Shahaboddin Ghajari
Resolution-Adaptive All-Digital Spatial Equalization for mmWave Massive MU-MIMO
Jul 23, 2021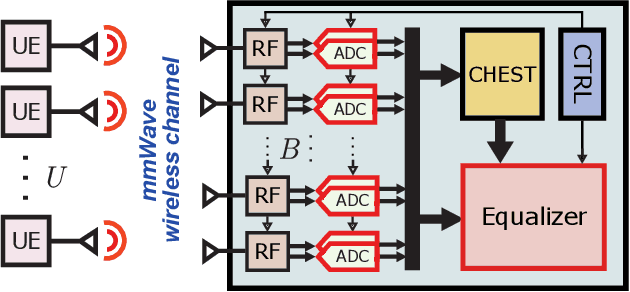
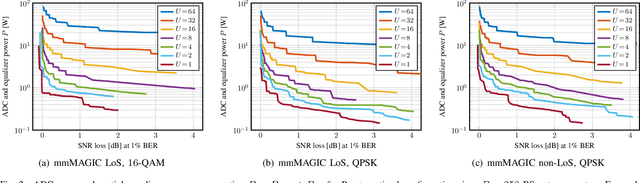
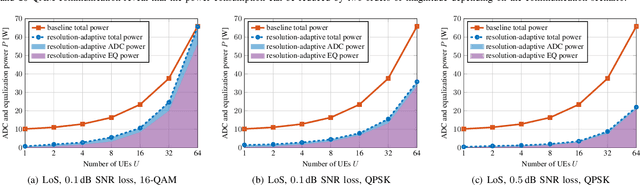
Abstract:All-digital basestation (BS) architectures for millimeter-wave (mmWave) massive multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO), which equip each radio-frequency chain with dedicated data converters, have advantages in spectral efficiency, flexibility, and baseband-processing simplicity over hybrid analog-digital solutions. For all-digital architectures to be competitive with hybrid solutions in terms of power consumption, novel signal-processing methods and baseband architectures are necessary. In this paper, we demonstrate that adapting the resolution of the analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and spatial equalizer of an all-digital system to the communication scenario (e.g., the number of users, modulation scheme, and propagation conditions) enables orders-of-magnitude power savings for realistic mmWave channels. For example, for a 256-BS-antenna 16-user system supporting 1 GHz bandwidth, a traditional baseline architecture designed for a 64-user worst-case scenario would consume 23 W in 28 nm CMOS for the ADC array and the spatial equalizer, whereas a resolution-adaptive architecture is able to reduce the power consumption by 6.7x.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge