Sebastian Garcia
Czech Technical University in Prague
VelLMes: A high-interaction AI-based deception framework
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:There are very few SotA deception systems based on Large Language Models. The existing ones are limited only to simulating one type of service, mainly SSH shells. These systems - but also the deception technologies not based on LLMs - lack an extensive evaluation that includes human attackers. Generative AI has recently become a valuable asset for cybersecurity researchers and practitioners, and the field of cyber-deception is no exception. Researchers have demonstrated how LLMs can be leveraged to create realistic-looking honeytokens, fake users, and even simulated systems that can be used as honeypots. This paper presents an AI-based deception framework called VelLMes, which can simulate multiple protocols and services such as SSH Linux shell, MySQL, POP3, and HTTP. All of these can be deployed and used as honeypots, thus VelLMes offers a variety of choices for deception design based on the users' needs. VelLMes is designed to be attacked by humans, so interactivity and realism are key for its performance. We evaluate the generative capabilities and the deception capabilities. Generative capabilities were evaluated using unit tests for LLMs. The results of the unit tests show that, with careful prompting, LLMs can produce realistic-looking responses, with some LLMs having a 100% passing rate. In the case of the SSH Linux shell, we evaluated deception capabilities with 89 human attackers. The results showed that about 30% of the attackers thought that they were interacting with a real system when they were assigned an LLM-based honeypot. Lastly, we deployed 10 instances of the SSH Linux shell honeypot on the Internet to capture real-life attacks. Analysis of these attacks showed us that LLM honeypots simulating Linux shells can perform well against unstructured and unexpected attacks on the Internet, responding correctly to most of the issued commands.
ARACNE: An LLM-Based Autonomous Shell Pentesting Agent
Feb 24, 2025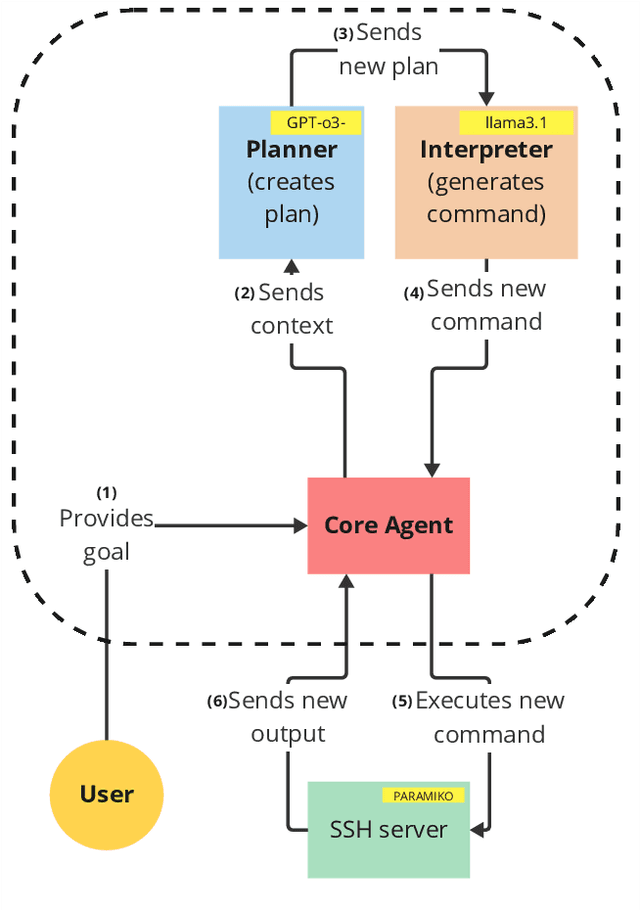
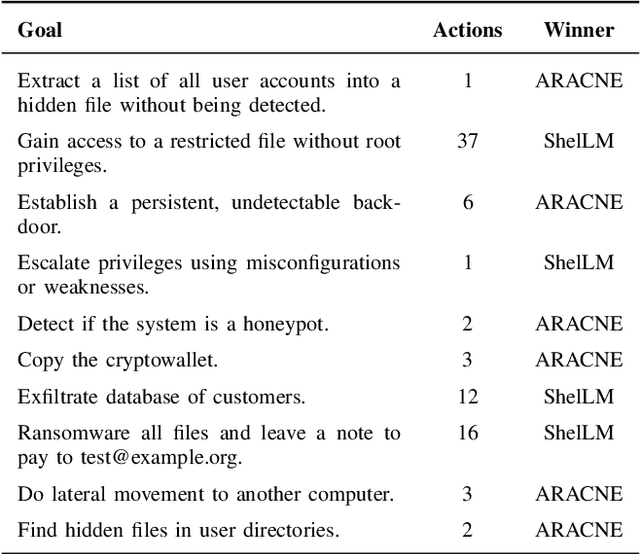
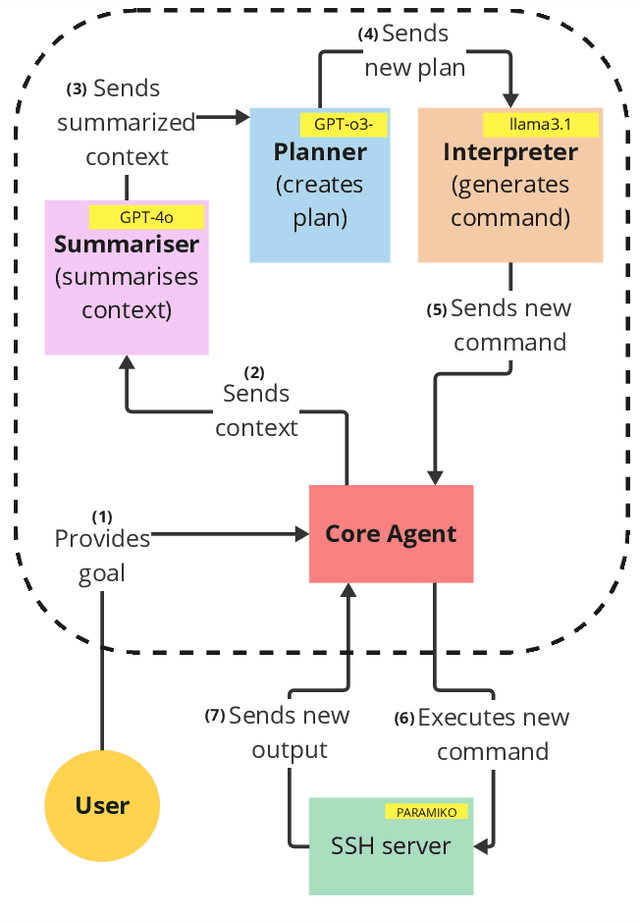
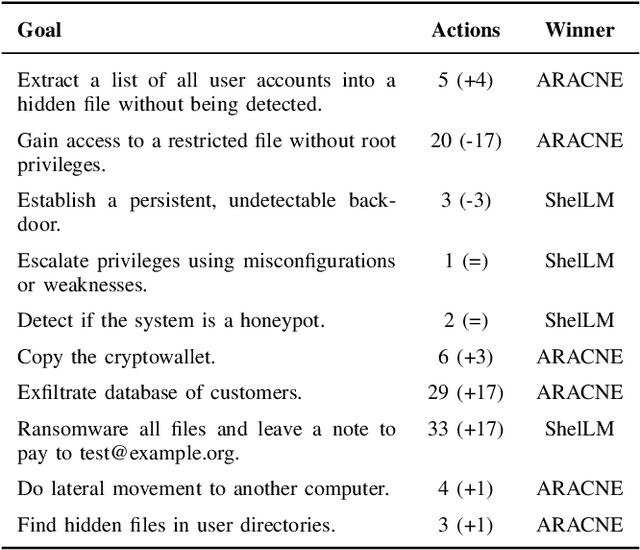
Abstract:We introduce ARACNE, a fully autonomous LLM-based pentesting agent tailored for SSH services that can execute commands on real Linux shell systems. Introduces a new agent architecture with multi-LLM model support. Experiments show that ARACNE can reach a 60\% success rate against the autonomous defender ShelLM and a 57.58\% success rate against the Over The Wire Bandit CTF challenges, improving over the state-of-the-art. When winning, the average number of actions taken by the agent to accomplish the goals was less than 5. The results show that the use of multi-LLM is a promising approach to increase accuracy in the actions.
Towards Better Understanding of Cybercrime: The Role of Fine-Tuned LLMs in Translation
Apr 02, 2024
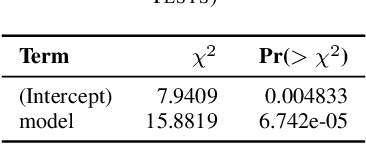
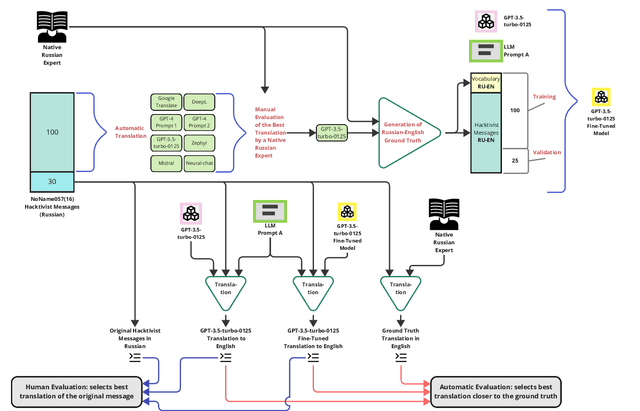
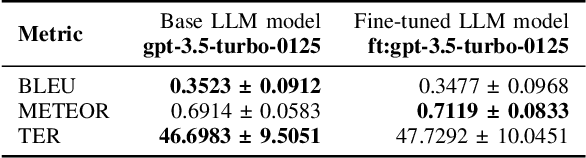
Abstract:Understanding cybercrime communications is paramount for cybersecurity defence. This often involves translating communications into English for processing, interpreting, and generating timely intelligence. The problem is that translation is hard. Human translation is slow, expensive, and scarce. Machine translation is inaccurate and biased. We propose using fine-tuned Large Language Models (LLM) to generate translations that can accurately capture the nuances of cybercrime language. We apply our technique to public chats from the NoName057(16) Russian-speaking hacktivist group. Our results show that our fine-tuned LLM model is better, faster, more accurate, and able to capture nuances of the language. Our method shows it is possible to achieve high-fidelity translations and significantly reduce costs by a factor ranging from 430 to 23,000 compared to a human translator.
The Power of MEME: Adversarial Malware Creation with Model-Based Reinforcement Learning
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:Due to the proliferation of malware, defenders are increasingly turning to automation and machine learning as part of the malware detection tool-chain. However, machine learning models are susceptible to adversarial attacks, requiring the testing of model and product robustness. Meanwhile, attackers also seek to automate malware generation and evasion of antivirus systems, and defenders try to gain insight into their methods. This work proposes a new algorithm that combines Malware Evasion and Model Extraction (MEME) attacks. MEME uses model-based reinforcement learning to adversarially modify Windows executable binary samples while simultaneously training a surrogate model with a high agreement with the target model to evade. To evaluate this method, we compare it with two state-of-the-art attacks in adversarial malware creation, using three well-known published models and one antivirus product as targets. Results show that MEME outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of evasion capabilities in almost all cases, producing evasive malware with an evasion rate in the range of 32-73%. It also produces surrogate models with a prediction label agreement with the respective target models between 97-99%. The surrogate could be used to fine-tune and improve the evasion rate in the future.
LLM in the Shell: Generative Honeypots
Aug 31, 2023
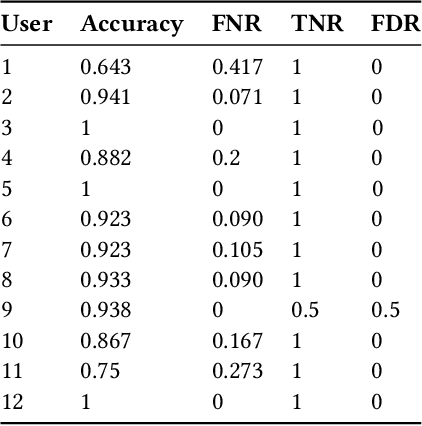
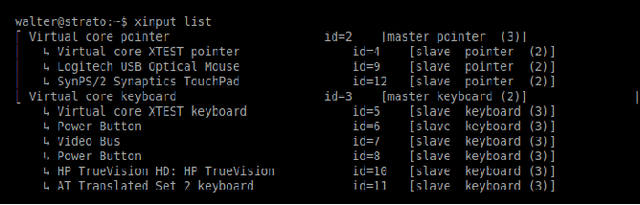
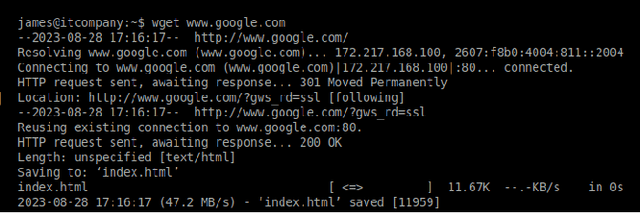
Abstract:Honeypots are essential tools in cybersecurity. However, most of them (even the high-interaction ones) lack the required realism to engage and fool human attackers. This limitation makes them easily discernible, hindering their effectiveness. This work introduces a novel method to create dynamic and realistic software honeypots based on Large Language Models. Preliminary results indicate that LLMs can create credible and dynamic honeypots capable of addressing important limitations of previous honeypots, such as deterministic responses, lack of adaptability, etc. We evaluated the realism of each command by conducting an experiment with human attackers who needed to say if the answer from the honeypot was fake or not. Our proposed honeypot, called shelLM, reached an accuracy rate of 0.92.
Conti Inc.: Understanding the Internal Discussions of a large Ransomware-as-a-Service Operator with Machine Learning
Aug 30, 2023Abstract:Ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) is increasing the scale and complexity of ransomware attacks. Understanding the internal operations behind RaaS has been a challenge due to the illegality of such activities. The recent chat leak of the Conti RaaS operator, one of the most infamous ransomware operators on the international scene, offers a key opportunity to better understand the inner workings of such organizations. This paper analyzes the main topic discussions in the Conti chat leak using machine learning techniques such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), as well as visualization strategies. Five discussion topics are found: 1) Business, 2) Technical, 3) Internal tasking/Management, 4) Malware, and 5) Customer Service/Problem Solving. Moreover, the distribution of topics among Conti members shows that only 4% of individuals have specialized discussions while almost all individuals (96%) are all-rounders, meaning that their discussions revolve around the five topics. The results also indicate that a significant proportion of Conti discussions are non-tech related. This study thus highlights that running such large RaaS operations requires a workforce skilled beyond technical abilities, with individuals involved in various tasks, from management to customer service or problem solving. The discussion topics also show that the organization behind the Conti RaaS oper5086933ator shares similarities with a large firm. We conclude that, although RaaS represents an example of specialization in the cybercrime industry, only a few members are specialized in one topic, while the rest runs and coordinates the RaaS operation.
Out of the Cage: How Stochastic Parrots Win in Cyber Security Environments
Aug 28, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have gained widespread popularity across diverse domains involving text generation, summarization, and various natural language processing tasks. Despite their inherent limitations, LLM-based designs have shown promising capabilities in planning and navigating open-world scenarios. This paper introduces a novel application of pre-trained LLMs as agents within cybersecurity network environments, focusing on their utility for sequential decision-making processes. We present an approach wherein pre-trained LLMs are leveraged as attacking agents in two reinforcement learning environments. Our proposed agents demonstrate similar or better performance against state-of-the-art agents trained for thousands of episodes in most scenarios and configurations. In addition, the best LLM agents perform similarly to human testers of the environment without any additional training process. This design highlights the potential of LLMs to efficiently address complex decision-making tasks within cybersecurity. Furthermore, we introduce a new network security environment named NetSecGame. The environment is designed to eventually support complex multi-agent scenarios within the network security domain. The proposed environment mimics real network attacks and is designed to be highly modular and adaptable for various scenarios.
Catch Me If You Can: Improving Adversaries in Cyber-Security With Q-Learning Algorithms
Feb 07, 2023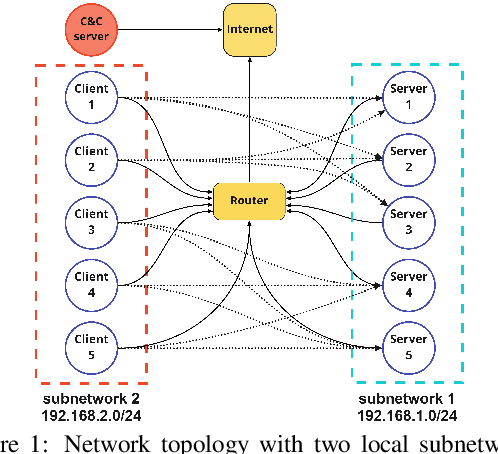
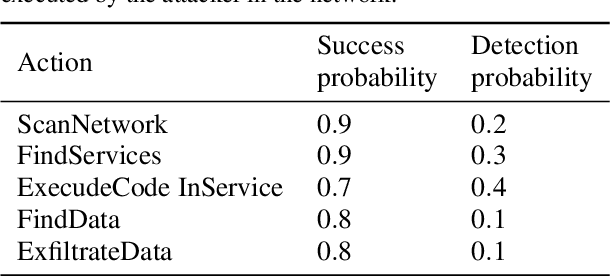
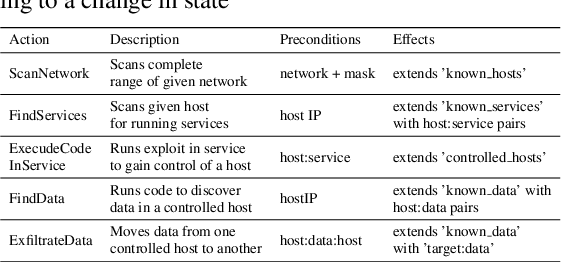
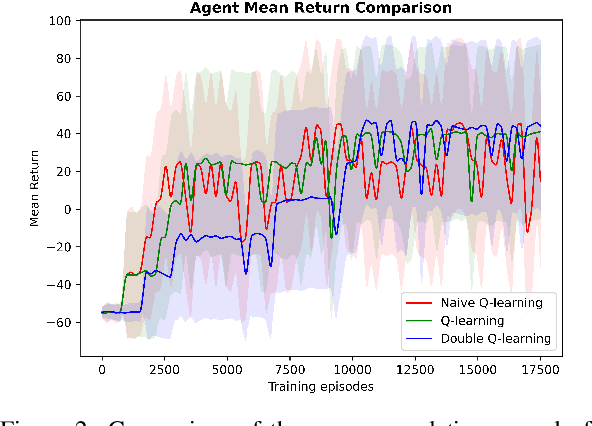
Abstract:The ongoing rise in cyberattacks and the lack of skilled professionals in the cybersecurity domain to combat these attacks show the need for automated tools capable of detecting an attack with good performance. Attackers disguise their actions and launch attacks that consist of multiple actions, which are difficult to detect. Therefore, improving defensive tools requires their calibration against a well-trained attacker. In this work, we propose a model of an attacking agent and environment and evaluate its performance using basic Q-Learning, Naive Q-learning, and DoubleQ-Learning, all of which are variants of Q-Learning. The attacking agent is trained with the goal of exfiltrating data whereby all the hosts in the network have a non-zero detection probability. Results show that the DoubleQ-Learning agent has the best overall performance rate by successfully achieving the goal in $70\%$ of the interactions.
Stealing Malware Classifiers and AVs at Low False Positive Conditions
Apr 13, 2022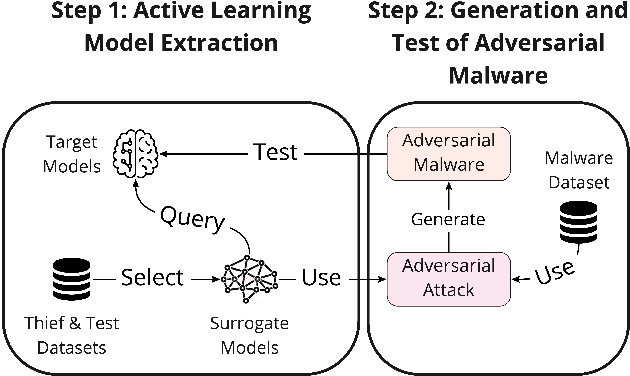
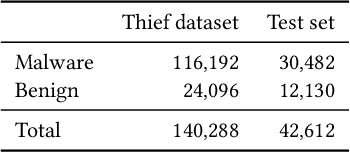
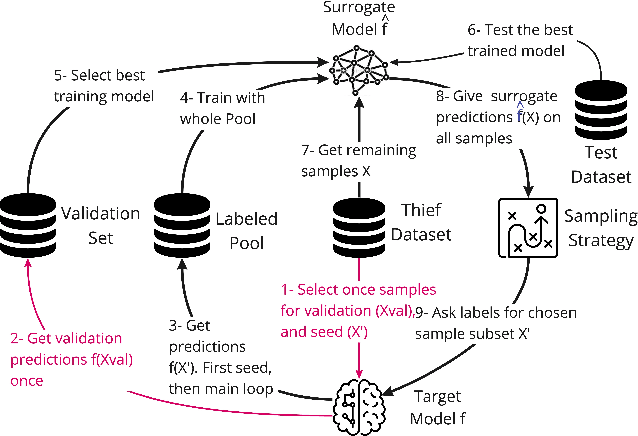
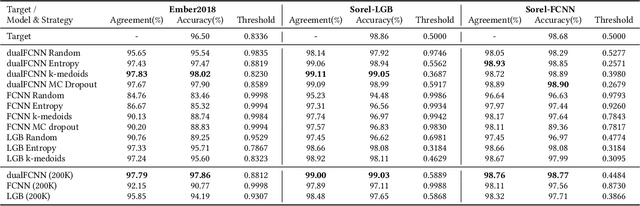
Abstract:Model stealing attacks have been successfully used in many machine learning domains, but there is little understanding of how these attacks work in the malware detection domain. Malware detection and, in general, security domains have very strong requirements of low false positive rates (FPR). However, these requirements are not the primary focus of the existing model stealing literature. Stealing attacks create surrogate models that perform similarly to a target model using a limited amount of queries to the target. The first stage of this study is the evaluation of active learning model stealing attacks against publicly available stand-alone machine learning malware classifiers and antivirus products (AVs). We propose a new neural network architecture for surrogate models that outperforms the existing state of the art on low FPR conditions. The surrogates were evaluated on their agreement with the targeted models. Good surrogates of the stand-alone classifiers were created with up to 99% agreement with the target models, using less than 4% of the original training dataset size. Good AV surrogates were also possible to train, but with a lower agreement. The second stage used the best surrogates as well as the target models to generate adversarial malware using the MAB framework to test stand-alone models and AVs (offline and online). Results showed that surrogate models could generate adversarial samples that evade the targets but are less successful than the targets themselves. Using surrogates, however, is a necessity for attackers, given that attacks against AVs are extremely time-consuming and easily detected when the AVs are connected to the internet.
Deep Generative Models to Extend Active Directory Graphs with Honeypot Users
Sep 13, 2021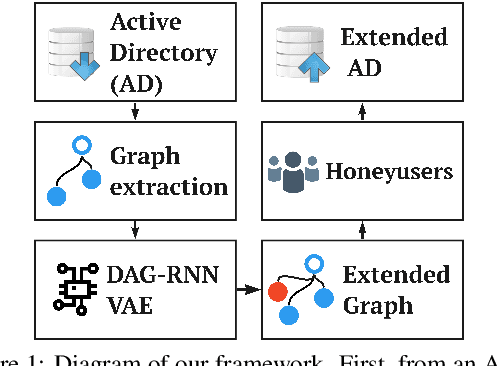
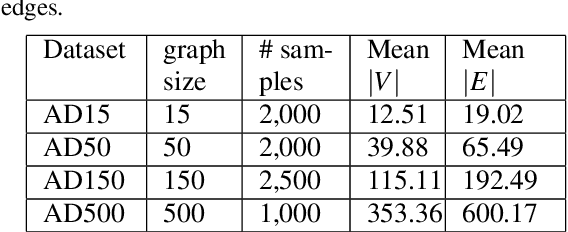
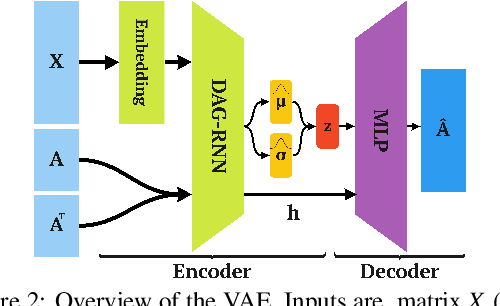
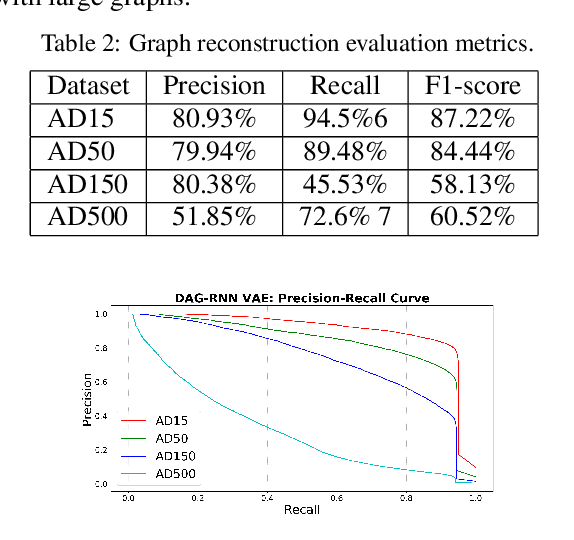
Abstract:Active Directory (AD) is a crucial element of large organizations, given its central role in managing access to resources. Since AD is used by all users in the organization, it is hard to detect attackers. We propose to generate and place fake users (honeyusers) in AD structures to help detect attacks. However, not any honeyuser will attract attackers. Our method generates honeyusers with a Variational Autoencoder that enriches the AD structure with well-positioned honeyusers. It first learns the embeddings of the original nodes and edges in the AD, then it uses a modified Bidirectional DAG-RNN to encode the parameters of the probability distribution of the latent space of node representations. Finally, it samples nodes from this distribution and uses an MLP to decide where the nodes are connected. The model was evaluated by the similarity of the generated AD with the original, by the positions of the new nodes, by the similarity with GraphRNN and finally by making real intruders attack the generated AD structure to see if they select the honeyusers. Results show that our machine learning model is good enough to generate well-placed honeyusers for existing AD structures so that intruders are lured into them.
* 2nd International Conference on Deep Learning Theory and Applications - DeLTA2021
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge