Sacha Jungerman
Radiance Fields from Photons
Jul 12, 2024Abstract:Neural radiance fields, or NeRFs, have become the de facto approach for high-quality view synthesis from a collection of images captured from multiple viewpoints. However, many issues remain when capturing images in-the-wild under challenging conditions, such as low light, high dynamic range, or rapid motion leading to smeared reconstructions with noticeable artifacts. In this work, we introduce quanta radiance fields, a novel class of neural radiance fields that are trained at the granularity of individual photons using single-photon cameras (SPCs). We develop theory and practical computational techniques for building radiance fields and estimating dense camera poses from unconventional, stochastic, and high-speed binary frame sequences captured by SPCs. We demonstrate, both via simulations and a SPC hardware prototype, high-fidelity reconstructions under high-speed motion, in low light, and for extreme dynamic range settings.
Towards 3D Vision with Low-Cost Single-Photon Cameras
Mar 29, 2024Abstract:We present a method for reconstructing 3D shape of arbitrary Lambertian objects based on measurements by miniature, energy-efficient, low-cost single-photon cameras. These cameras, operating as time resolved image sensors, illuminate the scene with a very fast pulse of diffuse light and record the shape of that pulse as it returns back from the scene at a high temporal resolution. We propose to model this image formation process, account for its non-idealities, and adapt neural rendering to reconstruct 3D geometry from a set of spatially distributed sensors with known poses. We show that our approach can successfully recover complex 3D shapes from simulated data. We further demonstrate 3D object reconstruction from real-world captures, utilizing measurements from a commodity proximity sensor. Our work draws a connection between image-based modeling and active range scanning and is a step towards 3D vision with single-photon cameras.
Panoramas from Photons
Sep 07, 2023Abstract:Scene reconstruction in the presence of high-speed motion and low illumination is important in many applications such as augmented and virtual reality, drone navigation, and autonomous robotics. Traditional motion estimation techniques fail in such conditions, suffering from too much blur in the presence of high-speed motion and strong noise in low-light conditions. Single-photon cameras have recently emerged as a promising technology capable of capturing hundreds of thousands of photon frames per second thanks to their high speed and extreme sensitivity. Unfortunately, traditional computer vision techniques are not well suited for dealing with the binary-valued photon data captured by these cameras because these are corrupted by extreme Poisson noise. Here we present a method capable of estimating extreme scene motion under challenging conditions, such as low light or high dynamic range, from a sequence of high-speed image frames such as those captured by a single-photon camera. Our method relies on iteratively improving a motion estimate by grouping and aggregating frames after-the-fact, in a stratified manner. We demonstrate the creation of high-quality panoramas under fast motion and extremely low light, and super-resolution results using a custom single-photon camera prototype. For code and supplemental material see our $\href{https://wisionlab.com/project/panoramas-from-photons/}{\text{project webpage}}$.
3D Scene Inference from Transient Histograms
Nov 09, 2022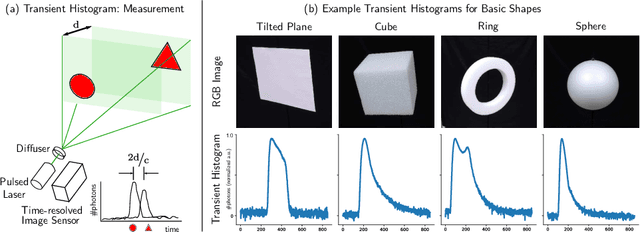

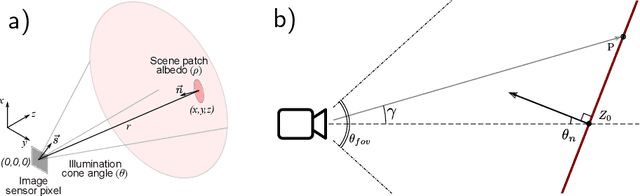
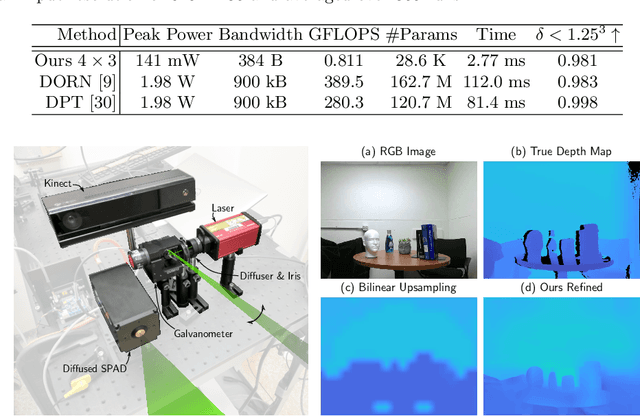
Abstract:Time-resolved image sensors that capture light at pico-to-nanosecond timescales were once limited to niche applications but are now rapidly becoming mainstream in consumer devices. We propose low-cost and low-power imaging modalities that capture scene information from minimal time-resolved image sensors with as few as one pixel. The key idea is to flood illuminate large scene patches (or the entire scene) with a pulsed light source and measure the time-resolved reflected light by integrating over the entire illuminated area. The one-dimensional measured temporal waveform, called \emph{transient}, encodes both distances and albedoes at all visible scene points and as such is an aggregate proxy for the scene's 3D geometry. We explore the viability and limitations of the transient waveforms by themselves for recovering scene information, and also when combined with traditional RGB cameras. We show that plane estimation can be performed from a single transient and that using only a few more it is possible to recover a depth map of the whole scene. We also show two proof-of-concept hardware prototypes that demonstrate the feasibility of our approach for compact, mobile, and budget-limited applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge