Ries Uittenbogaard
Privacy Protection in Street-View Panoramas using Depth and Multi-View Imagery
Mar 27, 2019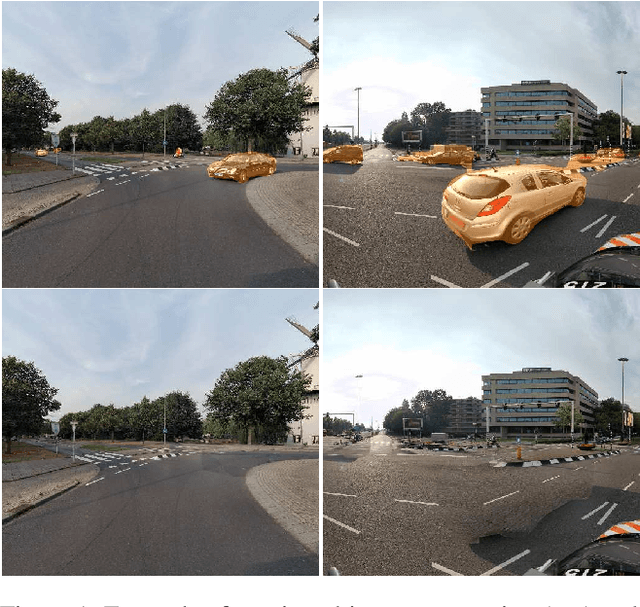
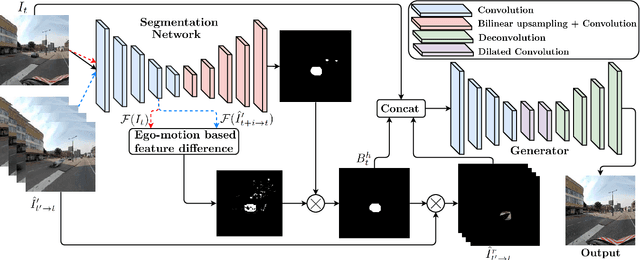

Abstract:The current paradigm in privacy protection in street-view images is to detect and blur sensitive information. In this paper, we propose a framework that is an alternative to blurring, which automatically removes and inpaints moving objects (e.g. pedestrians, vehicles) in street-view imagery. We propose a novel moving object segmentation algorithm exploiting consistencies in depth across multiple street-view images that are later combined with the results of a segmentation network. The detected moving objects are removed and inpainted with information from other views, to obtain a realistic output image such that the moving object is not visible anymore. We evaluate our results on a dataset of 1000 images to obtain a peak noise-to-signal ratio (PSNR) and L1 loss of 27.2 dB and 2.5%, respectively. To ensure the subjective quality, To assess overall quality, we also report the results of a survey conducted on 35 professionals, asked to visually inspect the images whether object removal and inpainting had taken place. The inpainting dataset will be made publicly available for scientific benchmarking purposes at https://research.cyclomedia.com
Conditional Transfer with Dense Residual Attention: Synthesizing traffic signs from street-view imagery
Sep 05, 2018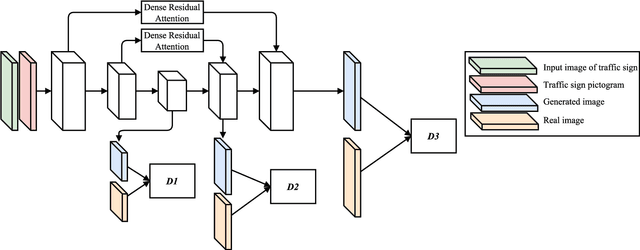
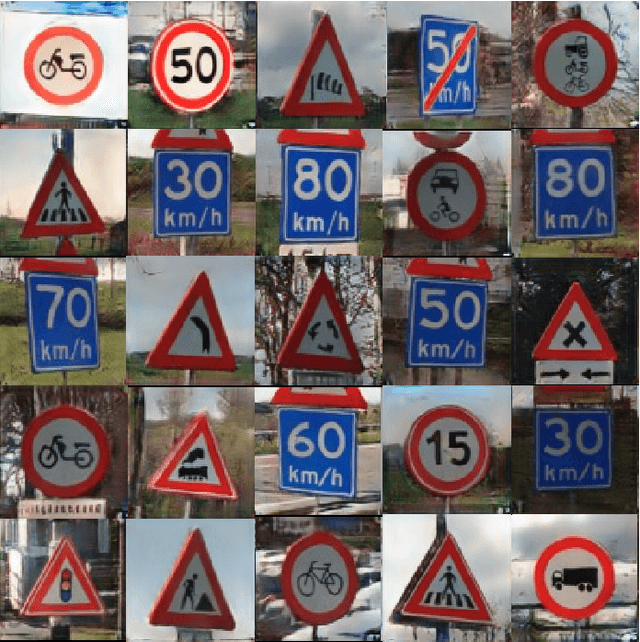
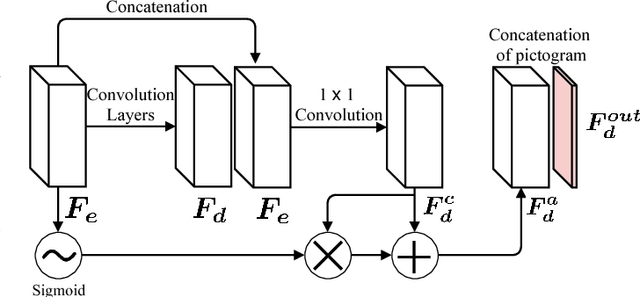
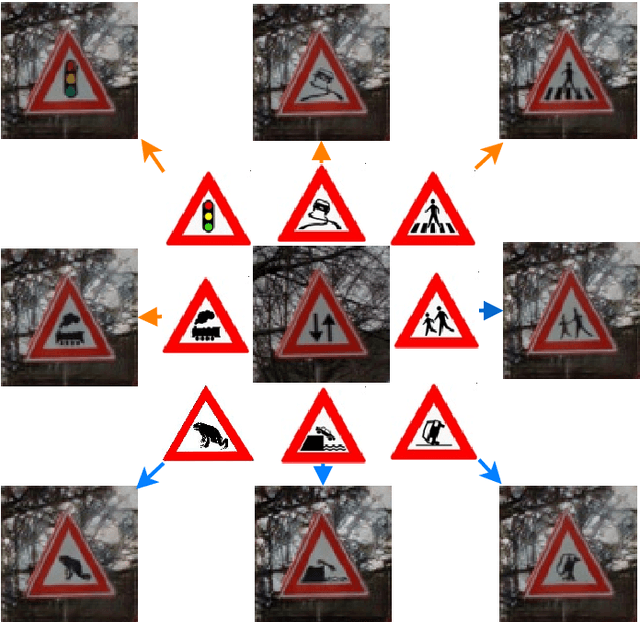

Abstract:Object detection and classification of traffic signs in street-view imagery is an essential element for asset management, map making and autonomous driving. However, some traffic signs occur rarely and consequently, they are difficult to recognize automatically. To improve the detection and classification rates, we propose to generate images of traffic signs, which are then used to train a detector/classifier. In this research, we present an end-to-end framework that generates a realistic image of a traffic sign from a given image of a traffic sign and a pictogram of the target class. We propose a residual attention mechanism with dense concatenation called Dense Residual Attention, that preserves the background information while transferring the object information. We also propose to utilize multi-scale discriminators, so that the smaller scales of the output guide the higher resolution output. We have performed detection and classification tests across a large number of traffic sign classes, by training the detector using the combination of real and generated data. The newly trained model reduces the number of false positives by 1.2 - 1.5% at 99% recall in the detection tests and an absolute improvement of 4.65% (top-1 accuracy) in the classification tests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge