Roman Vasiliev
DapStep: Deep Assignee Prediction for Stack Trace Error rePresentation
Jan 14, 2022
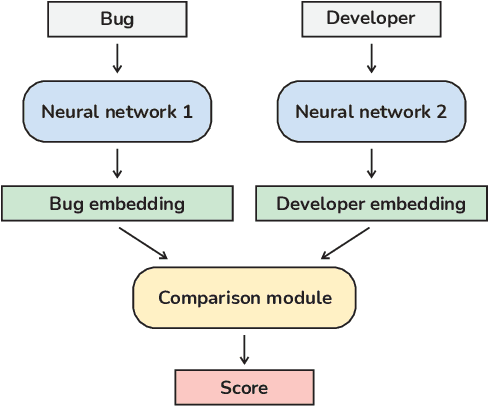
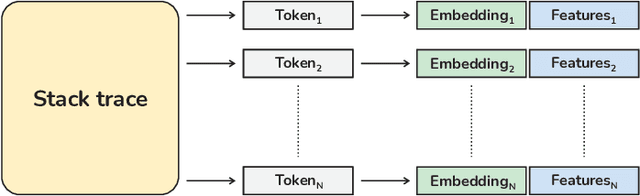
Abstract:The task of finding the best developer to fix a bug is called bug triage. Most of the existing approaches consider the bug triage task as a classification problem, however, classification is not appropriate when the sets of classes change over time (as developers often do in a project). Furthermore, to the best of our knowledge, all the existing models use textual sources of information, i.e., bug descriptions, which are not always available. In this work, we explore the applicability of existing solutions for the bug triage problem when stack traces are used as the main data source of bug reports. Additionally, we reformulate this task as a ranking problem and propose new deep learning models to solve it. The models are based on a bidirectional recurrent neural network with attention and on a convolutional neural network, with the weights of the models optimized using a ranking loss function. To improve the quality of ranking, we propose using additional information from version control system annotations. Two approaches are proposed for extracting features from annotations: manual and using an additional neural network. To evaluate our models, we collected two datasets of real-world stack traces. Our experiments show that the proposed models outperform existing models adapted to handle stack traces. To facilitate further research in this area, we publish the source code of our models and one of the collected datasets.
S3M: Siamese Stack (Trace) Similarity Measure
Mar 18, 2021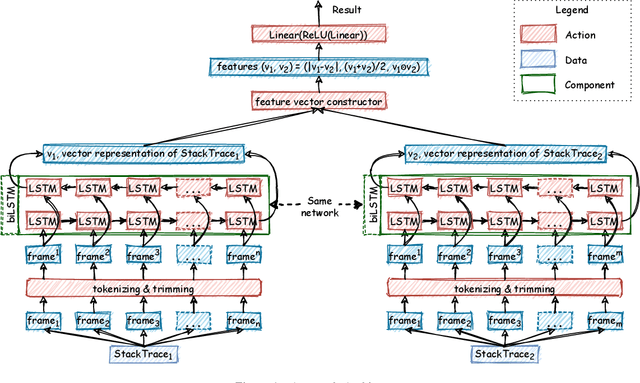
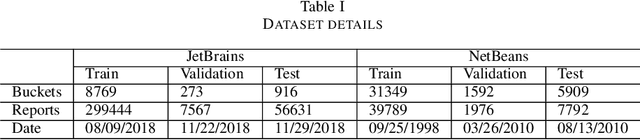
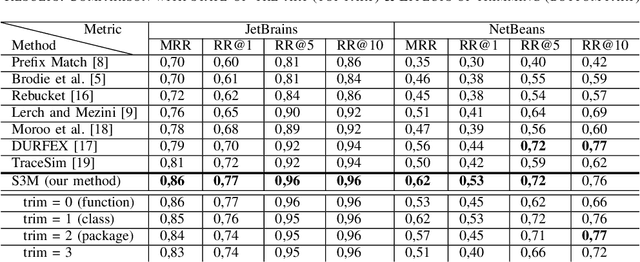
Abstract:Automatic crash reporting systems have become a de-facto standard in software development. These systems monitor target software, and if a crash occurs they send details to a backend application. Later on, these reports are aggregated and used in the development process to 1) understand whether it is a new or an existing issue, 2) assign these bugs to appropriate developers, and 3) gain a general overview of the application's bug landscape. The efficiency of report aggregation and subsequent operations heavily depends on the quality of the report similarity metric. However, a distinctive feature of this kind of report is that no textual input from the user (i.e., bug description) is available: it contains only stack trace information. In this paper, we present S3M ("extreme") -- the first approach to computing stack trace similarity based on deep learning. It is based on a siamese architecture that uses a biLSTM encoder and a fully-connected classifier to compute similarity. Our experiments demonstrate the superiority of our approach over the state-of-the-art on both open-sourced data and a private JetBrains dataset. Additionally, we review the impact of stack trace trimming on the quality of the results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge