Robert Rein
Extraction of Positional Player Data from Broadcast Soccer Videos
Oct 21, 2021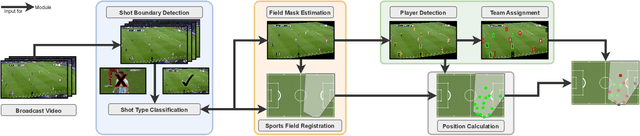
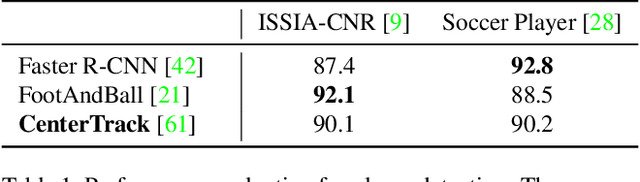
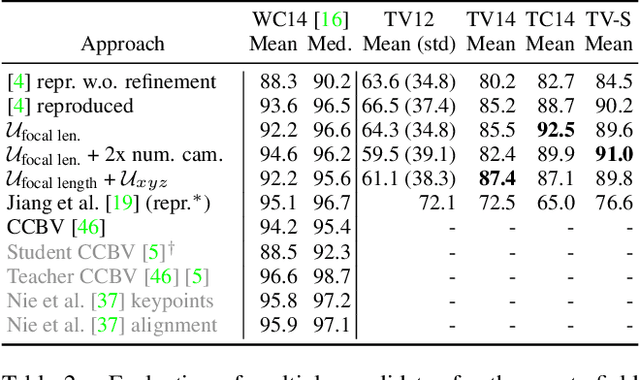
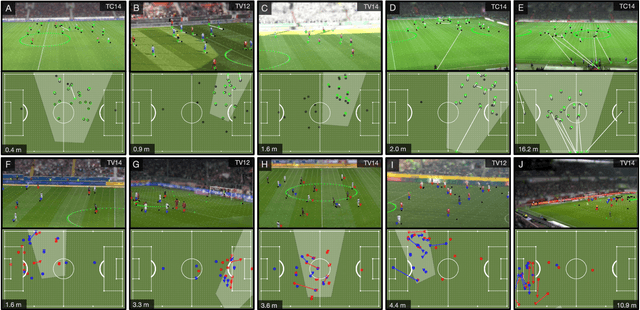
Abstract:Computer-aided support and analysis are becoming increasingly important in the modern world of sports. The scouting of potential prospective players, performance as well as match analysis, and the monitoring of training programs rely more and more on data-driven technologies to ensure success. Therefore, many approaches require large amounts of data, which are, however, not easy to obtain in general. In this paper, we propose a pipeline for the fully-automated extraction of positional data from broadcast video recordings of soccer matches. In contrast to previous work, the system integrates all necessary sub-tasks like sports field registration, player detection, or team assignment that are crucial for player position estimation. The quality of the modules and the entire system is interdependent. A comprehensive experimental evaluation is presented for the individual modules as well as the entire pipeline to identify the influence of errors to subsequent modules and the overall result. In this context, we propose novel evaluation metrics to compare the output with ground-truth positional data.
"Does 4-4-2 exist?" -- An Analytics Approach to Understand and Classify Football Team Formations in Single Match Situations
Sep 02, 2019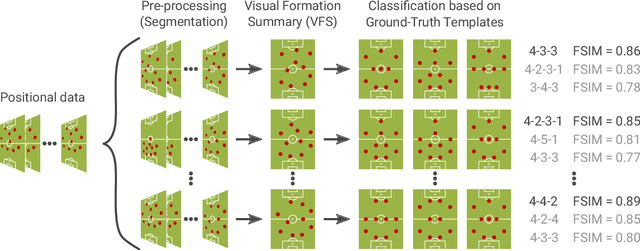

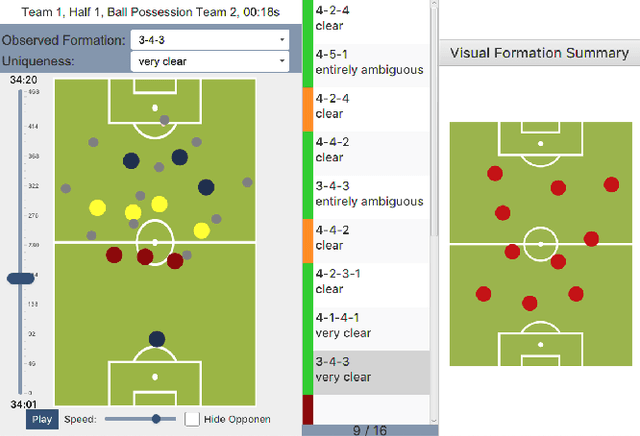

Abstract:The chances to win a football match can be significantly increased if the right tactic is chosen and the behavior of the opposite team is well anticipated. For this reason, every professional football club employs a team of game analysts. However, at present game performance analysis is done manually and therefore highly time-consuming. Consequently, automated tools to support the analysis process are required. In this context, one of the main tasks is to summarize team formations by patterns such as 4-4-2. In this paper, we introduce an analytics approach that automatically classifies and visualizes the team formation based on the players' position data. We focus on single match situations instead of complete halftimes or matches to provide a more detailed analysis. A detailed analysis of individual match situations depending on ball possession and match segment length is provided. For this purpose, a visual summary is utilized that summarizes the team formation in a match segment. An expert annotation study is conducted that demonstrates 1) the complexity of the task and 2) the usefulness of the visualization of single situations to understand team formations. The suggested classification approach outperforms existing methods for formation classification. In particular, our approach gives insights about the shortcomings of using patterns like 4-4-2 to describe team formations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge