Roman Plaud
Ignore the KL Penalty! Boosting Exploration on Critical Tokens to Enhance RL Fine-Tuning
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:The ability to achieve long-term goals is a key challenge in the current development of large language models (LLMs). To address this, pre-trained LLMs can be fine-tuned with reinforcement learning (RL) to explore solutions that optimize a given goal. However, exploration with LLMs is difficult, as a balance has to be struck between discovering new solutions and staying close enough to the pre-trained model, so as not to degrade basic capabilities. This is typically controlled with a Kullback-Leibler (KL) penalty. In this paper, we investigate the exploration dynamics of a small language model on a simple arithmetic task. We show how varying degrees of pre-training influence exploration and demonstrate the importance of "critical tokens" which have a dramatic impact on the final outcome. Consequently, we introduce a simple modification to the KL penalty that favors exploration on critical tokens, increasing the efficiency of the RL fine-tuning stage.
Revisiting Hierarchical Text Classification: Inference and Metrics
Oct 02, 2024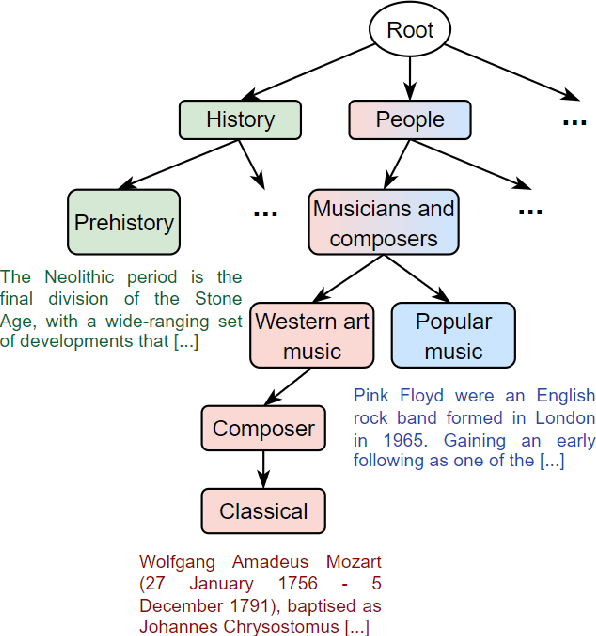
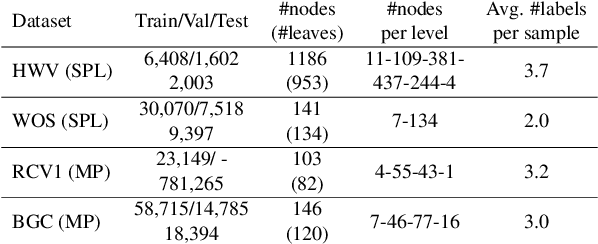
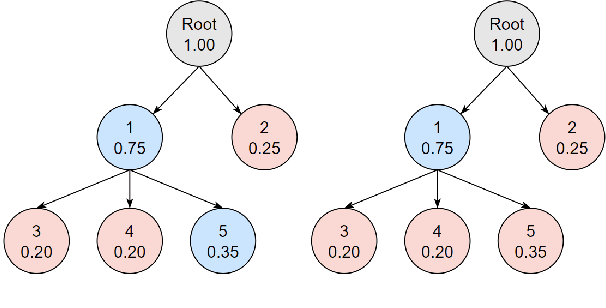
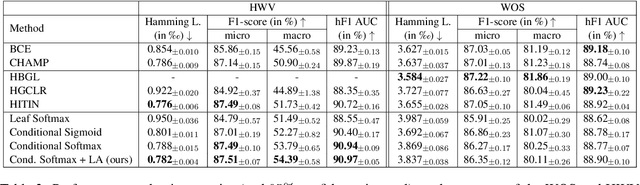
Abstract:Hierarchical text classification (HTC) is the task of assigning labels to a text within a structured space organized as a hierarchy. Recent works treat HTC as a conventional multilabel classification problem, therefore evaluating it as such. We instead propose to evaluate models based on specifically designed hierarchical metrics and we demonstrate the intricacy of metric choice and prediction inference method. We introduce a new challenging dataset and we evaluate fairly, recent sophisticated models, comparing them with a range of simple but strong baselines, including a new theoretically motivated loss. Finally, we show that those baselines are very often competitive with the latest models. This highlights the importance of carefully considering the evaluation methodology when proposing new methods for HTC. Code implementation and dataset are available at \url{https://github.com/RomanPlaud/revisitingHTC}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge