Sarvar Hussain Nengroo
Frequency Hopping Synchronization by Reinforcement Learning for Satellite Communication System
Mar 06, 2025



Abstract:Satellite communication systems (SCSs) used for tactical purposes require robust security and anti-jamming capabilities, making frequency hopping (FH) a powerful option. However, the current FH systems face challenges due to significant interference from other devices and the considerable path loss inherent in satellite communication. This misalignment leads to inefficient synchronization, crucial for maintaining reliable communication. Traditional methods, such as those employing long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, have made improvements, but they still struggle in dynamic conditions of satellite environments. This paper presents a novel method for synchronizing FH signals in tactical SCSs by combining serial search and reinforcement learning to achieve coarse and fine acquisition, respectively. The mathematical analysis and simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method reduces the average number of hops required for synchronization by 58.17% and mean squared error (MSE) of the uplink hop timing estimation by 76.95%, as compared to the conventional serial search method. Comparing with the early late gate synchronization method based on serial search and use of LSTM network, the average number of hops for synchronization is reduced by 12.24% and the MSE by 18.5%.
Power Management in Smart Residential Building with Deep Learning Model for Occupancy Detection by Usage Pattern of Electric Appliances
Sep 23, 2022



Abstract:With the growth of smart building applications, occupancy information in residential buildings is becoming more and more significant. In the context of the smart buildings' paradigm, this kind of information is required for a wide range of purposes, including enhancing energy efficiency and occupant comfort. In this study, occupancy detection in residential building is implemented using deep learning based on technical information of electric appliances. To this end, a novel approach of occupancy detection for smart residential building system is proposed. The dataset of electric appliances, sensors, light, and HVAC, which is measured by smart metering system and is collected from 50 households, is used for simulations. To classify the occupancy among datasets, the support vector machine and autoencoder algorithm are used. Confusion matrix is utilized for accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 to demonstrate the comparative performance of the proposed method in occupancy detection. The proposed algorithm achieves occupancy detection using technical information of electric appliances by 95.7~98.4%. To validate occupancy detection data, principal component analysis and the t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) algorithm are employed. Power consumption with renewable energy system is reduced to 11.1~13.1% in smart buildings by using occupancy detection.
Reinforcement Learning Based Cooperative P2P Energy Trading between DC Nanogrid Clusters with Wind and PV Energy Resources
Sep 16, 2022



Abstract:In order to replace fossil fuels with the use of renewable energy resources, unbalanced resource production of intermittent wind and photovoltaic (PV) power is a critical issue for peer-to-peer (P2P) power trading. To resolve this problem, a reinforcement learning (RL) technique is introduced in this paper. For RL, graph convolutional network (GCN) and bi-directional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) network are jointly applied to P2P power trading between nanogrid clusters based on cooperative game theory. The flexible and reliable DC nanogrid is suitable to integrate renewable energy for distribution system. Each local nanogrid cluster takes the position of prosumer, focusing on power production and consumption simultaneously. For the power management of nanogrid clusters, multi-objective optimization is applied to each local nanogrid cluster with the Internet of Things (IoT) technology. Charging/discharging of electric vehicle (EV) is performed considering the intermittent characteristics of wind and PV power production. RL algorithms, such as deep Q-learning network (DQN), deep recurrent Q-learning network (DRQN), Bi-DRQN, proximal policy optimization (PPO), GCN-DQN, GCN-DRQN, GCN-Bi-DRQN, and GCN-PPO, are used for simulations. Consequently, the cooperative P2P power trading system maximizes the profit utilizing the time of use (ToU) tariff-based electricity cost and system marginal price (SMP), and minimizes the amount of grid power consumption. Power management of nanogrid clusters with P2P power trading is simulated on the distribution test feeder in real-time and proposed GCN-PPO technique reduces the electricity cost of nanogrid clusters by 36.7%.
Path Planning of Cleaning Robot with Reinforcement Learning
Aug 17, 2022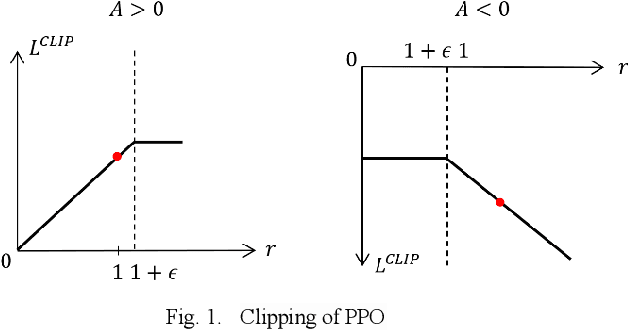
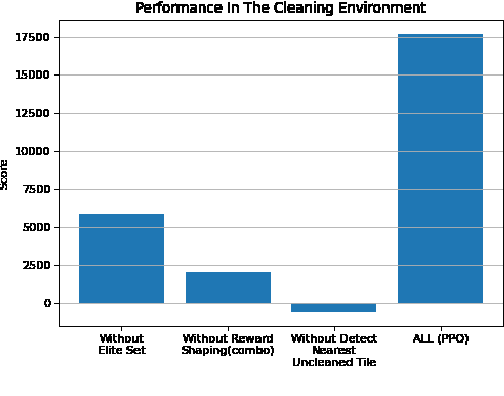
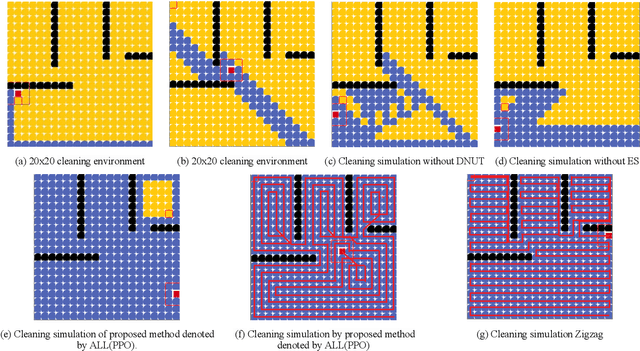
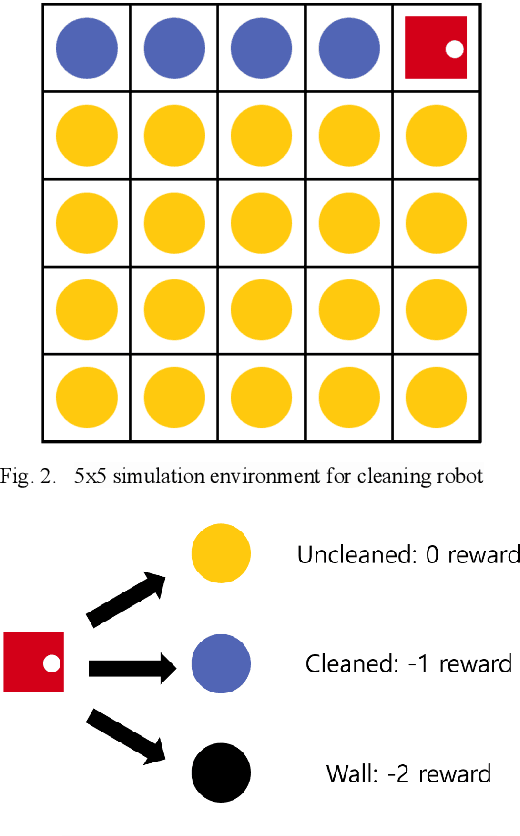
Abstract:Recently, as the demand for cleaning robots has steadily increased, therefore household electricity consumption is also increasing. To solve this electricity consumption issue, the problem of efficient path planning for cleaning robot has become important and many studies have been conducted. However, most of them are about moving along a simple path segment, not about the whole path to clean all places. As the emerging deep learning technique, reinforcement learning (RL) has been adopted for cleaning robot. However, the models for RL operate only in a specific cleaning environment, not the various cleaning environment. The problem is that the models have to retrain whenever the cleaning environment changes. To solve this problem, the proximal policy optimization (PPO) algorithm is combined with an efficient path planning that operates in various cleaning environments, using transfer learning (TL), detection nearest cleaned tile, reward shaping, and making elite set methods. The proposed method is validated with an ablation study and comparison with conventional methods such as random and zigzag. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method achieves improved training performance and increased convergence speed over the original PPO. And it also demonstrates that this proposed method is better performance than conventional methods (random, zigzag).
Learning Dense Features for Point Cloud Registration Using Graph Attention Network
Jun 14, 2022



Abstract:Point cloud registration is a fundamental task in many applications such as localization, mapping, tracking, and reconstruction. The successful registration relies on extracting robust and discriminative geometric features. Existing learning-based methods require high computing capacity for processing a large number of raw points at the same time. Although these approaches achieve convincing results, they are difficult to apply in real-world situations due to high computational costs. In this paper, we introduce a framework that efficiently and economically extracts dense features using graph attention network for point cloud matching and registration (DFGAT). The detector of the DFGAT is responsible for finding highly reliable key points in large raw data sets. The descriptor of the DFGAT takes these key points combined with their neighbors to extract invariant density features in preparation for the matching. The graph attention network uses the attention mechanism that enriches the relationships between point clouds. Finally, we consider this as an optimal transport problem and use the Sinkhorn algorithm to find positive and negative matches. We perform thorough tests on the KITTI dataset and evaluate the effectiveness of this approach. The results show that this method with the efficiently compact keypoint selection and description can achieve the best performance matching metrics and reach highest success ratio of 99.88% registration in comparison with other state-of-the-art approaches.
Reinforcement Learning for Navigation of Mobile Robot with LiDAR
Dec 07, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents a technique for navigation of mobile robot with Deep Q-Network (DQN) combined with Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU). The DQN integrated with the GRU allows action skipping for improved navigation performance. This technique aims at efficient navigation of mobile robot such as autonomous parking robot. Framework for reinforcement learning can be applied to the DQN combined with the GRU in a real environment, which can be modeled by the Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP). By allowing action skipping, the ability of the DQN combined with the GRU in learning key-action can be improved. The proposed algorithm is applied to explore the feasibility of solution in real environment by the ROS-Gazebo simulator, and the simulation results show that the proposed algorithm achieves improved performance in navigation and collision avoidance as compared to the results obtained by DQN alone and DQN combined with GRU without allowing action skipping.
Smart Metering System Capable of Anomaly Detection by Bi-directional LSTM Autoencoder
Dec 06, 2021



Abstract:Anomaly detection is concerned with a wide range of applications such as fault detection, system monitoring, and event detection. Identifying anomalies from metering data obtained from smart metering system is a critical task to enhance reliability, stability, and efficiency of the power system. This paper presents an anomaly detection process to find outliers observed in the smart metering system. In the proposed approach, bi-directional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) based autoencoder is used and finds the anomalous data point. It calculates the reconstruction error through autoencoder with the non-anomalous data, and the outliers to be classified as anomalies are separated from the non-anomalous data by predefined threshold. Anomaly detection method based on the BiLSTM autoencoder is tested with the metering data corresponding to 4 types of energy sources electricity/water/heating/hot water collected from 985 households.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge