Samira Ziyadidegan
Machine Learning, Deep Learning and Data Preprocessing Techniques for Detection, Prediction, and Monitoring of Stress and Stress-related Mental Disorders: A Scoping Review
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:This comprehensive review systematically evaluates Machine Learning (ML) methodologies employed in the detection, prediction, and analysis of mental stress and its consequent mental disorders (MDs). Utilizing a rigorous scoping review process, the investigation delves into the latest ML algorithms, preprocessing techniques, and data types employed in the context of stress and stress-related MDs. The findings highlight that Support Vector Machine (SVM), Neural Network (NN), and Random Forest (RF) models consistently exhibit superior accuracy and robustness among all machine learning algorithms examined. Furthermore, the review underscores that physiological parameters, such as heart rate measurements and skin response, are prevalently used as stress predictors in ML algorithms. This is attributed to their rich explanatory information concerning stress and stress-related MDs, as well as the relative ease of data acquisition. Additionally, the application of dimensionality reduction techniques, including mappings, feature selection, filtering, and noise reduction, is frequently observed as a crucial step preceding the training of ML algorithms. The synthesis of this review identifies significant research gaps and outlines future directions for the field. These encompass areas such as model interpretability, model personalization, the incorporation of naturalistic settings, and real-time processing capabilities for detection and prediction of stress and stress-related MDs.
Factors affecting the COVID-19 risk in the US counties: an innovative approach by combining unsupervised and supervised learning
Jun 24, 2021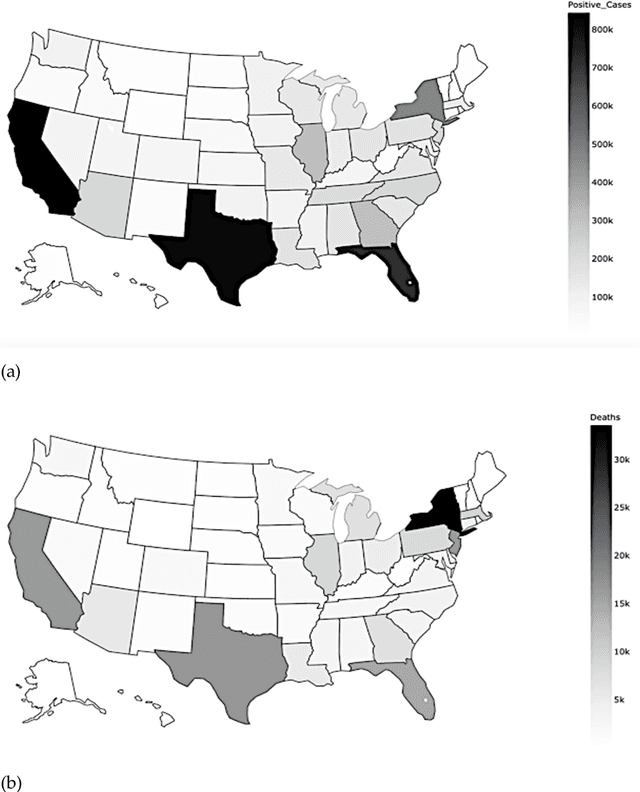
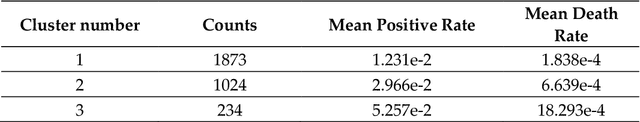
Abstract:The COVID-19 disease spreads swiftly, and nearly three months after the first positive case was confirmed in China, Coronavirus started to spread all over the United States. Some states and counties reported high number of positive cases and deaths, while some reported lower COVID-19 related cases and mortality. In this paper, the factors that could affect the risk of COVID-19 infection and mortality were analyzed in county level. An innovative method by using K-means clustering and several classification models is utilized to determine the most critical factors. Results showed that mean temperature, percent of people below poverty, percent of adults with obesity, air pressure, population density, wind speed, longitude, and percent of uninsured people were the most significant attributes
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge