Runxuan Liu
Graph Reasoning Paradigm: Structured and Symbolic Reasoning with Topology-Aware Reinforcement Learning for Large Language Models
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Long Chain-of-Thought (LCoT), achieved by Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR), has proven effective in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, reasoning in current LLMs is primarily generated as plain text, where performing semantic evaluation on such unstructured data creates a computational bottleneck during training. Despite RLVR-based optimization, existing methods still suffer from coarse-grained supervision, reward hacking, high training costs, and poor generalization. To address these issues, we propose the Graph Reasoning Paradigm (GRP), which realizes structured and symbolic reasoning, implemented via graph-structured representations with step-level cognitive labels. Building upon GRP, we further design Process-Aware Stratified Clipping Group Relative Policy Optimization (PASC-GRPO), which leverages structured evaluation to replace semantic evaluation, achieves process-aware verification through graph-structured outcome rewards, and mitigates reward hacking via stratified clipping advantage estimation. Experiments demonstrate significant improvements across mathematical reasoning and code generation tasks. Data, models, and code will be released later.
AI Meets Brain: Memory Systems from Cognitive Neuroscience to Autonomous Agents
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Memory serves as the pivotal nexus bridging past and future, providing both humans and AI systems with invaluable concepts and experience to navigate complex tasks. Recent research on autonomous agents has increasingly focused on designing efficient memory workflows by drawing on cognitive neuroscience. However, constrained by interdisciplinary barriers, existing works struggle to assimilate the essence of human memory mechanisms. To bridge this gap, we systematically synthesizes interdisciplinary knowledge of memory, connecting insights from cognitive neuroscience with LLM-driven agents. Specifically, we first elucidate the definition and function of memory along a progressive trajectory from cognitive neuroscience through LLMs to agents. We then provide a comparative analysis of memory taxonomy, storage mechanisms, and the complete management lifecycle from both biological and artificial perspectives. Subsequently, we review the mainstream benchmarks for evaluating agent memory. Additionally, we explore memory security from dual perspectives of attack and defense. Finally, we envision future research directions, with a focus on multimodal memory systems and skill acquisition.
Ontology-Guided Reverse Thinking Makes Large Language Models Stronger on Knowledge Graph Question Answering
Feb 17, 2025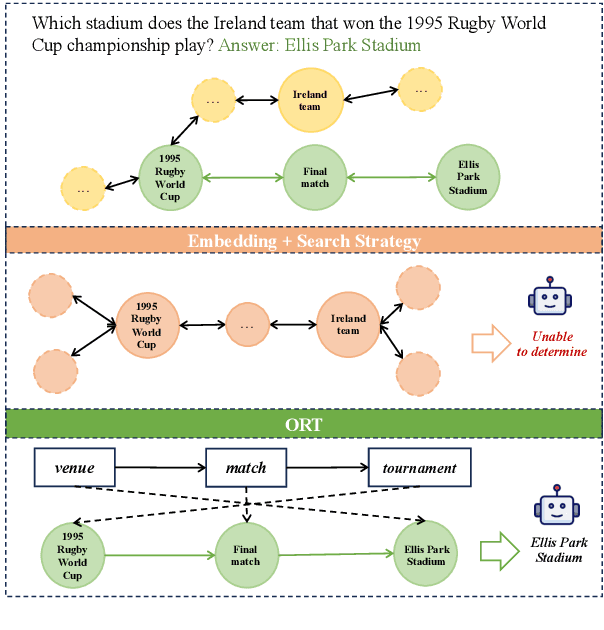

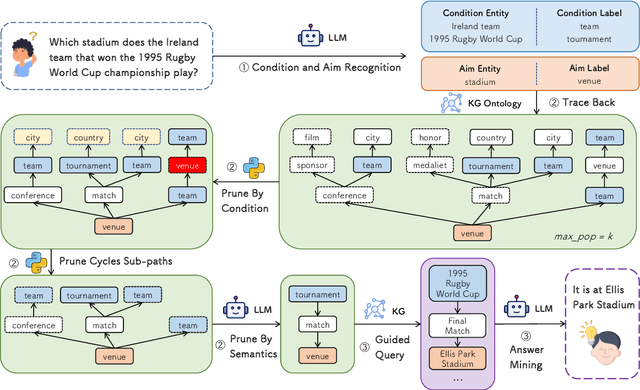

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in natural language processing. However, in knowledge graph question answering tasks (KGQA), there remains the issue of answering questions that require multi-hop reasoning. Existing methods rely on entity vector matching, but the purpose of the question is abstract and difficult to match with specific entities. As a result, it is difficult to establish reasoning paths to the purpose, which leads to information loss and redundancy. To address this issue, inspired by human reverse thinking, we propose Ontology-Guided Reverse Thinking (ORT), a novel framework that constructs reasoning paths from purposes back to conditions. ORT operates in three key phases: (1) using LLM to extract purpose labels and condition labels, (2) constructing label reasoning paths based on the KG ontology, and (3) using the label reasoning paths to guide knowledge retrieval. Experiments on the WebQSP and CWQ datasets show that ORT achieves state-of-the-art performance and significantly enhances the capability of LLMs for KGQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge