Rosin Claude Ngueveu
Fair mapping
Sep 01, 2022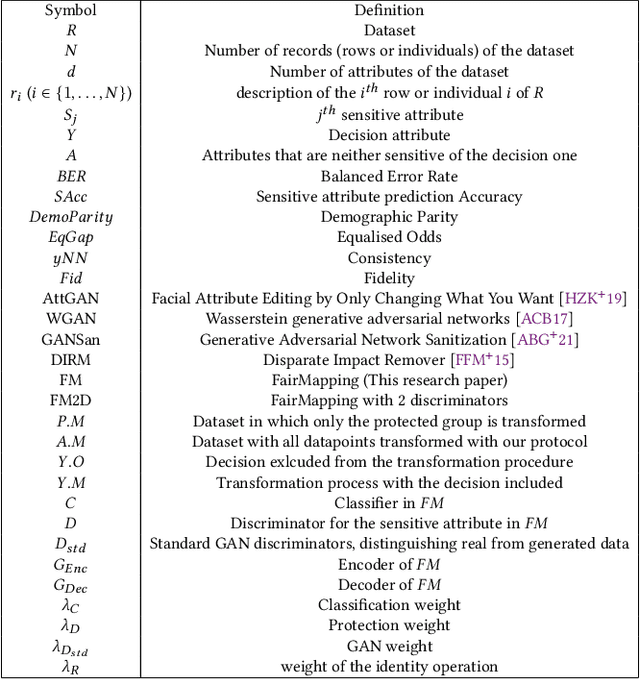



Abstract:To mitigate the effects of undesired biases in models, several approaches propose to pre-process the input dataset to reduce the risks of discrimination by preventing the inference of sensitive attributes. Unfortunately, most of these pre-processing methods lead to the generation a new distribution that is very different from the original one, thus often leading to unrealistic data. As a side effect, this new data distribution implies that existing models need to be re-trained to be able to make accurate predictions. To address this issue, we propose a novel pre-processing method, that we coin as fair mapping, based on the transformation of the distribution of protected groups onto a chosen target one, with additional privacy constraints whose objective is to prevent the inference of sensitive attributes. More precisely, we leverage on the recent works of the Wasserstein GAN and AttGAN frameworks to achieve the optimal transport of data points coupled with a discriminator enforcing the protection against attribute inference. Our proposed approach, preserves the interpretability of data and can be used without defining exactly the sensitive groups. In addition, our approach can be specialized to model existing state-of-the-art approaches, thus proposing a unifying view on these methods. Finally, several experiments on real and synthetic datasets demonstrate that our approach is able to hide the sensitive attributes, while limiting the distortion of the data and improving the fairness on subsequent data analysis tasks.
Agnostic data debiasing through a local sanitizer learnt from an adversarial network approach
Jun 19, 2019

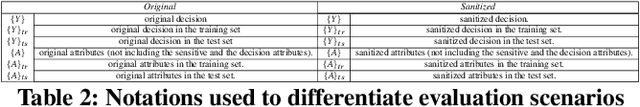

Abstract:The widespread use of automated decision processes in many areas of our society raises serious ethical issues concerning the fairness of the process and the possible resulting discriminations. In this work, we propose a novel approach called \gansan whose objective is to prevent the possibility of \emph{any} discrimination i.e., direct and indirect) based on a sensitive attribute by removing the attribute itself as well as the existing correlations with the remaining attributes. Our sanitization algorithm \gansan is partially inspired by the powerful framework of generative adversarial networks (in particuler the Cycle-GANs), which offers a flexible way to learn a distribution empirically or to translate between two different distributions. In contrast to prior work, one of the strengths of our approach is that the sanitization is performed in the same space as the original data by only modifying the other attributes as little as possible and thus preserving the interpretability of the sanitized data. As a consequence, once the sanitizer is trained, it can be applied to new data, such as for instance, locally by an individual on his profile before releasing it. Finally, experiments on a real dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach as well as the achievable trade-off between fairness and utility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge