Salman Ahmadi-Asl
Lightweight Attribute Localizing Models for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Jun 16, 2023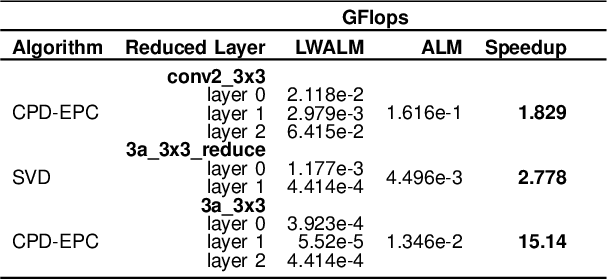
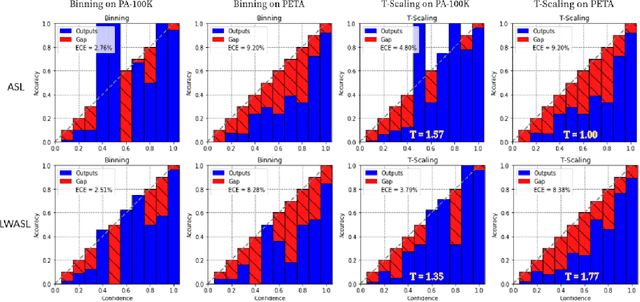
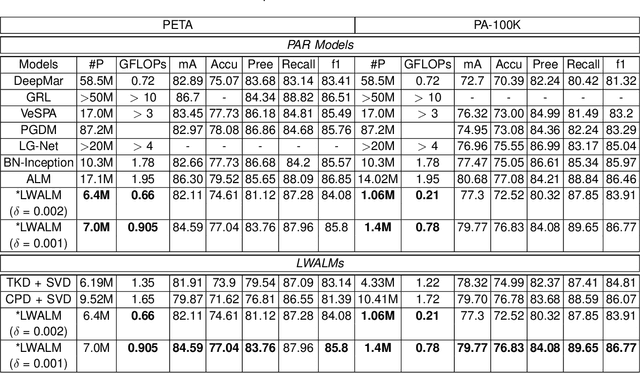
Abstract:Pedestrian Attribute Recognition (PAR) deals with the problem of identifying features in a pedestrian image. It has found interesting applications in person retrieval, suspect re-identification and soft biometrics. In the past few years, several Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have been designed to solve the task; however, the developed DNNs predominantly suffer from over-parameterization and high computational complexity. These problems hinder them from being exploited in resource-constrained embedded devices with limited memory and computational capacity. By reducing a network's layers using effective compression techniques, such as tensor decomposition, neural network compression is an effective method to tackle these problems. We propose novel Lightweight Attribute Localizing Models (LWALM) for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition (PAR). LWALM is a compressed neural network obtained after effective layer-wise compression of the Attribute Localization Model (ALM) using the Canonical Polyadic Decomposition with Error Preserving Correction (CPD-EPC) algorithm.
Image Reconstruction using Superpixel Clustering and Tensor Completion
May 16, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a pixel selection method for compact image representation based on superpixel segmentation and tensor completion. Our method divides the image into several regions that capture important textures or semantics and selects a representative pixel from each region to store. We experiment with different criteria for choosing the representative pixel and find that the centroid pixel performs the best. We also propose two smooth tensor completion algorithms that can effectively reconstruct different types of images from the selected pixels. Our experiments show that our superpixel-based method achieves better results than uniform sampling for various missing ratios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge