Süleyman Özdel
Exploring Context-aware and LLM-driven Locomotion for Immersive Virtual Reality
Apr 24, 2025
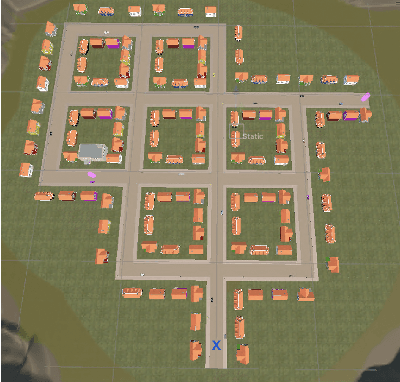
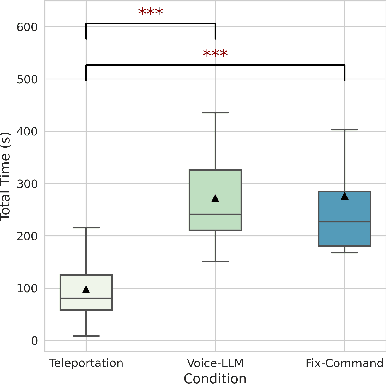
Abstract:Locomotion plays a crucial role in shaping the user experience within virtual reality environments. In particular, hands-free locomotion offers a valuable alternative by supporting accessibility and freeing users from reliance on handheld controllers. To this end, traditional speech-based methods often depend on rigid command sets, limiting the naturalness and flexibility of interaction. In this study, we propose a novel locomotion technique powered by large language models (LLMs), which allows users to navigate virtual environments using natural language with contextual awareness. We evaluate three locomotion methods: controller-based teleportation, voice-based steering, and our language model-driven approach. Our evaluation measures include eye-tracking data analysis, including explainable machine learning through SHAP analysis as well as standardized questionnaires for usability, presence, cybersickness, and cognitive load to examine user attention and engagement. Our findings indicate that the LLM-driven locomotion possesses comparable usability, presence, and cybersickness scores to established methods like teleportation, demonstrating its novel potential as a comfortable, natural language-based, hands-free alternative. In addition, it enhances user attention within the virtual environment, suggesting greater engagement. Complementary to these findings, SHAP analysis revealed that fixation, saccade, and pupil-related features vary across techniques, indicating distinct patterns of visual attention and cognitive processing. Overall, we state that our method can facilitate hands-free locomotion in virtual spaces, especially in supporting accessibility.
CUIfy the XR: An Open-Source Package to Embed LLM-powered Conversational Agents in XR
Nov 07, 2024

Abstract:Recent developments in computer graphics, machine learning, and sensor technologies enable numerous opportunities for extended reality (XR) setups for everyday life, from skills training to entertainment. With large corporations offering consumer-grade head-mounted displays (HMDs) in an affordable way, it is likely that XR will become pervasive, and HMDs will develop as personal devices like smartphones and tablets. However, having intelligent spaces and naturalistic interactions in XR is as important as technological advances so that users grow their engagement in virtual and augmented spaces. To this end, large language model (LLM)--powered non-player characters (NPCs) with speech-to-text (STT) and text-to-speech (TTS) models bring significant advantages over conventional or pre-scripted NPCs for facilitating more natural conversational user interfaces (CUIs) in XR. In this paper, we provide the community with an open-source, customizable, extensible, and privacy-aware Unity package, CUIfy, that facilitates speech-based NPC-user interaction with various LLMs, STT, and TTS models. Our package also supports multiple LLM-powered NPCs per environment and minimizes the latency between different computational models through streaming to achieve usable interactions between users and NPCs. We publish our source code in the following repository: https://gitlab.lrz.de/hctl/cuify
From Passive Watching to Active Learning: Empowering Proactive Participation in Digital Classrooms with AI Video Assistant
Sep 24, 2024Abstract:In online education, innovative tools are crucial for enhancing learning outcomes. SAM (Study with AI Mentor) is an advanced platform that integrates educational videos with a context-aware chat interface powered by large language models. SAM encourages students to ask questions and explore unclear concepts in real-time, offering personalized, context-specific assistance, including explanations of formulas, slides, and images. In a crowdsourced user study involving 140 participants, SAM was evaluated through pre- and post-knowledge tests, comparing a group using SAM with a control group. The results demonstrated that SAM users achieved greater knowledge gains, with a 96.8% answer accuracy. Participants also provided positive feedback on SAM's usability and effectiveness. SAM's proactive approach to learning not only enhances learning outcomes but also empowers students to take full ownership of their educational experience, representing a promising future direction for online learning tools.
Embedding Large Language Models into Extended Reality: Opportunities and Challenges for Inclusion, Engagement, and Privacy
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Recent developments in computer graphics, hardware, artificial intelligence (AI), and human-computer interaction likely lead to extended reality (XR) devices and setups being more pervasive. While these devices and setups provide users with interactive, engaging, and immersive experiences with different sensing modalities, such as eye and hand trackers, many non-player characters are utilized in a pre-scripted way or by conventional AI techniques. In this paper, we argue for using large language models (LLMs) in XR by embedding them in virtual avatars or as narratives to facilitate more inclusive experiences through prompt engineering according to user profiles and fine-tuning the LLMs for particular purposes. We argue that such inclusion will facilitate diversity for XR use. In addition, we believe that with the versatile conversational capabilities of LLMs, users will engage more with XR environments, which might help XR be more used in everyday life. Lastly, we speculate that combining the information provided to LLM-powered environments by the users and the biometric data obtained through the sensors might lead to novel privacy invasions. While studying such possible privacy invasions, user privacy concerns and preferences should also be investigated. In summary, despite some challenges, embedding LLMs into XR is a promising and novel research area with several opportunities.
Eye-tracked Virtual Reality: A Comprehensive Survey on Methods and Privacy Challenges
May 23, 2023



Abstract:Latest developments in computer hardware, sensor technologies, and artificial intelligence can make virtual reality (VR) and virtual spaces an important part of human everyday life. Eye tracking offers not only a hands-free way of interaction but also the possibility of a deeper understanding of human visual attention and cognitive processes in VR. Despite these possibilities, eye-tracking data also reveal privacy-sensitive attributes of users when it is combined with the information about the presented stimulus. To address these possibilities and potential privacy issues, in this survey, we first cover major works in eye tracking, VR, and privacy areas between the years 2012 and 2022. While eye tracking in the VR part covers the complete pipeline of eye-tracking methodology from pupil detection and gaze estimation to offline use and analyses, as for privacy and security, we focus on eye-based authentication as well as computational methods to preserve the privacy of individuals and their eye-tracking data in VR. Later, taking all into consideration, we draw three main directions for the research community by mainly focusing on privacy challenges. In summary, this survey provides an extensive literature review of the utmost possibilities with eye tracking in VR and the privacy implications of those possibilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge