Sahar Moradizeyveh
When Eye-Tracking Meets Machine Learning: A Systematic Review on Applications in Medical Image Analysis
Mar 12, 2024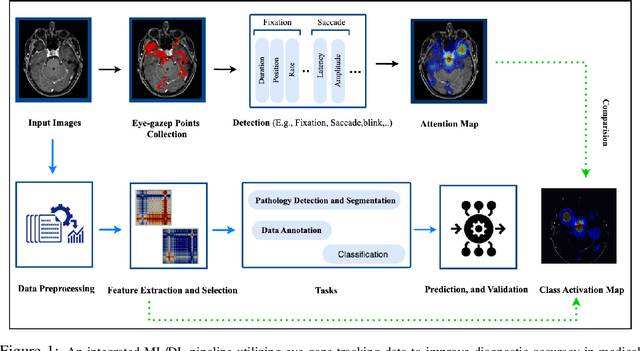
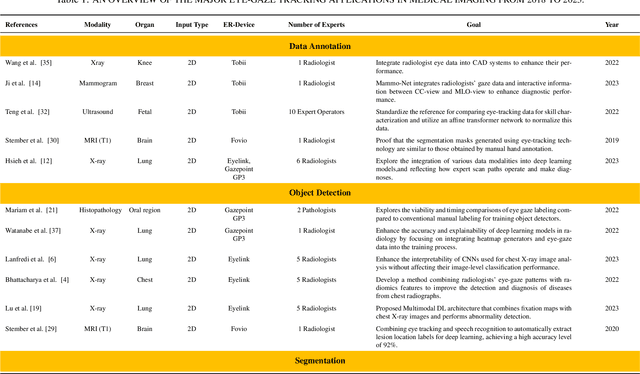
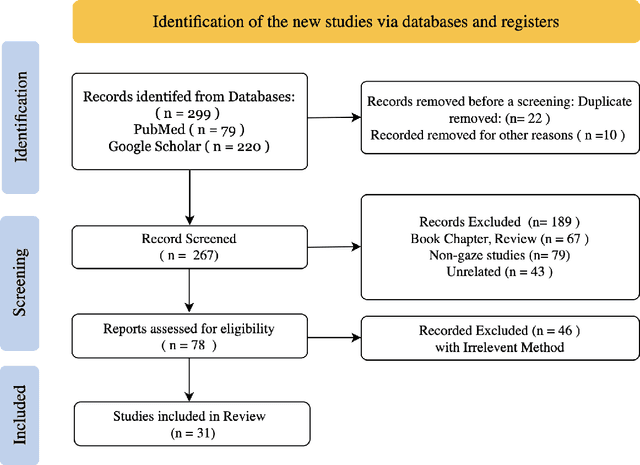
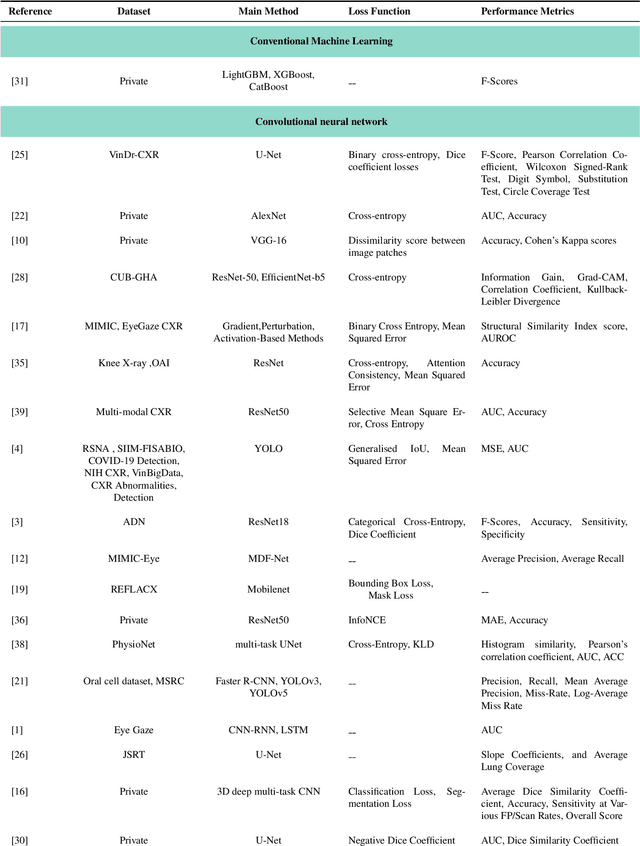
Abstract:Eye-gaze tracking research offers significant promise in enhancing various healthcare-related tasks, above all in medical image analysis and interpretation. Eye tracking, a technology that monitors and records the movement of the eyes, provides valuable insights into human visual attention patterns. This technology can transform how healthcare professionals and medical specialists engage with and analyze diagnostic images, offering a more insightful and efficient approach to medical diagnostics. Hence, extracting meaningful features and insights from medical images by leveraging eye-gaze data improves our understanding of how radiologists and other medical experts monitor, interpret, and understand images for diagnostic purposes. Eye-tracking data, with intricate human visual attention patterns embedded, provides a bridge to integrating artificial intelligence (AI) development and human cognition. This integration allows novel methods to incorporate domain knowledge into machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) approaches to enhance their alignment with human-like perception and decision-making. Moreover, extensive collections of eye-tracking data have also enabled novel ML/DL methods to analyze human visual patterns, paving the way to a better understanding of human vision, attention, and cognition. This systematic review investigates eye-gaze tracking applications and methodologies for enhancing ML/DL algorithms for medical image analysis in depth.
Intent Recognition in Conversational Recommender Systems
Dec 06, 2022Abstract:Any organization needs to improve their products, services, and processes. In this context, engaging with customers and understanding their journey is essential. Organizations have leveraged various techniques and technologies to support customer engagement, from call centres to chatbots and virtual agents. Recently, these systems have used Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to analyze large volumes of customer feedback and engagement data. The goal is to understand customers in context and provide meaningful answers across various channels. Despite multiple advances in Conversational Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Recommender Systems (RS), it is still challenging to understand the intent behind customer questions during the customer journey. To address this challenge, in this paper, we study and analyze the recent work in Conversational Recommender Systems (CRS) in general and, more specifically, in chatbot-based CRS. We introduce a pipeline to contextualize the input utterances in conversations. We then take the next step towards leveraging reverse feature engineering to link the contextualized input and learning model to support intent recognition. Since performance evaluation is achieved based on different ML models, we use transformer base models to evaluate the proposed approach using a labelled dialogue dataset (MSDialogue) of question-answering interactions between information seekers and answer providers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge