Sarah E. Houts
Ford Highway Driving RTK Dataset: 30,000 km of North American Highways
Oct 05, 2020

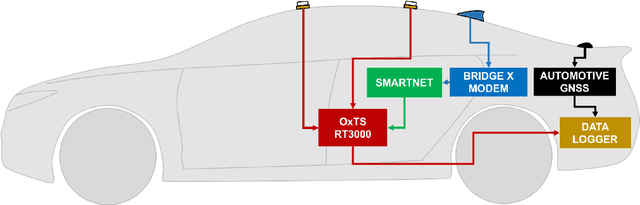

Abstract:There is a growing need for vehicle positioning information to support Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), Connectivity (V2X), and Autonomous Driving (AD) features. These range from a need for road determination ($<$5 meters), lane determination ($<$1.5 meters), and determining where the vehicle is within the lane ($<$0.3 meters). This paper presents the Ford Highway Driving RTK (Ford-HDR) dataset. This dataset includes nearly 30,000 km of data collected primarily on North American highways during a driving campaign designed to validate driver assistance features in 2018. This includes data from a representative automotive production GNSS used primarily for turn-by-turn navigation as well as an Inertial Navigation System (INS) which couples two survey-grade GNSS receivers with a tactical grade Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) to act as ground truth. The latter utilized networked Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GNSS corrections delivered over a cellular modem in real-time. This dataset is being released into the public domain to spark further research in the community.
Standalone and RTK GNSS on 30,000 km of North American Highways
Jul 17, 2019



Abstract:There is a growing need for vehicle positioning information to support Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS), Connectivity (V2X), and Automated Driving (AD) features. These range from a need for road determination (<5 meters), lane determination (<1.5 meters), and determining where the vehicle is within the lane (<0.3 meters). This work examines the performance of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) on 30,000 km of North American highways to better understand the automotive positioning needs it meets today and what might be possible in the near future with wide area GNSS correction services and multi-frequency receivers. This includes data from a representative automotive production GNSS used primarily for turn-by-turn navigation as well as an Inertial Navigation System which couples two survey grade GNSS receivers with a tactical grade Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) to act as ground truth. The latter utilized networked Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) GNSS corrections delivered over a cellular modem in real-time. We assess on-road GNSS accuracy, availability, and continuity. Availability and continuity are broken down in terms of satellite visibility, satellite geometry, position type (RTK fixed, RTK float, or standard positioning), and RTK correction latency over the network. Results show that current automotive solutions are best suited to meet road determination requirements at 98% availability but are less suitable for lane determination at 57%. Multi-frequency receivers with RTK corrections were found more capable with road determination at 99.5%, lane determination at 98%, and highway-level lane departure protection at 91%.
Localization Requirements for Autonomous Vehicles
Jun 03, 2019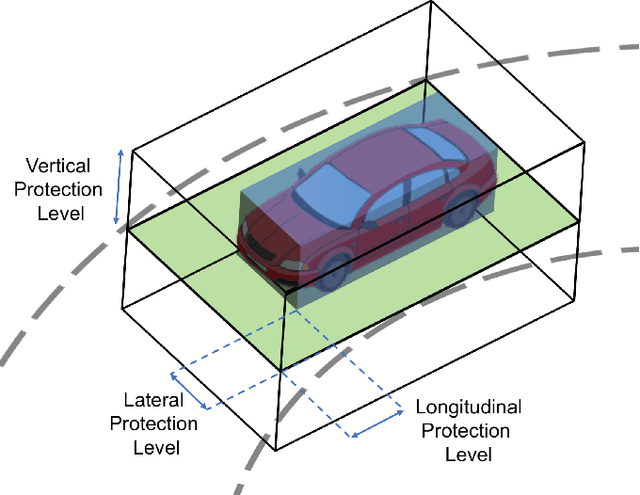



Abstract:Autonomous vehicles require precise knowledge of their position and orientation in all weather and traffic conditions for path planning, perception, control, and general safe operation. Here we derive these requirements for autonomous vehicles based on first principles. We begin with the safety integrity level, defining the allowable probability of failure per hour of operation based on desired improvements on road safety today. This draws comparisons with the localization integrity levels required in aviation and rail where similar numbers are derived at 10^-8 probability of failure per hour of operation. We then define the geometry of the problem, where the aim is to maintain knowledge that the vehicle is within its lane and to determine what road level it is on. Longitudinal, lateral, and vertical localization error bounds (alert limits) and 95% accuracy requirements are derived based on US road geometry standards (lane width, curvature, and vertical clearance) and allowable vehicle dimensions. For passenger vehicles operating on freeway roads, the result is a required lateral error bound of 0.57 m (0.20 m, 95%), a longitudinal bound of 1.40 m (0.48 m, 95%), a vertical bound of 1.30 m (0.43 m, 95%), and an attitude bound in each direction of 1.50 deg (0.51 deg, 95%). On local streets, the road geometry makes requirements more stringent where lateral and longitudinal error bounds of 0.29 m (0.10 m, 95%) are needed with an orientation requirement of 0.50 deg (0.17 deg, 95%).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge