, we extend our system to the multi-robot case. We use a strategic variation of Q-tables to perform multi-agent Q-learning. We successfully test the performance of our model in a 2D simulation environment for both the single and multi-robot cases.
Autonomous Intruder Detection Using a ROS-Based Multi-Robot System Equipped with 2D-LiDAR Sensors
Nov 07, 2020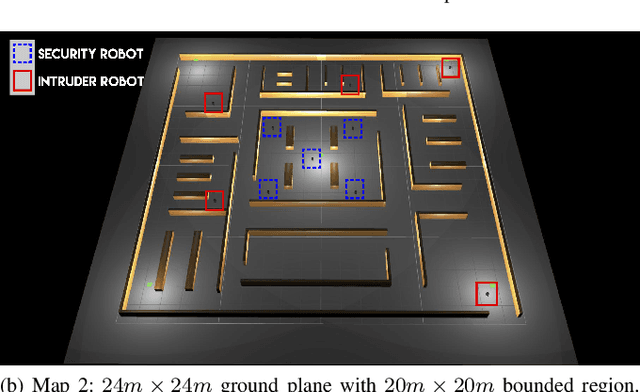
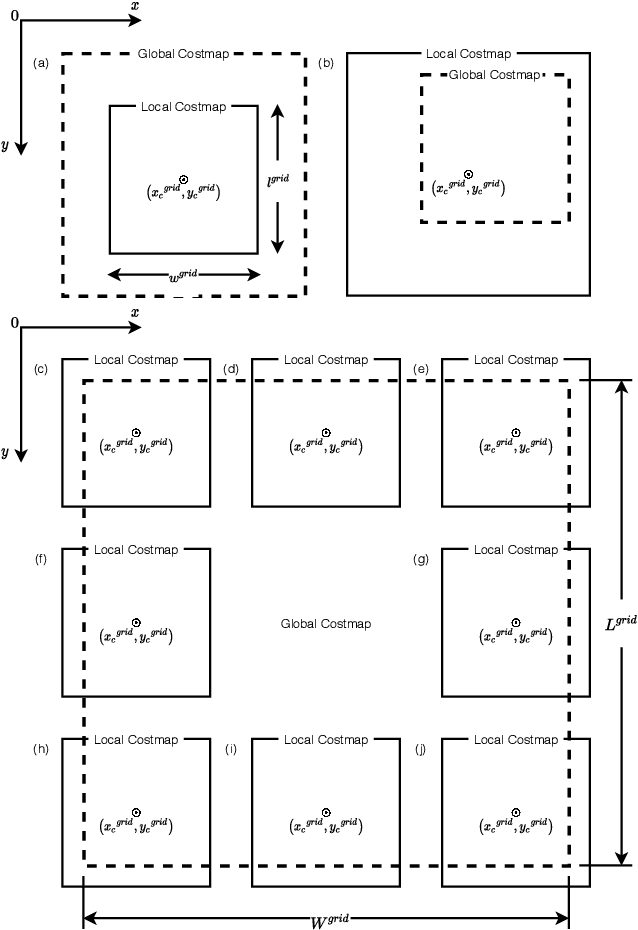
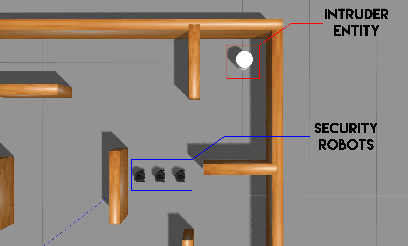
Abstract:The application of autonomous mobile robots in robotic security platforms is becoming a promising field of innovation due to their adaptive capability of responding to potential disturbances perceived through a wide range of sensors. Researchers have proposed systems that either focus on utilizing a single mobile robot or a system of cooperative multiple robots. However, very few of the proposed works, particularly in the field of multi-robot systems, are completely dependent on LiDAR sensors for achieving various tasks. This is essential when other sensors on a robot fail to provide peak performance in particular conditions, such as a camera operating in the absence of light. This paper proposes a multi-robot system that is developed using ROS (Robot Operating System) for intruder detection in a single-range-sensor-per-robot scenario with centralized processing of detections from all robots by our central bot MIDNet (Multiple Intruder Detection Network). This work is aimed at providing an autonomous multi-robot security solution for a warehouse in the absence of human personnel.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge