Sariya Karimova
Heidelberg University
LibriVoxDeEn: A Corpus for German-to-English Speech Translation and Speech Recognition
Oct 18, 2019



Abstract:We present a corpus of sentence-aligned triples of German audio, German text, and English translation, based on German audio books. The corpus consists of over 100 hours of audio material and over 50k parallel sentences. The audio data is read speech and thus low in disfluencies. The quality of audio and sentence alignments has been checked by a manual evaluation, showing that speech alignment quality is in general very high. The sentence alignment quality is comparable to well-used parallel translation data and can be adjusted by cutoffs on the automatic alignment score. To our knowledge, this corpus is to date the largest resource for end-to-end speech translation for German.
A User-Study on Online Adaptation of Neural Machine Translation to Human Post-Edits
Sep 18, 2018


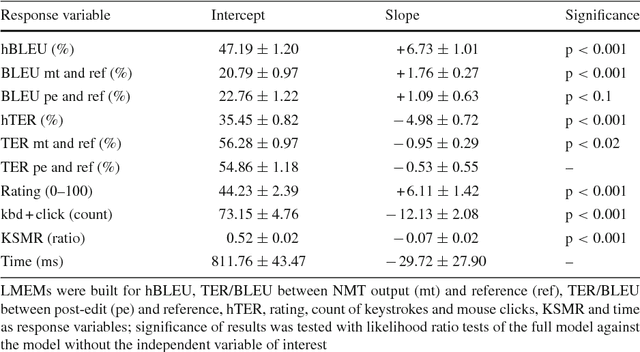
Abstract:The advantages of neural machine translation (NMT) have been extensively validated for offline translation of several language pairs for different domains of spoken and written language. However, research on interactive learning of NMT by adaptation to human post-edits has so far been confined to simulation experiments. We present the first user study on online adaptation of NMT to user post-edits in the domain of patent translation. Our study involves 29 human subjects (translation students) whose post-editing effort and translation quality were measured on about 4,500 interactions of a human post-editor and a machine translation system integrating an online adaptive learning algorithm. Our experimental results show a significant reduction of human post-editing effort due to online adaptation in NMT according to several evaluation metrics, including hTER, hBLEU, and KSMR. Furthermore, we found significant improvements in BLEU/TER between NMT outputs and professional translations in granted patents, providing further evidence for the advantages of online adaptive NMT in an interactive setup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge