Ryan C. DuToit
Learned Monocular Depth Priors in Visual-Inertial Initialization
Apr 20, 2022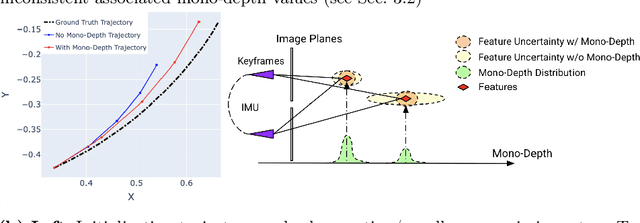
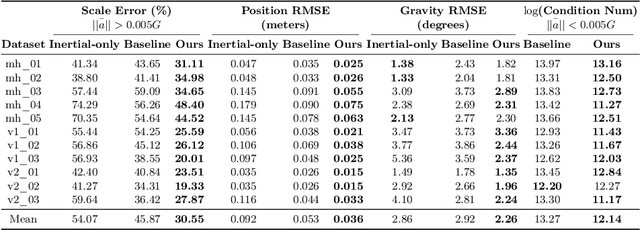
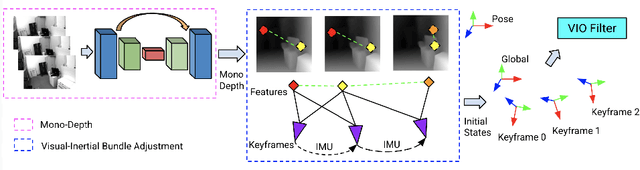
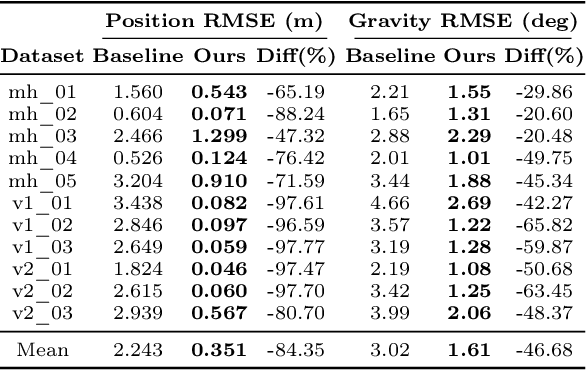
Abstract:Visual-inertial odometry (VIO) is the pose estimation backbone for most AR/VR and autonomous robotic systems today, in both academia and industry. However, these systems are highly sensitive to the initialization of key parameters such as sensor biases, gravity direction, and metric scale. In practical scenarios where high-parallax or variable acceleration assumptions are rarely met (e.g. hovering aerial robot, smartphone AR user not gesticulating with phone), classical visual-inertial initialization formulations often become ill-conditioned and/or fail to meaningfully converge. In this paper we target visual-inertial initialization specifically for these low-excitation scenarios critical to in-the-wild usage. We propose to circumvent the limitations of classical visual-inertial structure-from-motion (SfM) initialization by incorporating a new learning-based measurement as a higher-level input. We leverage learned monocular depth images (mono-depth) to constrain the relative depth of features, and upgrade the mono-depth to metric scale by jointly optimizing for its scale and shift. Our experiments show a significant improvement in problem conditioning compared to a classical formulation for visual-inertial initialization, and demonstrate significant accuracy and robustness improvements relative to the state-of-the-art on public benchmarks, particularly under motion-restricted scenarios. We further extend this improvement to implementation within an existing odometry system to illustrate the impact of our improved initialization method on resulting tracking trajectories.
Consistent Map-based 3D Localization on Mobile Devices
Apr 27, 2016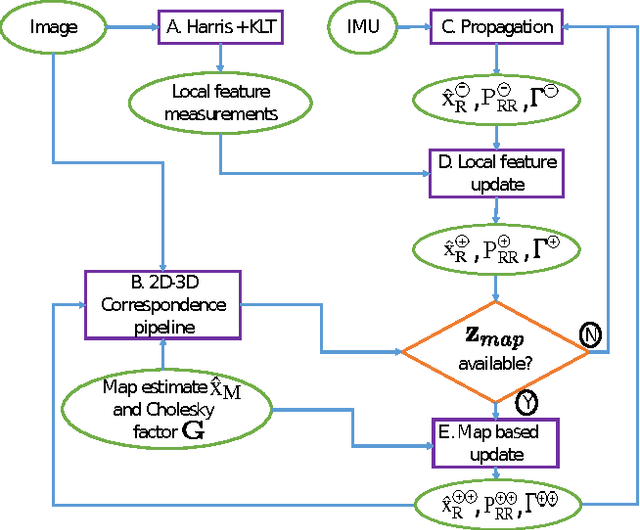
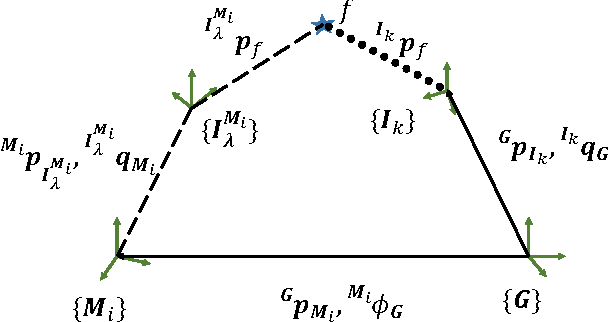
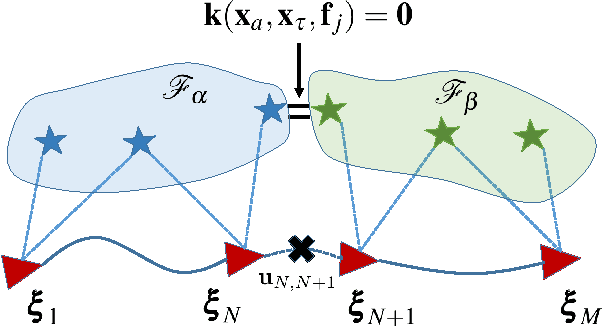
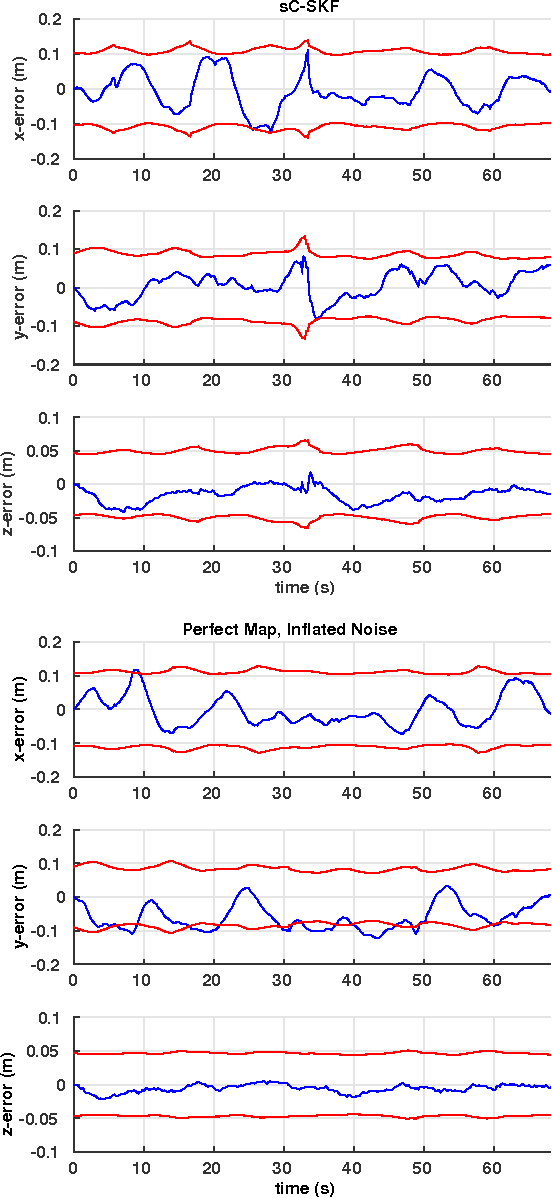
Abstract:The objective of this paper is to provide consistent, real-time 3D localization capabilities to mobile devices navigating within previously mapped areas. To this end, we introduce the Cholesky-Schmidt-Kalman filter (C-SKF), which explicitly considers the uncertainty of the prior map, by employing the sparse Cholesky factor of the map's Hessian, instead of its dense covariance--as is the case for the Schmidt-Kalman filter (SKF). By doing so, the C-SKF has memory requirements typically linear in the size of the map, as opposed to quadratic for storing the map's covariance. Moreover, and in order to bound the processing needs of the C-SKF (between linear and quadratic in the size of the map), we introduce a relaxation of the C-SKF algorithm, the sC-SKF, which operates on the Cholesky factors of independent sub-maps resulting from dividing the trajectory and observations used for constructing the map into overlapping segments. Lastly, we assess the processing and memory requirements of the proposed C-SKF and sC-SKF algorithms, and compare their positioning accuracy against other approximate map-based localization approaches that employ measurement-noise-covariance inflation to compensate for the map's uncertainty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge