Sayandeep Saha
TT-TFHE: a Torus Fully Homomorphic Encryption-Friendly Neural Network Architecture
Feb 03, 2023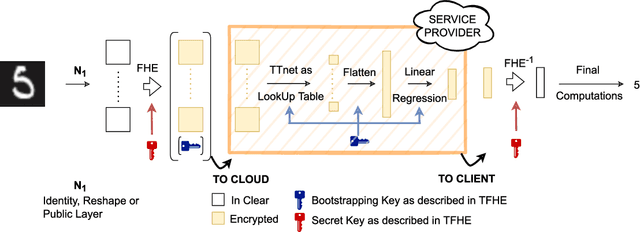
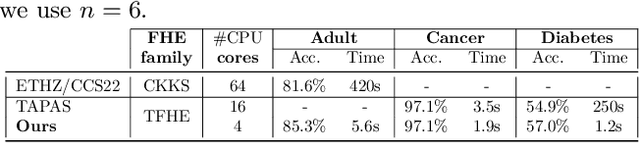
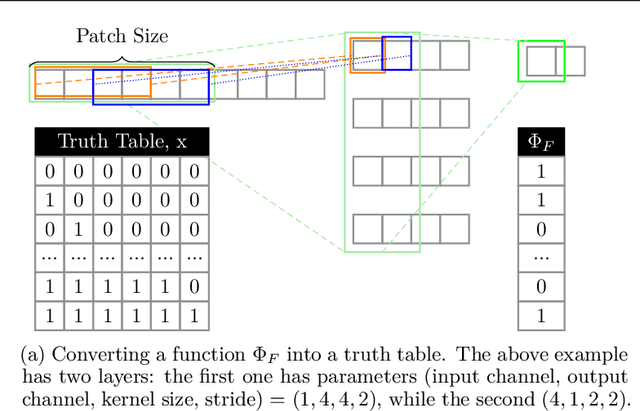
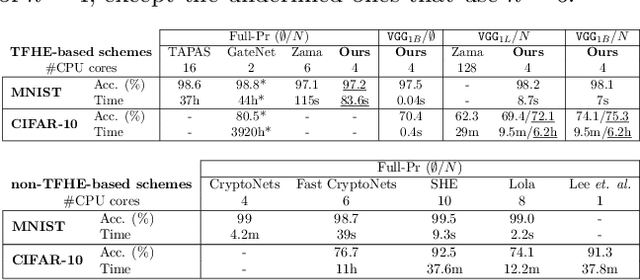
Abstract:This paper presents TT-TFHE, a deep neural network Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) framework that effectively scales Torus FHE (TFHE) usage to tabular and image datasets using a recent family of convolutional neural networks called Truth-Table Neural Networks (TTnet). The proposed framework provides an easy-to-implement, automated TTnet-based design toolbox with an underlying (python-based) open-source Concrete implementation (CPU-based and implementing lookup tables) for inference over encrypted data. Experimental evaluation shows that TT-TFHE greatly outperforms in terms of time and accuracy all Homomorphic Encryption (HE) set-ups on three tabular datasets, all other features being equal. On image datasets such as MNIST and CIFAR-10, we show that TT-TFHE consistently and largely outperforms other TFHE set-ups and is competitive against other HE variants such as BFV or CKKS (while maintaining the same level of 128-bit encryption security guarantees). In addition, our solutions present a very low memory footprint (down to dozens of MBs for MNIST), which is in sharp contrast with other HE set-ups that typically require tens to hundreds of GBs of memory per user (in addition to their communication overheads). This is the first work presenting a fully practical solution of private inference (i.e. a few seconds for inference time and a few dozens MBs of memory) on both tabular datasets and MNIST, that can easily scale to multiple threads and users on server side.
Deep-Lock: Secure Authorization for Deep Neural Networks
Aug 13, 2020
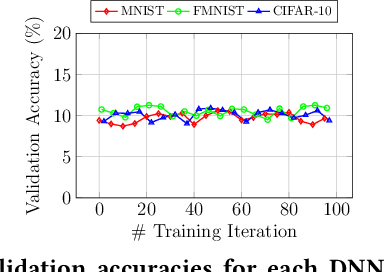
Abstract:Trained Deep Neural Network (DNN) models are considered valuable Intellectual Properties (IP) in several business models. Prevention of IP theft and unauthorized usage of such DNN models has been raised as of significant concern by industry. In this paper, we address the problem of preventing unauthorized usage of DNN models by proposing a generic and lightweight key-based model-locking scheme, which ensures that a locked model functions correctly only upon applying the correct secret key. The proposed scheme, known as Deep-Lock, utilizes S-Boxes with good security properties to encrypt each parameter of a trained DNN model with secret keys generated from a master key via a key scheduling algorithm. The resulting dense network of encrypted weights is found robust against model fine-tuning attacks. Finally, Deep-Lock does not require any intervention in the structure and training of the DNN models, making it applicable for all existing software and hardware implementations of DNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge