Sakib Haque
Statement-based Memory for Neural Source Code Summarization
Jul 21, 2023Abstract:Source code summarization is the task of writing natural language descriptions of source code behavior. Code summarization underpins software documentation for programmers. Short descriptions of code help programmers understand the program quickly without having to read the code itself. Lately, neural source code summarization has emerged as the frontier of research into automated code summarization techniques. By far the most popular targets for summarization are program subroutines. The idea, in a nutshell, is to train an encoder-decoder neural architecture using large sets of examples of subroutines extracted from code repositories. The encoder represents the code and the decoder represents the summary. However, most current approaches attempt to treat the subroutine as a single unit. For example, by taking the entire subroutine as input to a Transformer or RNN-based encoder. But code behavior tends to depend on the flow from statement to statement. Normally dynamic analysis may shed light on this flow, but dynamic analysis on hundreds of thousands of examples in large datasets is not practical. In this paper, we present a statement-based memory encoder that learns the important elements of flow during training, leading to a statement-based subroutine representation without the need for dynamic analysis. We implement our encoder for code summarization and demonstrate a significant improvement over the state-of-the-art.
Project-Level Encoding for Neural Source Code Summarization of Subroutines
Mar 22, 2021
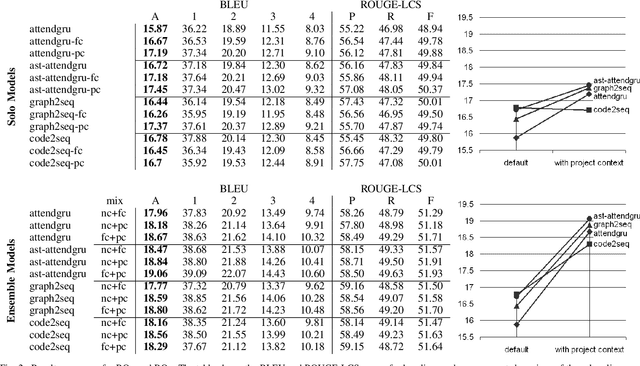
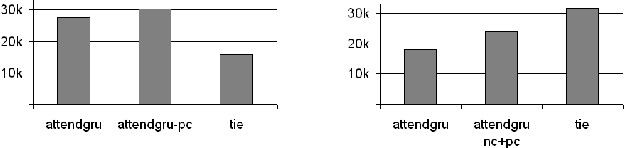
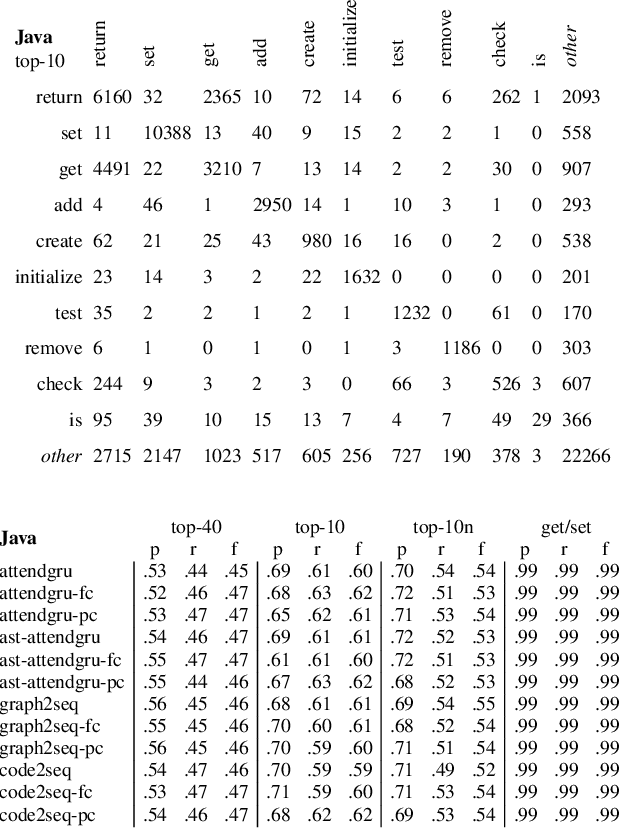
Abstract:Source code summarization of a subroutine is the task of writing a short, natural language description of that subroutine. The description usually serves in documentation aimed at programmers, where even brief phrase (e.g. "compresses data to a zip file") can help readers rapidly comprehend what a subroutine does without resorting to reading the code itself. Techniques based on neural networks (and encoder-decoder model designs in particular) have established themselves as the state-of-the-art. Yet a problem widely recognized with these models is that they assume the information needed to create a summary is present within the code being summarized itself - an assumption which is at odds with program comprehension literature. Thus a current research frontier lies in the question of encoding source code context into neural models of summarization. In this paper, we present a project-level encoder to improve models of code summarization. By project-level, we mean that we create a vectorized representation of selected code files in a software project, and use that representation to augment the encoder of state-of-the-art neural code summarization techniques. We demonstrate how our encoder improves several existing models, and provide guidelines for maximizing improvement while controlling time and resource costs in model size.
Improved Code Summarization via a Graph Neural Network
Apr 07, 2020


Abstract:Automatic source code summarization is the task of generating natural language descriptions for source code. Automatic code summarization is a rapidly expanding research area, especially as the community has taken greater advantage of advances in neural network and AI technologies. In general, source code summarization techniques use the source code as input and outputs a natural language description. Yet a strong consensus is developing that using structural information as input leads to improved performance. The first approaches to use structural information flattened the AST into a sequence. Recently, more complex approaches based on random AST paths or graph neural networks have improved on the models using flattened ASTs. However, the literature still does not describe the using a graph neural network together with source code sequence as separate inputs to a model. Therefore, in this paper, we present an approach that uses a graph-based neural architecture that better matches the default structure of the AST to generate these summaries. We evaluate our technique using a data set of 2.1 million Java method-comment pairs and show improvement over four baseline techniques, two from the software engineering literature, and two from machine learning literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge