Sangyeon Kim
VisAgent: Narrative-Preserving Story Visualization Framework
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Story visualization is the transformation of narrative elements into image sequences. While existing research has primarily focused on visual contextual coherence, the deeper narrative essence of stories often remains overlooked. This limitation hinders the practical application of these approaches, as generated images frequently fail to capture the intended meaning and nuances of the narrative fully. To address these challenges, we propose VisAgent, a training-free multi-agent framework designed to comprehend and visualize pivotal scenes within a given story. By considering story distillation, semantic consistency, and contextual coherence, VisAgent employs an agentic workflow. In this workflow, multiple specialized agents collaborate to: (i) refine layered prompts based on the narrative structure and (ii) seamlessly integrate \gt{generated} elements, including refined prompts, scene elements, and subject placement, into the final image. The empirically validated effectiveness confirms the framework's suitability for practical story visualization applications.
A Framework for Portrait Stylization with Skin-Tone Awareness and Nudity Identification
Mar 21, 2024
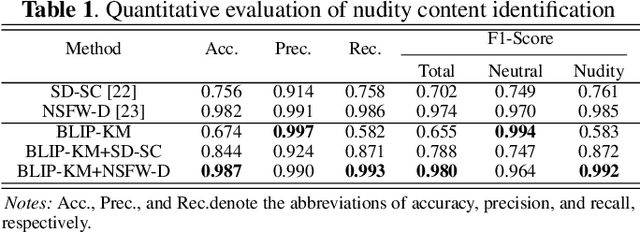
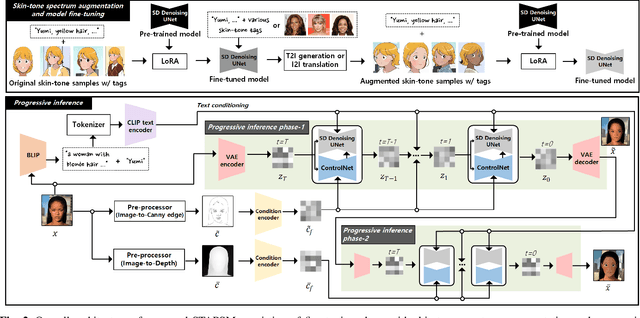

Abstract:Portrait stylization is a challenging task involving the transformation of an input portrait image into a specific style while preserving its inherent characteristics. The recent introduction of Stable Diffusion (SD) has significantly improved the quality of outcomes in this field. However, a practical stylization framework that can effectively filter harmful input content and preserve the distinct characteristics of an input, such as skin-tone, while maintaining the quality of stylization remains lacking. These challenges have hindered the wide deployment of such a framework. To address these issues, this study proposes a portrait stylization framework that incorporates a nudity content identification module (NCIM) and a skin-tone-aware portrait stylization module (STAPSM). In experiments, NCIM showed good performance in enhancing explicit content filtering, and STAPSM accurately represented a diverse range of skin tones. Our proposed framework has been successfully deployed in practice, and it has effectively satisfied critical requirements of real-world applications.
Financial series prediction using Attention LSTM
Feb 28, 2019



Abstract:Financial time series prediction, especially with machine learning techniques, is an extensive field of study. In recent times, deep learning methods (especially time series analysis) have performed outstandingly for various industrial problems, with better prediction than machine learning methods. Moreover, many researchers have used deep learning methods to predict financial time series with various models in recent years. In this paper, we will compare various deep learning models, such as multilayer perceptron (MLP), one-dimensional convolutional neural networks (1D CNN), stacked long short-term memory (stacked LSTM), attention networks, and weighted attention networks for financial time series prediction. In particular, attention LSTM is not only used for prediction, but also for visualizing intermediate outputs to analyze the reason of prediction; therefore, we will show an example for understanding the model prediction intuitively with attention vectors. In addition, we focus on time and factors, which lead to an easy understanding of why certain trends are predicted when accessing a given time series table. We also modify the loss functions of the attention models with weighted categorical cross entropy; our proposed model produces a 0.76 hit ratio, which is superior to those of other methods for predicting the trends of the KOSPI 200.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge