Sahil Badyal
Deconstructing Instruction-Following: A New Benchmark for Granular Evaluation of Large Language Model Instruction Compliance Abilities
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Reliably ensuring Large Language Models (LLMs) follow complex instructions is a critical challenge, as existing benchmarks often fail to reflect real-world use or isolate compliance from task success. We introduce MOSAIC (MOdular Synthetic Assessment of Instruction Compliance), a modular framework that uses a dynamically generated dataset with up to 20 application-oriented generation constraints to enable a granular and independent analysis of this capability. Our evaluation of five LLMs from different families based on this new benchmark demonstrates that compliance is not a monolithic capability but varies significantly with constraint type, quantity, and position. The analysis reveals model-specific weaknesses, uncovers synergistic and conflicting interactions between instructions, and identifies distinct positional biases such as primacy and recency effects. These granular insights are critical for diagnosing model failures and developing more reliable LLMs for systems that demand strict adherence to complex instructions.
Enhancing LLM Instruction Following: An Evaluation-Driven Multi-Agentic Workflow for Prompt Instructions Optimization
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often generate substantively relevant content but fail to adhere to formal constraints, leading to outputs that are conceptually correct but procedurally flawed. Traditional prompt refinement approaches focus on rephrasing the description of the primary task an LLM has to perform, neglecting the granular constraints that function as acceptance criteria for its response. We propose a novel multi-agentic workflow that decouples optimization of the primary task description from its constraints, using quantitative scores as feedback to iteratively rewrite and improve them. Our evaluation demonstrates this method produces revised prompts that yield significantly higher compliance scores from models like Llama 3.1 8B and Mixtral-8x 7B.
Multiagent Rollout and Policy Iteration for POMDP with Application to Multi-Robot Repair Problems
Nov 09, 2020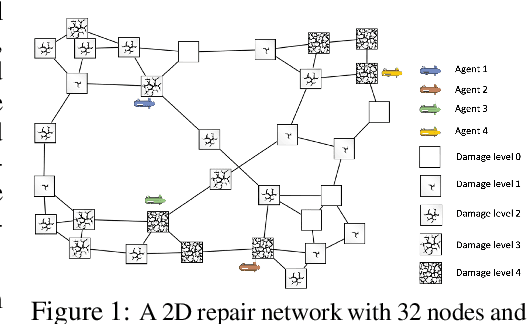
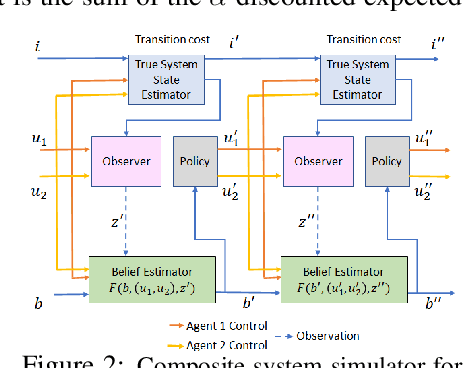
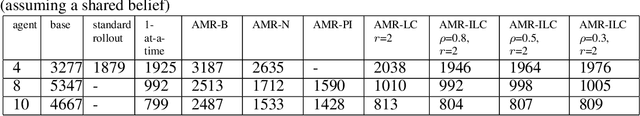
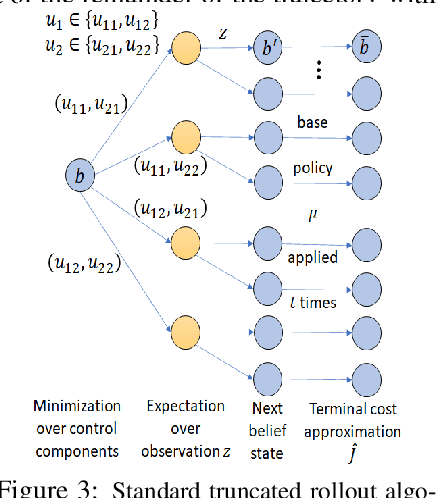
Abstract:In this paper we consider infinite horizon discounted dynamic programming problems with finite state and control spaces, partial state observations, and a multiagent structure. We discuss and compare algorithms that simultaneously or sequentially optimize the agents' controls by using multistep lookahead, truncated rollout with a known base policy, and a terminal cost function approximation. Our methods specifically address the computational challenges of partially observable multiagent problems. In particular: 1) We consider rollout algorithms that dramatically reduce required computation while preserving the key cost improvement property of the standard rollout method. The per-step computational requirements for our methods are on the order of $O(Cm)$ as compared with $O(C^m)$ for standard rollout, where $C$ is the maximum cardinality of the constraint set for the control component of each agent, and $m$ is the number of agents. 2) We show that our methods can be applied to challenging problems with a graph structure, including a class of robot repair problems whereby multiple robots collaboratively inspect and repair a system under partial information. 3) We provide a simulation study that compares our methods with existing methods, and demonstrate that our methods can handle larger and more complex partially observable multiagent problems (state space size $10^{37}$ and control space size $10^{7}$, respectively). Finally, we incorporate our multiagent rollout algorithms as building blocks in an approximate policy iteration scheme, where successive rollout policies are approximated by using neural network classifiers. While this scheme requires a strictly off-line implementation, it works well in our computational experiments and produces additional significant performance improvement over the single online rollout iteration method.
Reinforcement Learning for POMDP: Partitioned Rollout and Policy Iteration with Application to Autonomous Sequential Repair Problems
Feb 11, 2020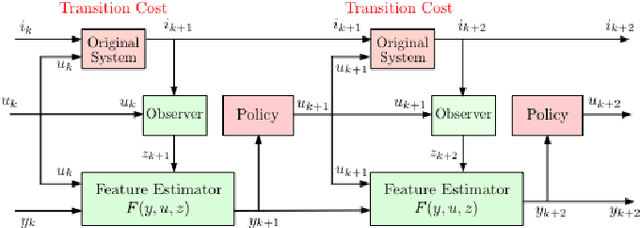


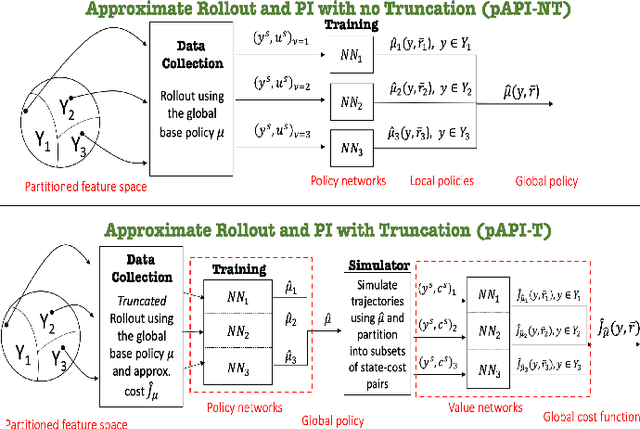
Abstract:In this paper we consider infinite horizon discounted dynamic programming problems with finite state and control spaces, and partial state observations. We discuss an algorithm that uses multistep lookahead, truncated rollout with a known base policy, and a terminal cost function approximation. This algorithm is also used for policy improvement in an approximate policy iteration scheme, where successive policies are approximated by using a neural network classifier. A novel feature of our approach is that it is well suited for distributed computation through an extended belief space formulation and the use of a partitioned architecture, which is trained with multiple neural networks. We apply our methods in simulation to a class of sequential repair problems where a robot inspects and repairs a pipeline with potentially several rupture sites under partial information about the state of the pipeline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge