Sayantari Ghosh
Bridging the Applicator Gap with Data-Doping:Dual-Domain Learning for Precise Bladder Segmentation in CT-Guided Brachytherapy
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Performance degradation due to covariate shift remains a major challenge for deep learning models in medical image segmentation. An open question is whether samples from a shifted distribution can effectively support learning when combined with limited target domain data. We investigate this problem in the context of bladder segmentation in CT guided gynecological brachytherapy, a critical task for accurate dose optimization and organ at risk sparing. While CT scans without brachytherapy applicators (no applicator: NA) are widely available, scans with applicators inserted (with applicator: WA) are scarce and exhibit substantial anatomical deformation and imaging artifacts, making automated segmentation particularly difficult. We propose a dual domain learning strategy that integrates NA and WA CT data to improve robustness and generalizability under covariate shift. Using a curated assorted dataset, we show that NA data alone fail to capture the anatomical and artifact related characteristics of WA images. However, introducing a modest proportion of WA data into a predominantly NA training set leads to significant performance improvements. Through systematic experiments across axial, coronal, and sagittal planes using multiple deep learning architectures, we demonstrate that doping only 10 to 30 percent WA data achieves segmentation performance comparable to models trained exclusively on WA data. The proposed approach attains Dice similarity coefficients of up to 0.94 and Intersection over Union scores of up to 0.92, indicating effective domain adaptation and improved clinical reliability. This study highlights the value of integrating anatomically similar but distribution shifted datasets to overcome data scarcity and enhance deep learning based segmentation for brachytherapy treatment planning.
F-ANcGAN: An Attention-Enhanced Cycle Consistent Generative Adversarial Architecture for Synthetic Image Generation of Nanoparticles
May 23, 2025Abstract:Nanomaterial research is becoming a vital area for energy, medicine, and materials science, and accurate analysis of the nanoparticle topology is essential to determine their properties. Unfortunately, the lack of high-quality annotated datasets drastically hinders the creation of strong segmentation models for nanoscale imaging. To alleviate this problem, we introduce F-ANcGAN, an attention-enhanced cycle consistent generative adversarial system that can be trained using a limited number of data samples and generates realistic scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images directly from segmentation maps. Our model uses a Style U-Net generator and a U-Net segmentation network equipped with self-attention to capture structural relationships and applies augmentation methods to increase the variety of the dataset. The architecture reached a raw FID score of 17.65 for TiO$_2$ dataset generation, with a further reduction in FID score to nearly 10.39 by using efficient post-processing techniques. By facilitating scalable high-fidelity synthetic dataset generation, our approach can improve the effectiveness of downstream segmentation task training, overcoming severe data shortage issues in nanoparticle analysis, thus extending its applications to resource-limited fields.
Federated Self-Supervised Learning for One-Shot Cross-Modal and Cross-Imaging Technique Segmentation
Mar 30, 2025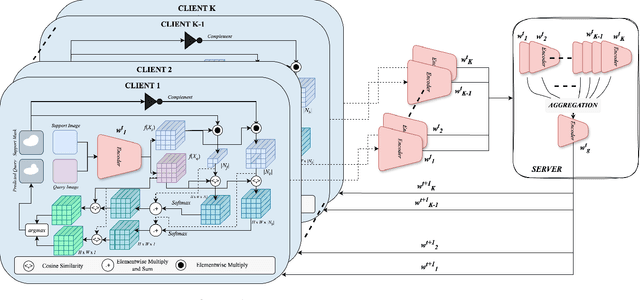



Abstract:Decentralized federated learning enables learning of data representations from multiple sources without compromising the privacy of the clients. In applications like medical image segmentation, where obtaining a large annotated dataset from a single source is a distressing problem, federated self-supervised learning can provide some solace. In this work, we push the limits further by exploring a federated self-supervised one-shot segmentation task representing a more data-scarce scenario. We adopt a pre-existing self-supervised few-shot segmentation framework CoWPro and adapt it to the federated learning scenario. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first to attempt a self-supervised few-shot segmentation task in the federated learning domain. Moreover, we consider the clients to be constituted of data from different modalities and imaging techniques like MR or CT, which makes the problem even harder. Additionally, we reinforce and improve the baseline CoWPro method using a fused dice loss which shows considerable improvement in performance over the baseline CoWPro. Finally, we evaluate this novel framework on a completely unseen held-out part of the local client dataset. We observe that the proposed framework can achieve performance at par or better than the FedAvg version of the CoWPro framework on the held-out validation dataset.
Attention W-Net: Improved Skip Connections for better Representations
Oct 17, 2021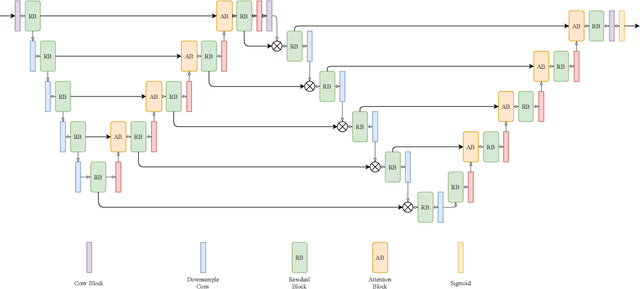
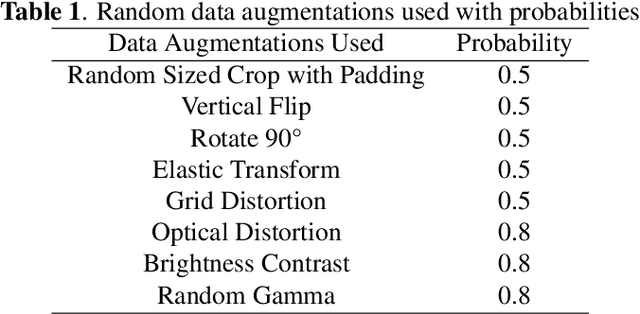
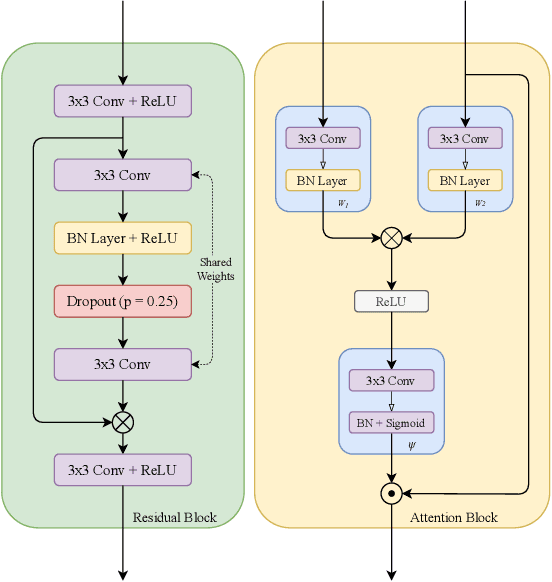
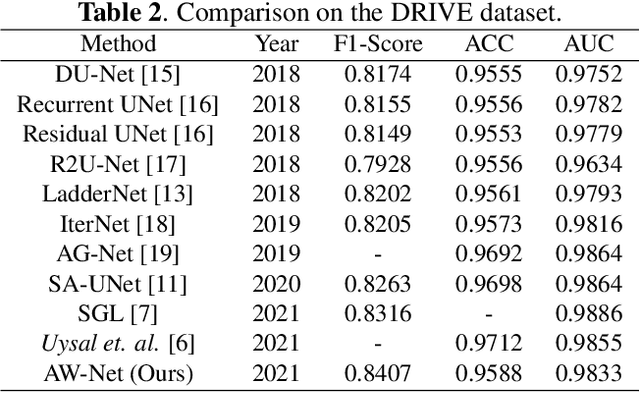
Abstract:Segmentation of macro and microvascular structures in fundoscopic retinal images plays a crucial role in detection of multiple retinal and systemic diseases, yet it is a difficult problem to solve. Most deep learning approaches for this task involve an autoencoder based architecture, but they face several issues such as lack of enough parameters, overfitting when there are enough parameters and incompatibility between internal feature-spaces. Due to such issues, these techniques are hence not able to extract the best semantic information from the limited data present for such tasks. We propose Attention W-Net, a new U-Net based architecture for retinal vessel segmentation to address these problems. In this architecture with a LadderNet backbone, we have two main contributions: Attention Block and regularisation measures. Our Attention Block uses decoder features to attend over the encoder features from skip-connections during upsampling, resulting in higher compatibility when the encoder and decoder features are added. Our regularisation measures include image augmentation and modifications to the ResNet Block used, which prevent overfitting. With these additions, we observe an AUC and F1-Score of 0.8407 and 0.9833 - a sizeable improvement over its LadderNet backbone as well as competitive performance among the contemporary state-of-the-art methods.
Detection Of Concrete Cracks using Dual-channel Deep Convolutional Network
Sep 22, 2020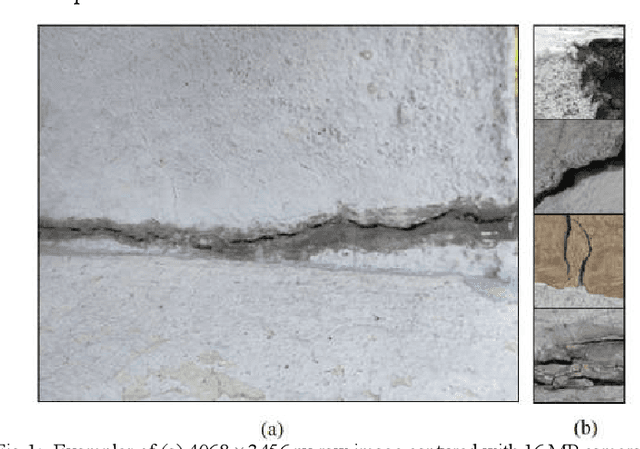
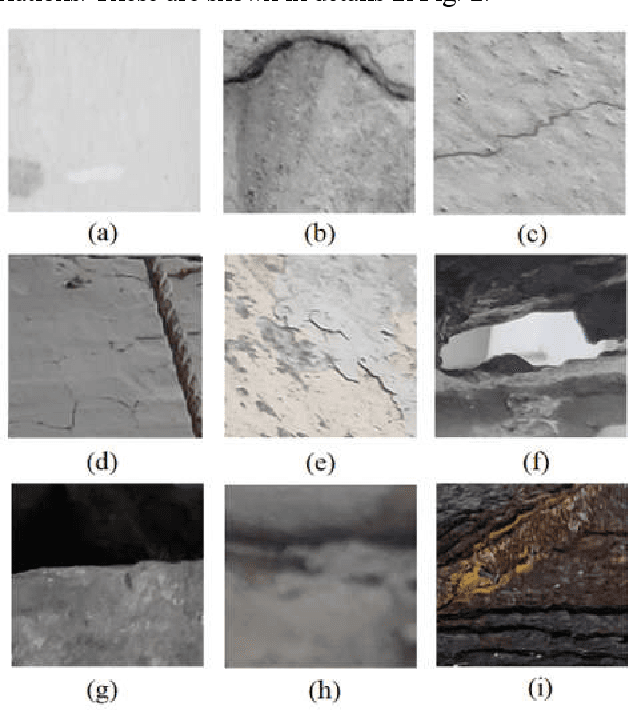

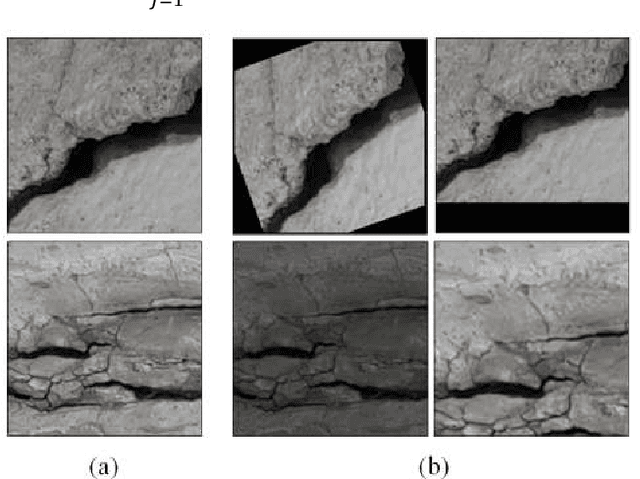
Abstract:Due to cyclic loading and fatigue stress cracks are generated, which affect the safety of any civil infrastructure. Nowadays machine vision is being used to assist us for appropriate maintenance, monitoring and inspection of concrete structures by partial replacement of human-conducted onsite inspections. The current study proposes a crack detection method based on deep convolutional neural network (CNN) for detection of concrete cracks without explicitly calculating the defect features. In the course of the study, a database of 3200 labelled images with concrete cracks has been created, where the contrast, lighting conditions, orientations and severity of the cracks were extremely variable. In this paper, starting from a deep CNN trained with these images of 256 x 256 pixel-resolution, we have gradually optimized the model by identifying the difficulties. Using an augmented dataset, which takes into account the variations and degradations compatible to drone videos, like, random zooming, rotation and intensity scaling and exhaustive ablation studies, we have designed a dual-channel deep CNN which shows high accuracy (~ 92.25%) as well as robustness in finding concrete cracks in realis-tic situations. The model has been tested on the basis of performance and analyzed with the help of feature maps, which establishes the importance of the dual-channel structure.
A Data-driven Understanding of COVID-19 Dynamics Using Sequential Genetic Algorithm Based Probabilistic Cellular Automata
Aug 27, 2020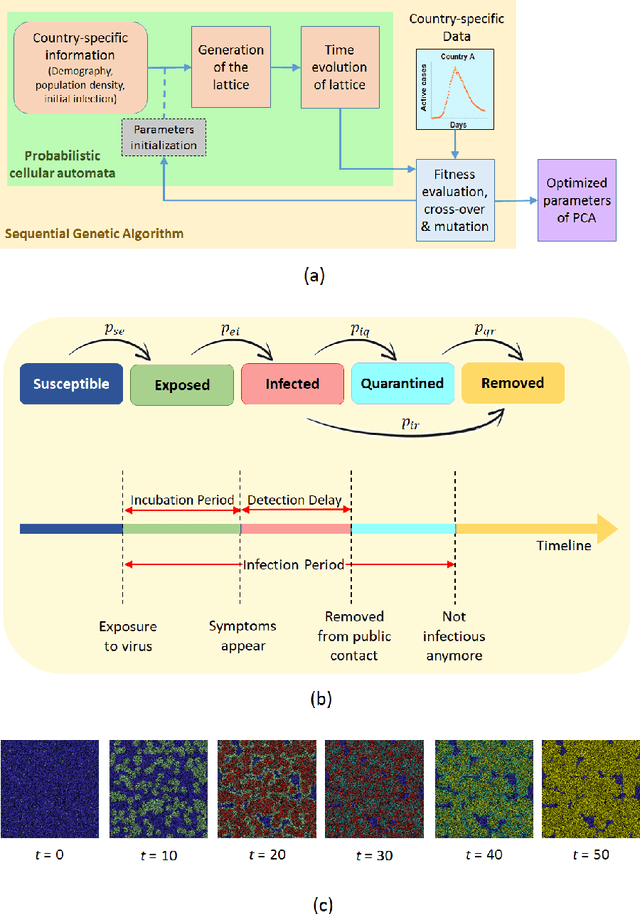
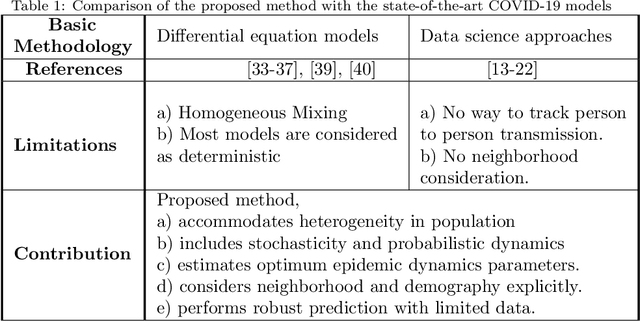
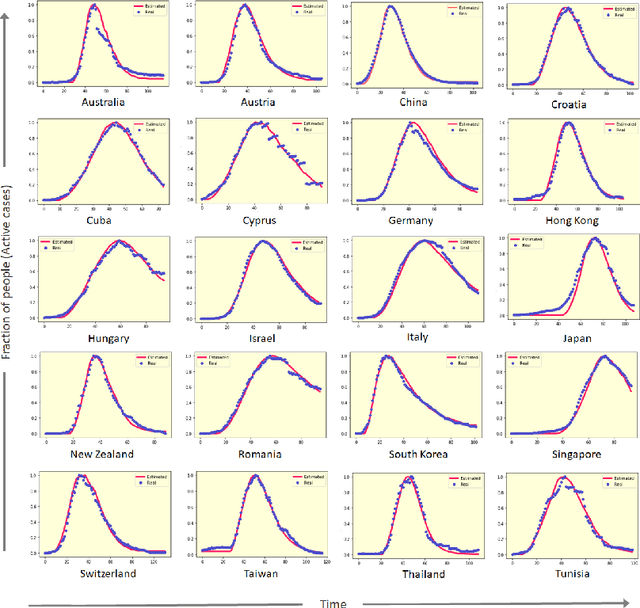
Abstract:COVID-19 pandemic is severely impacting the lives of billions across the globe. Even after taking massive protective measures like nation-wide lockdowns, discontinuation of international flight services, rigorous testing etc., the infection spreading is still growing steadily, causing thousands of deaths and serious socio-economic crisis. Thus, the identification of the major factors of this infection spreading dynamics is becoming crucial to minimize impact and lifetime of COVID-19 and any future pandemic. In this work, a probabilistic cellular automata based method has been employed to model the infection dynamics for a significant number of different countries. This study proposes that for an accurate data-driven modeling of this infection spread, cellular automata provides an excellent platform, with a sequential genetic algorithm for efficiently estimating the parameters of the dynamics. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to understand and interpret COVID-19 data using optimized cellular automata, through genetic algorithm. It has been demonstrated that the proposed methodology can be flexible and robust at the same time, and can be used to model the daily active cases, total number of infected people and total death cases through systematic parameter estimation. Elaborate analyses for COVID-19 statistics of forty countries from different continents have been performed, with markedly divergent time evolution of the infection spreading because of demographic and socioeconomic factors. The substantial predictive power of this model has been established with conclusions on the key players in this pandemic dynamics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge