Roberto de Alencar Lotufo
Retail-GPT: leveraging Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) for building E-commerce Chat Assistants
Aug 15, 2024


Abstract:This work presents Retail-GPT, an open-source RAG-based chatbot designed to enhance user engagement in retail e-commerce by guiding users through product recommendations and assisting with cart operations. The system is cross-platform and adaptable to various e-commerce domains, avoiding reliance on specific chat applications or commercial activities. Retail-GPT engages in human-like conversations, interprets user demands, checks product availability, and manages cart operations, aiming to serve as a virtual sales agent and test the viability of such assistants across different retail businesses.
w2v-SELD: A Sound Event Localization and Detection Framework for Self-Supervised Spatial Audio Pre-Training
Dec 30, 2023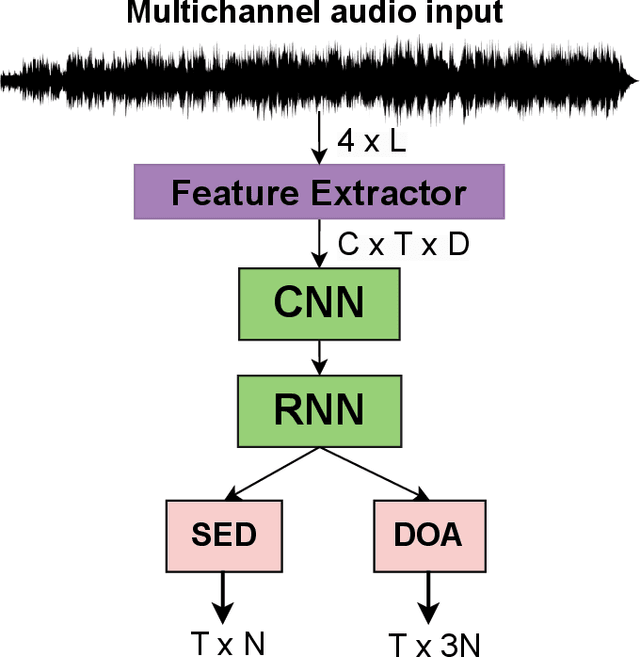
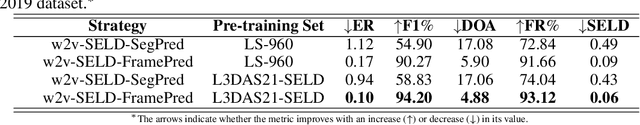
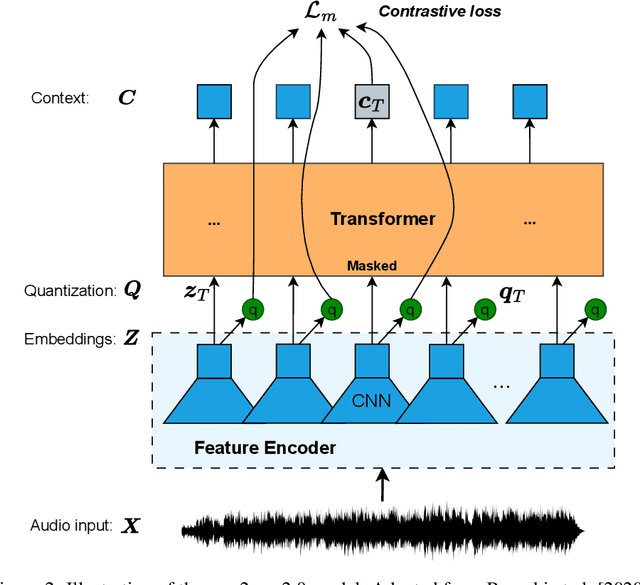

Abstract:Sound Event Detection and Localization (SELD) constitutes a complex task that depends on extensive multichannel audio recordings with annotated sound events and their respective locations. In this paper, we introduce a self-supervised approach for SELD adapted from the pre-training methodology of wav2vec 2.0, which learns representations directly from raw audio data, eliminating the need for supervision. By applying this approach to SELD, we can leverage a substantial amount of unlabeled 3D audio data to learn robust representations of sound events and their locations. Our method comprises two primary stages: pre-training and fine-tuning. In the pre-training phase, unlabeled 3D audio datasets are utilized to train our w2v-SELD model, capturing intricate high-level features and contextual information inherent in audio signals. Subsequently, in the fine-tuning stage, a smaller dataset with labeled SELD data fine-tunes the pre-trained model. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed self-supervised approach for SELD. The model surpasses baseline systems provided with the datasets and achieves competitive performance comparable to state-of-the-art supervised methods. The code and pre-trained parameters of our w2v-SELD model are available in this repository.
To Tune or Not To Tune? Zero-shot Models for Legal Case Entailment
Feb 07, 2022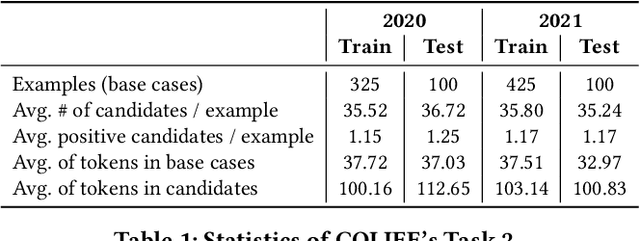
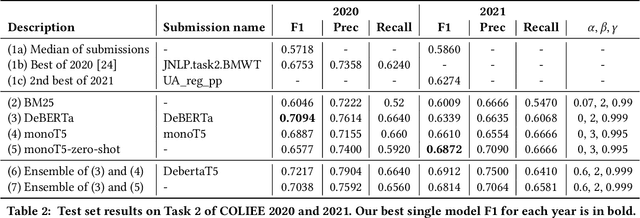
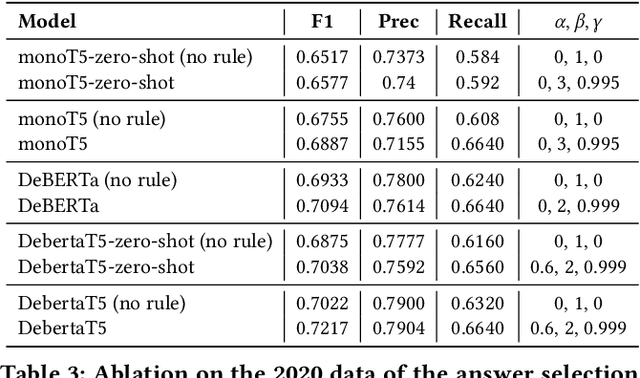
Abstract:There has been mounting evidence that pretrained language models fine-tuned on large and diverse supervised datasets can transfer well to a variety of out-of-domain tasks. In this work, we investigate this transfer ability to the legal domain. For that, we participated in the legal case entailment task of COLIEE 2021, in which we use such models with no adaptations to the target domain. Our submissions achieved the highest scores, surpassing the second-best team by more than six percentage points. Our experiments confirm a counter-intuitive result in the new paradigm of pretrained language models: given limited labeled data, models with little or no adaptation to the target task can be more robust to changes in the data distribution than models fine-tuned on it. Code is available at https://github.com/neuralmind-ai/coliee.
Evaluating software-based fingerprint liveness detection using Convolutional Networks and Local Binary Patterns
Aug 03, 2015



Abstract:With the growing use of biometric authentication systems in the past years, spoof fingerprint detection has become increasingly important. In this work, we implement and evaluate two different feature extraction techniques for software-based fingerprint liveness detection: Convolutional Networks with random weights and Local Binary Patterns. Both techniques were used in conjunction with a Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. Dataset Augmentation was used to increase classifier's performance and a variety of preprocessing operations were tested, such as frequency filtering, contrast equalization, and region of interest filtering. The experiments were made on the datasets used in The Liveness Detection Competition of years 2009, 2011 and 2013, which comprise almost 50,000 real and fake fingerprints' images. Our best method achieves an overall rate of 95.2% of correctly classified samples - an improvement of 35% in test error when compared with the best previously published results.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:1301.3557 by other authors
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge