Samarendra Chandan Bindu Dash
Evaluating LLM Reasoning in the Operations Research Domain with ORQA
Dec 22, 2024

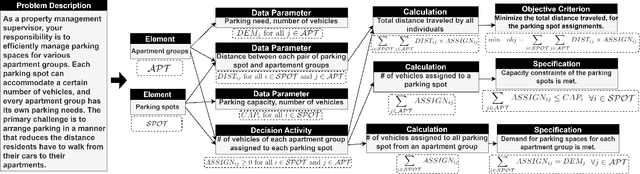
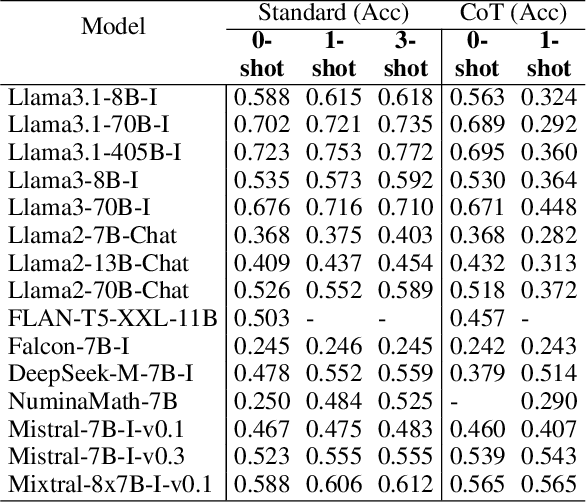
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce and apply Operations Research Question Answering (ORQA), a new benchmark designed to assess the generalization capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in the specialized technical domain of Operations Research (OR). This benchmark evaluates whether LLMs can emulate the knowledge and reasoning skills of OR experts when confronted with diverse and complex optimization problems. The dataset, developed by OR experts, features real-world optimization problems that demand multistep reasoning to construct their mathematical models. Our evaluations of various open source LLMs, such as LLaMA 3.1, DeepSeek, and Mixtral, reveal their modest performance, highlighting a gap in their ability to generalize to specialized technical domains. This work contributes to the ongoing discourse on LLMs generalization capabilities, offering valuable insights for future research in this area. The dataset and evaluation code are publicly available.
DADAgger: Disagreement-Augmented Dataset Aggregation
Jan 03, 2023

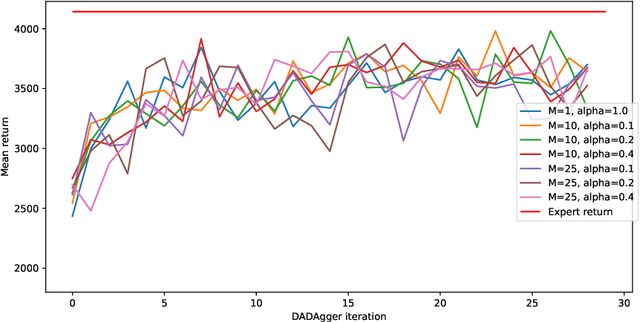
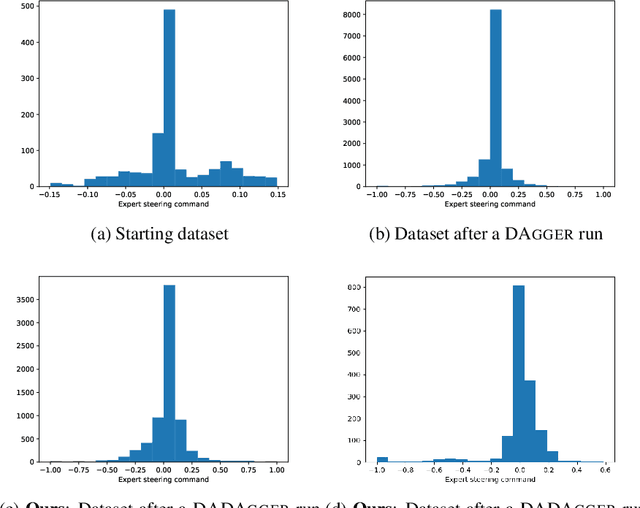
Abstract:DAgger is an imitation algorithm that aggregates its original datasets by querying the expert on all samples encountered during training. In order to reduce the number of samples queried, we propose a modification to DAgger, known as DADAgger, which only queries the expert for state-action pairs that are out of distribution (OOD). OOD states are identified by measuring the variance of the action predictions of an ensemble of models on each state, which we simulate using dropout. Testing on the Car Racing and Half Cheetah environments achieves comparable performance to DAgger but with reduced expert queries, and better performance than a random sampling baseline. We also show that our algorithm may be used to build efficient, well-balanced training datasets by running with no initial data and only querying the expert to resolve uncertainty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge