Sanja Karilanova
Low-Bit Data Processing Using Multiple-Output Spiking Neurons with Non-linear Reset Feedback
Aug 08, 2025



Abstract:Neuromorphic computing is an emerging technology enabling low-latency and energy-efficient signal processing. A key algorithmic tool in neuromorphic computing is spiking neural networks (SNNs). SNNs are biologically inspired neural networks which utilize stateful neurons, and provide low-bit data processing by encoding and decoding information using spikes. Similar to SNNs, deep state-space models (SSMs) utilize stateful building blocks. However, deep SSMs, which recently achieved competitive performance in various temporal modeling tasks, are typically designed with high-precision activation functions and no reset mechanisms. To bridge the gains offered by SNNs and the recent deep SSM models, we propose a novel multiple-output spiking neuron model that combines a linear, general SSM state transition with a non-linear feedback mechanism through reset. Compared to the existing neuron models for SNNs, our proposed model clearly conceptualizes the differences between the spiking function, the reset condition and the reset action. The experimental results on various tasks, i.e., a keyword spotting task, an event-based vision task and a sequential pattern recognition task, show that our proposed model achieves performance comparable to existing benchmarks in the SNN literature. Our results illustrate how the proposed reset mechanism can overcome instability and enable learning even when the linear part of neuron dynamics is unstable, allowing us to go beyond the strictly enforced stability of linear dynamics in recent deep SSM models.
* 15 pages, 7 Tables, 6 Figures
State-Space Model Inspired Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Spiking Neurons
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:In spiking neural networks (SNNs), the main unit of information processing is the neuron with an internal state. The internal state generates an output spike based on its component associated with the membrane potential. This spike is then communicated to other neurons in the network. Here, we propose a general multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) spiking neuron model that goes beyond this traditional single-input single-output (SISO) model in the SNN literature. Our proposed framework is based on interpreting the neurons as state-space models (SSMs) with linear state evolutions and non-linear spiking activation functions. We illustrate the trade-offs among various parameters of the proposed SSM-inspired neuron model, such as the number of hidden neuron states, the number of input and output channels, including single-input multiple-output (SIMO) and multiple-input single-output (MISO) models. We show that for SNNs with a small number of neurons with large internal state spaces, significant performance gains may be obtained by increasing the number of output channels of a neuron. In particular, a network with spiking neurons with multiple-output channels may achieve the same level of accuracy with the baseline with the continuous-valued communications on the same reference network architecture.
* 9 pages, 3 figures, 6 tables, conference - 2025 Neuro Inspired Computational Elements (NICE)
Zero-Shot Temporal Resolution Domain Adaptation for Spiking Neural Networks
Nov 07, 2024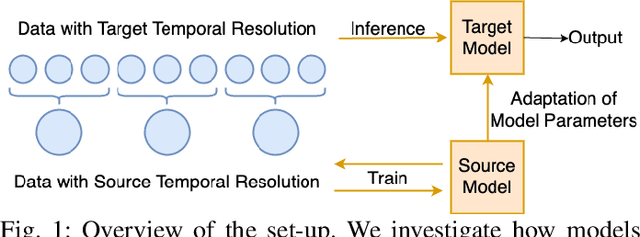


Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are biologically-inspired deep neural networks that efficiently extract temporal information while offering promising gains in terms of energy efficiency and latency when deployed on neuromorphic devices. However, SNN model parameters are sensitive to temporal resolution, leading to significant performance drops when the temporal resolution of target data at the edge is not the same with that of the pre-deployment source data used for training, especially when fine-tuning is not possible at the edge. To address this challenge, we propose three novel domain adaptation methods for adapting neuron parameters to account for the change in time resolution without re-training on target time-resolution. The proposed methods are based on a mapping between neuron dynamics in SNNs and State Space Models (SSMs); and are applicable to general neuron models. We evaluate the proposed methods under spatio-temporal data tasks, namely the audio keyword spotting datasets SHD and MSWC as well as the image classification NMINST dataset. Our methods provide an alternative to - and in majority of the cases significantly outperform - the existing reference method that simply scales the time constant. Moreover, our results show that high accuracy on high temporal resolution data can be obtained by time efficient training on lower temporal resolution data and model adaptation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge