Sara Romiti
Okapi: Generalising Better by Making Statistical Matches Match
Nov 07, 2022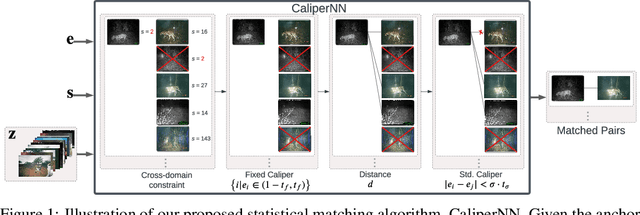
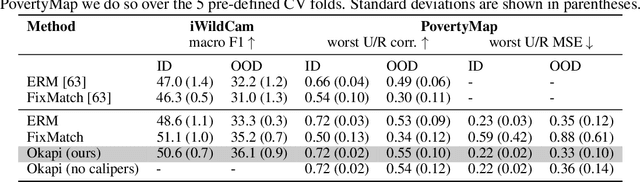
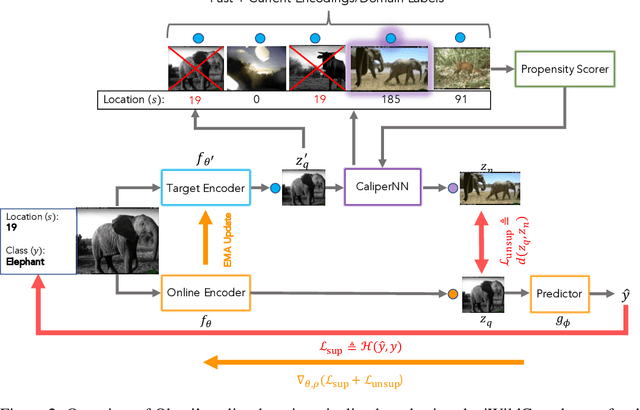

Abstract:We propose Okapi, a simple, efficient, and general method for robust semi-supervised learning based on online statistical matching. Our method uses a nearest-neighbours-based matching procedure to generate cross-domain views for a consistency loss, while eliminating statistical outliers. In order to perform the online matching in a runtime- and memory-efficient way, we draw upon the self-supervised literature and combine a memory bank with a slow-moving momentum encoder. The consistency loss is applied within the feature space, rather than on the predictive distribution, making the method agnostic to both the modality and the task in question. We experiment on the WILDS 2.0 datasets Sagawa et al., which significantly expands the range of modalities, applications, and shifts available for studying and benchmarking real-world unsupervised adaptation. Contrary to Sagawa et al., we show that it is in fact possible to leverage additional unlabelled data to improve upon empirical risk minimisation (ERM) results with the right method. Our method outperforms the baseline methods in terms of out-of-distribution (OOD) generalisation on the iWildCam (a multi-class classification task) and PovertyMap (a regression task) image datasets as well as the CivilComments (a binary classification task) text dataset. Furthermore, from a qualitative perspective, we show the matches obtained from the learned encoder are strongly semantically related. Code for our paper is publicly available at https://github.com/wearepal/okapi/.
RealPatch: A Statistical Matching Framework for Model Patching with Real Samples
Aug 03, 2022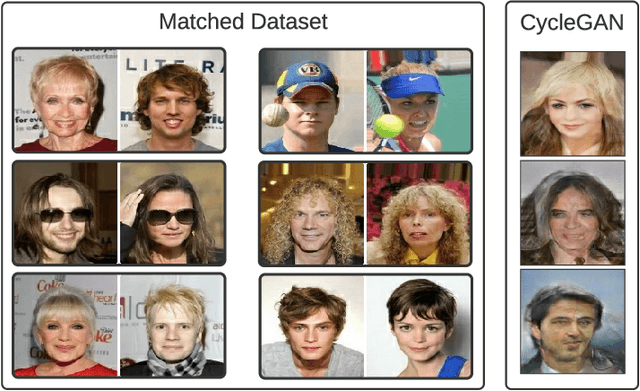
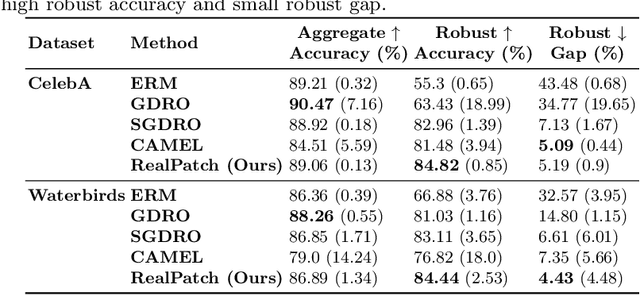
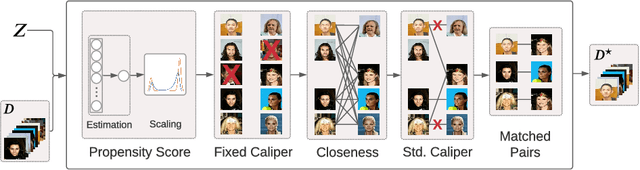

Abstract:Machine learning classifiers are typically trained to minimise the average error across a dataset. Unfortunately, in practice, this process often exploits spurious correlations caused by subgroup imbalance within the training data, resulting in high average performance but highly variable performance across subgroups. Recent work to address this problem proposes model patching with CAMEL. This previous approach uses generative adversarial networks to perform intra-class inter-subgroup data augmentations, requiring (a) the training of a number of computationally expensive models and (b) sufficient quality of model's synthetic outputs for the given domain. In this work, we propose RealPatch, a framework for simpler, faster, and more data-efficient data augmentation based on statistical matching. Our framework performs model patching by augmenting a dataset with real samples, mitigating the need to train generative models for the target task. We demonstrate the effectiveness of RealPatch on three benchmark datasets, CelebA, Waterbirds and a subset of iWildCam, showing improvements in worst-case subgroup performance and in subgroup performance gap in binary classification. Furthermore, we conduct experiments with the imSitu dataset with 211 classes, a setting where generative model-based patching such as CAMEL is impractical. We show that RealPatch can successfully eliminate dataset leakage while reducing model leakage and maintaining high utility. The code for RealPatch can be found at https://github.com/wearepal/RealPatch.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge