A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Methods for Verbal Autopsy Text Classification
Paper and Code
Feb 18, 2014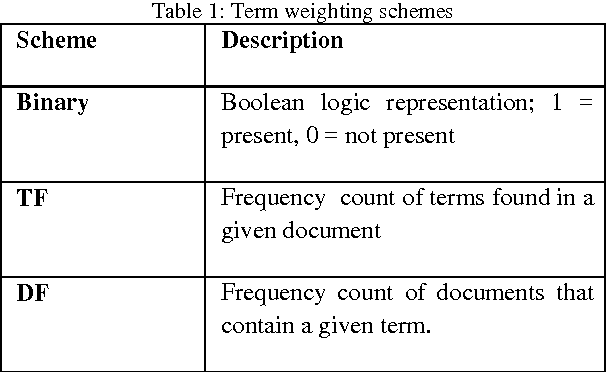
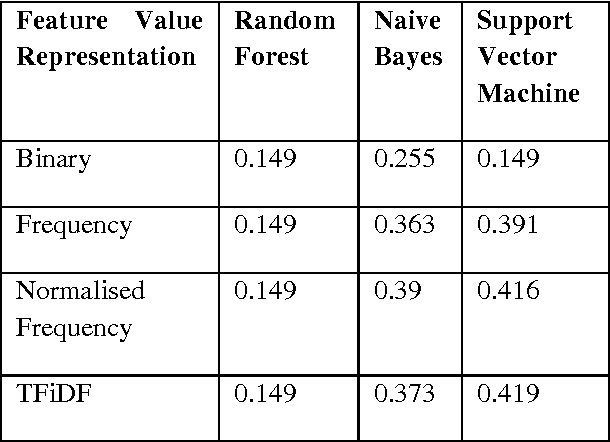
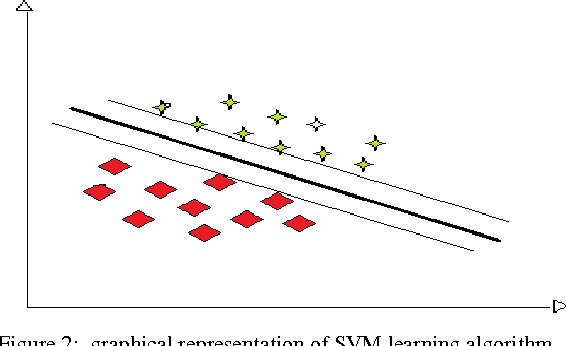
A Verbal Autopsy is the record of an interview about the circumstances of an uncertified death. In developing countries, if a death occurs away from health facilities, a field-worker interviews a relative of the deceased about the circumstances of the death; this Verbal Autopsy can be reviewed off-site. We report on a comparative study of the processes involved in Text Classification applied to classifying Cause of Death: feature value representation; machine learning classification algorithms; and feature reduction strategies in order to identify the suitable approaches applicable to the classification of Verbal Autopsy text. We demonstrate that normalised term frequency and the standard TFiDF achieve comparable performance across a number of classifiers. The results also show Support Vector Machine is superior to other classification algorithms employed in this research. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of employing a "locally-semi-supervised" feature reduction strategy in order to increase performance accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge