Sandeep Patil
Efficient Sequential Neural Network with Spatial-Temporal Attention and Linear LSTM for Robust Lane Detection Using Multi-Frame Images
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Lane detection is a crucial perception task for all levels of automated vehicles (AVs) and Advanced Driver Assistance Systems, particularly in mixed-traffic environments where AVs must interact with human-driven vehicles (HDVs) and challenging traffic scenarios. Current methods lack versatility in delivering accurate, robust, and real-time compatible lane detection, especially vision-based methods often neglect critical regions of the image and their spatial-temporal (ST) salience, leading to poor performance in difficult circumstances such as serious occlusion and dazzle lighting. This study introduces a novel sequential neural network model with a spatial-temporal attention mechanism to focus on key features of lane lines and exploit salient ST correlations among continuous image frames. The proposed model, built on a standard encoder-decoder structure and common neural network backbones, is trained and evaluated on three large-scale open-source datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate the strength and robustness of the proposed model, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in various testing scenarios. Furthermore, with the ST attention mechanism, the developed sequential neural network models exhibit fewer parameters and reduced Multiply-Accumulate Operations (MACs) compared to baseline sequential models, highlighting their computational efficiency. Relevant data, code, and models are released at https://doi.org/10.4121/4619cab6-ae4a-40d5-af77-582a77f3d821.
A Hybrid Spatial-temporal Deep Learning Architecture for Lane Detection
Oct 14, 2021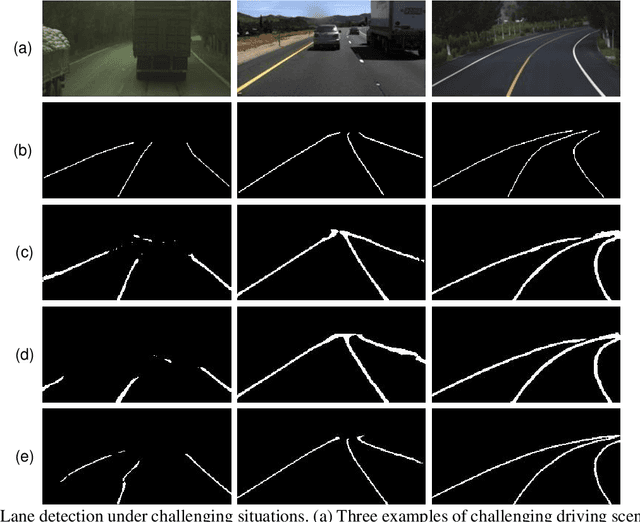
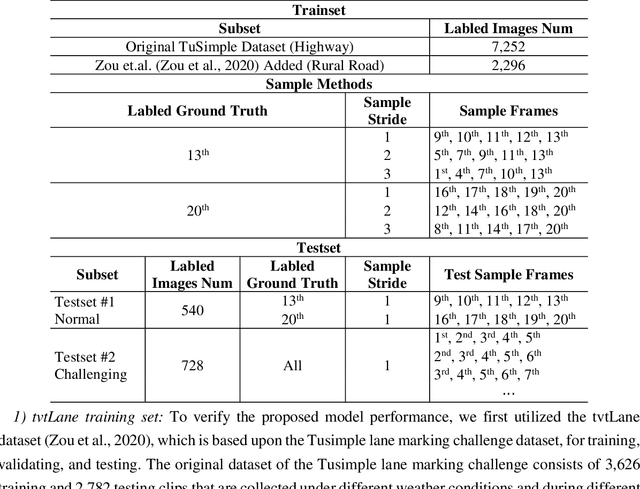
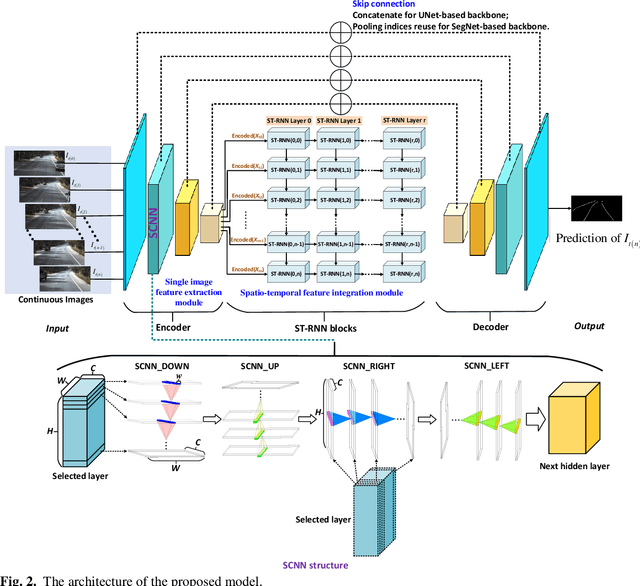
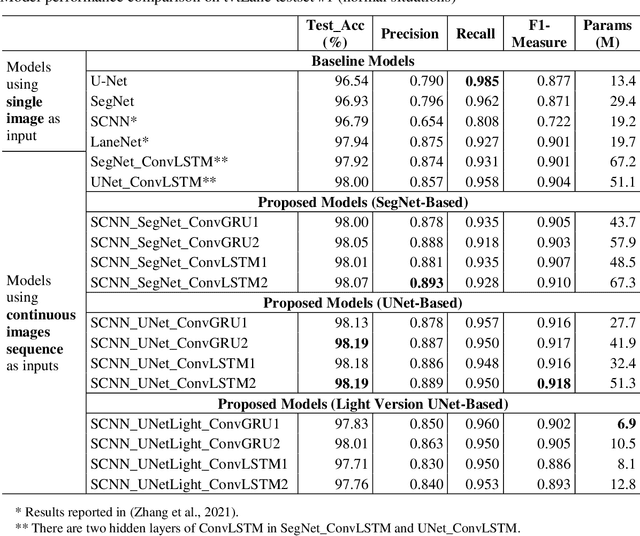
Abstract:Reliable and accurate lane detection is of vital importance for the safe performance of Lane Keeping Assistance and Lane Departure Warning systems. However, under certain challenging peculiar circumstances, it is difficult to get satisfactory performance in accurately detecting the lanes from one single image which is often the case in current literature. Since lane markings are continuous lines, the lanes that are difficult to be accurately detected in the single current image can potentially be better deduced if information from previous frames is incorporated. This study proposes a novel hybrid spatial-temporal sequence-to-one deep learning architecture making full use of the spatial-temporal information in multiple continuous image frames to detect lane markings in the very last current frame. Specifically, the hybrid model integrates the single image feature extraction module with the spatial convolutional neural network (SCNN) embedded for excavating spatial features and relationships in one single image, the spatial-temporal feature integration module with spatial-temporal recurrent neural network (ST-RNN), which can capture the spatial-temporal correlations and time dependencies among image sequences, and the encoder-decoder structure, which makes this image segmentation problem work in an end-to-end supervised learning format. Extensive experiments reveal that the proposed model can effectively handle challenging driving scenes and outperforms available state-of-the-art methods with a large margin.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge