Sami Hanhijärvi
Tell Me Something I Don't Know: Randomization Strategies for Iterative Data Mining
Jun 16, 2020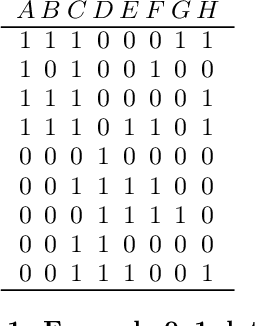
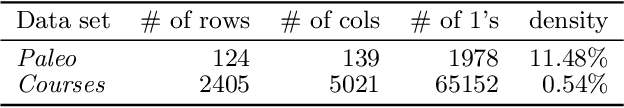
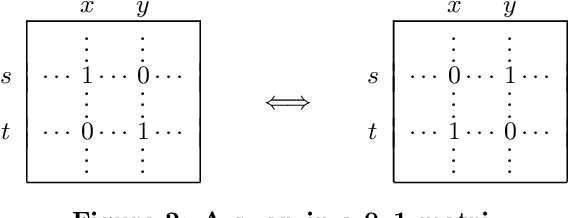
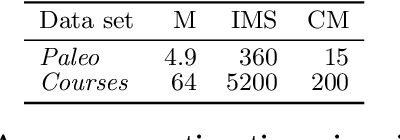
Abstract:There is a wide variety of data mining methods available, and it is generally useful in exploratory data analysis to use many different methods for the same dataset. This, however, leads to the problem of whether the results found by one method are a reflection of the phenomenon shown by the results of another method, or whether the results depict in some sense unrelated properties of the data. For example, using clustering can give indication of a clear cluster structure, and computing correlations between variables can show that there are many significant correlations in the data. However, it can be the case that the correlations are actually determined by the cluster structure. In this paper, we consider the problem of randomizing data so that previously discovered patterns or models are taken into account. The randomization methods can be used in iterative data mining. At each step in the data mining process, the randomization produces random samples from the set of data matrices satisfying the already discovered patterns or models. That is, given a data set and some statistics (e.g., cluster centers or co-occurrence counts) of the data, the randomization methods sample data sets having similar values of the given statistics as the original data set. We use Metropolis sampling based on local swaps to achieve this. We describe experiments on real data that demonstrate the usefulness of our approach. Our results indicate that in many cases, the results of, e.g., clustering actually imply the results of, say, frequent pattern discovery.
Multiple Hypothesis Testing in Pattern Discovery
Jun 29, 2009
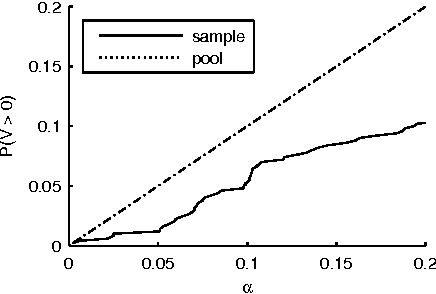
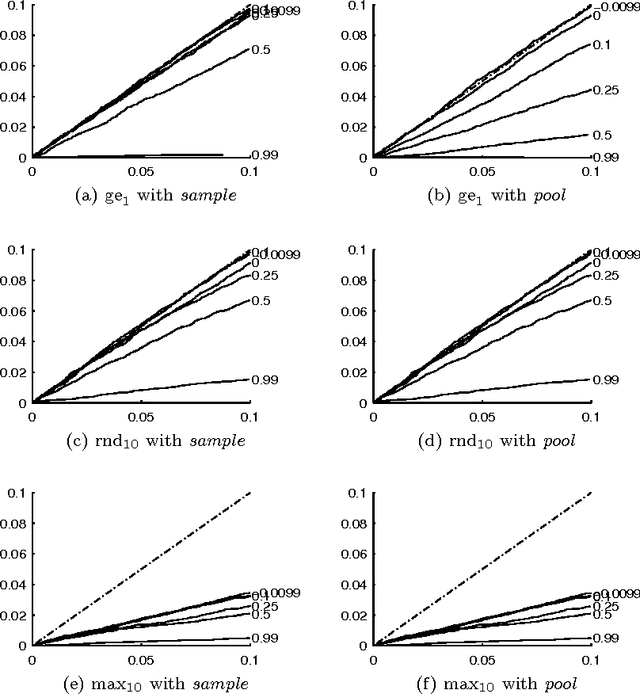
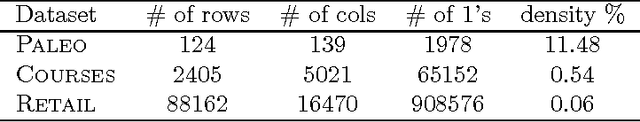
Abstract:The problem of multiple hypothesis testing arises when there are more than one hypothesis to be tested simultaneously for statistical significance. This is a very common situation in many data mining applications. For instance, assessing simultaneously the significance of all frequent itemsets of a single dataset entails a host of hypothesis, one for each itemset. A multiple hypothesis testing method is needed to control the number of false positives (Type I error). Our contribution in this paper is to extend the multiple hypothesis framework to be used with a generic data mining algorithm. We provide a method that provably controls the family-wise error rate (FWER, the probability of at least one false positive) in the strong sense. We evaluate the performance of our solution on both real and generated data. The results show that our method controls the FWER while maintaining the power of the test.
An Approximation Ratio for Biclustering
Aug 22, 2008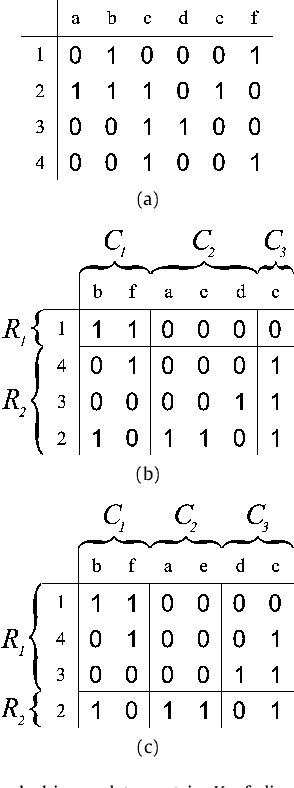
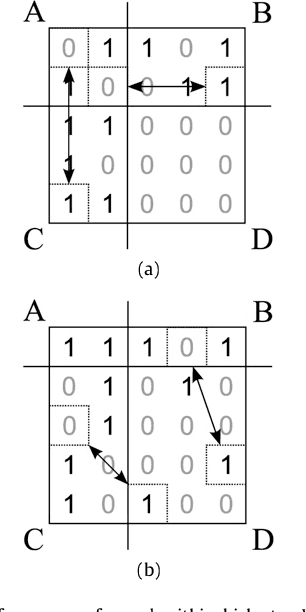
Abstract:The problem of biclustering consists of the simultaneous clustering of rows and columns of a matrix such that each of the submatrices induced by a pair of row and column clusters is as uniform as possible. In this paper we approximate the optimal biclustering by applying one-way clustering algorithms independently on the rows and on the columns of the input matrix. We show that such a solution yields a worst-case approximation ratio of 1+sqrt(2) under L1-norm for 0-1 valued matrices, and of 2 under L2-norm for real valued matrices.
* 9 pages, 2 figures; presentation clarified, replaced to match the version to be published in IPL
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge