Samuel Danso
Machine learning of neuroimaging to diagnose cognitive impairment and dementia: a systematic review and comparative analysis
Apr 11, 2018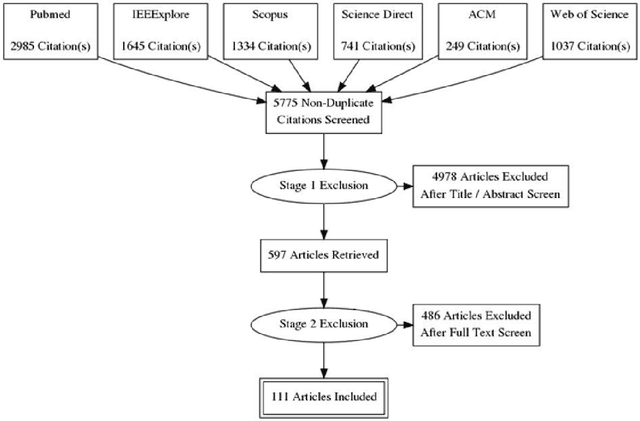
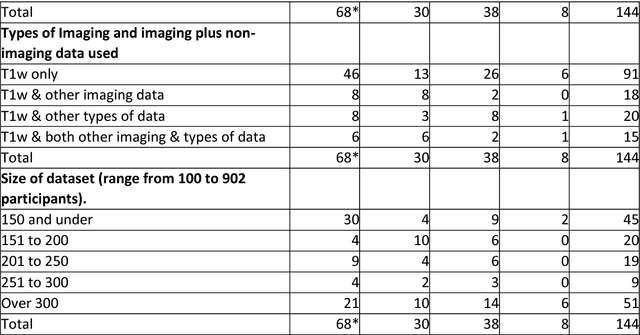
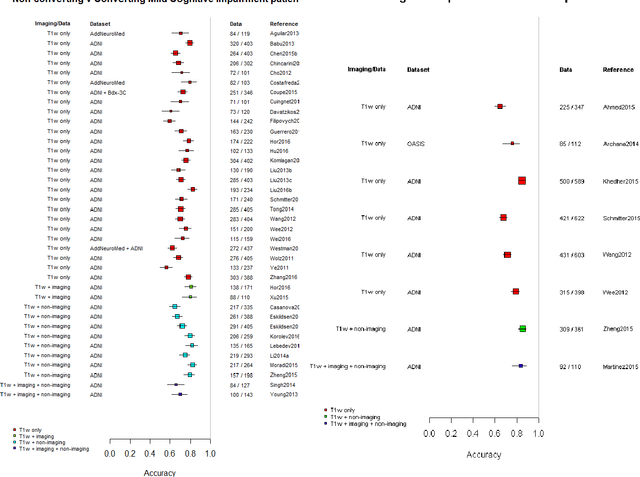
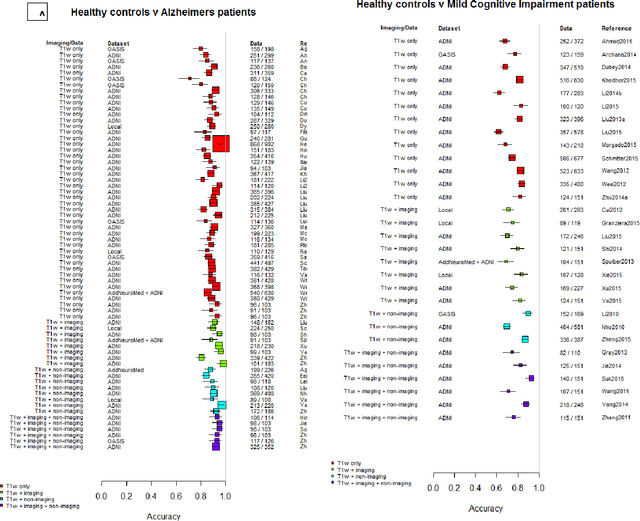
Abstract:INTRODUCTION: Advanced machine learning methods might help to identify dementia risk from neuroimaging, but their accuracy to date is unclear. METHODS: We systematically reviewed the literature, 2006 to late 2016, for machine learning studies differentiating healthy ageing through to dementia of various types, assessing study quality, and comparing accuracy at different disease boundaries. RESULTS: Of 111 relevant studies, most assessed Alzheimer's disease (AD) vs healthy controls, used ADNI data, support vector machines and only T1-weighted sequences. Accuracy was highest for differentiating AD from healthy controls, and poor for differentiating healthy controls vs MCI vs AD, or MCI converters vs non-converters. Accuracy increased using combined data types, but not by data source, sample size or machine learning method. DISCUSSION: Machine learning does not differentiate clinically-relevant disease categories yet. More diverse datasets, combinations of different types of data, and close clinical integration of machine learning would help to advance the field.
A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Methods for Verbal Autopsy Text Classification
Feb 18, 2014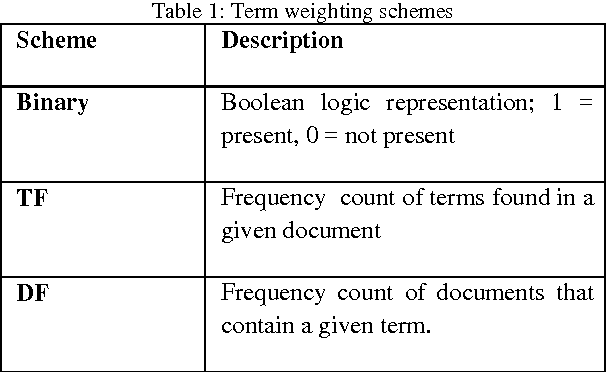
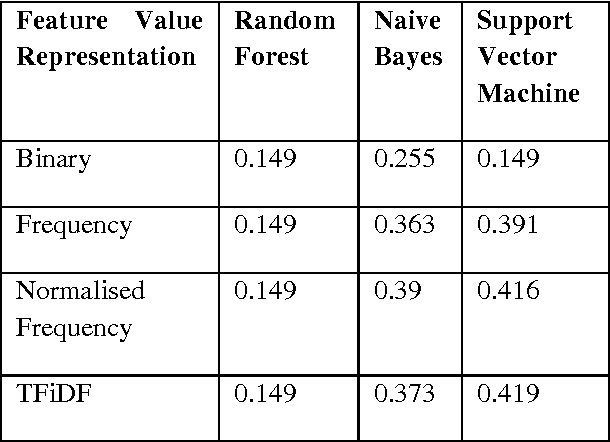
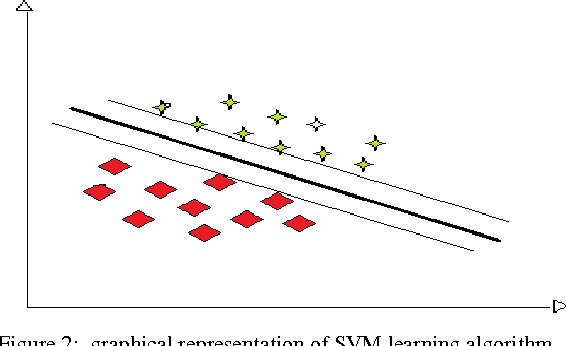
Abstract:A Verbal Autopsy is the record of an interview about the circumstances of an uncertified death. In developing countries, if a death occurs away from health facilities, a field-worker interviews a relative of the deceased about the circumstances of the death; this Verbal Autopsy can be reviewed off-site. We report on a comparative study of the processes involved in Text Classification applied to classifying Cause of Death: feature value representation; machine learning classification algorithms; and feature reduction strategies in order to identify the suitable approaches applicable to the classification of Verbal Autopsy text. We demonstrate that normalised term frequency and the standard TFiDF achieve comparable performance across a number of classifiers. The results also show Support Vector Machine is superior to other classification algorithms employed in this research. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of employing a "locally-semi-supervised" feature reduction strategy in order to increase performance accuracy.
* 10 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge