Ridam Pal
Benchmarking LLMs for Predictive Applications in the Intensive Care Units
Dec 23, 2025



Abstract:With the advent of LLMs, various tasks across the natural language processing domain have been transformed. However, their application in predictive tasks remains less researched. This study compares large language models, including GatorTron-Base (trained on clinical data), Llama 8B, and Mistral 7B, against models like BioBERT, DocBERT, BioClinicalBERT, Word2Vec, and Doc2Vec, setting benchmarks for predicting Shock in critically ill patients. Timely prediction of shock can enable early interventions, thus improving patient outcomes. Text data from 17,294 ICU stays of patients in the MIMIC III database were scored for length of stay > 24 hours and shock index (SI) > 0.7 to yield 355 and 87 patients with normal and abnormal SI-index, respectively. Both focal and cross-entropy losses were used during finetuning to address class imbalances. Our findings indicate that while GatorTron Base achieved the highest weighted recall of 80.5%, the overall performance metrics were comparable between SLMs and LLMs. This suggests that LLMs are not inherently superior to SLMs in predicting future clinical events despite their strong performance on text-based tasks. To achieve meaningful clinical outcomes, future efforts in training LLMs should prioritize developing models capable of predicting clinical trajectories rather than focusing on simpler tasks such as named entity recognition or phenotyping.
Characterizing the Emotion Carriers of COVID-19 Misinformation and Their Impact on Vaccination Outcomes in India and the United States
Jun 24, 2023



Abstract:The COVID-19 Infodemic had an unprecedented impact on health behaviors and outcomes at a global scale. While many studies have focused on a qualitative and quantitative understanding of misinformation, including sentiment analysis, there is a gap in understanding the emotion-carriers of misinformation and their differences across geographies. In this study, we characterized emotion carriers and their impact on vaccination rates in India and the United States. A manually labelled dataset was created from 2.3 million tweets and collated with three publicly available datasets (CoAID, AntiVax, CMU) to train deep learning models for misinformation classification. Misinformation labelled tweets were further analyzed for behavioral aspects by leveraging Plutchik Transformers to determine the emotion for each tweet. Time series analysis was conducted to study the impact of misinformation on spatial and temporal characteristics. Further, categorical classification was performed using transformer models to assign categories for the misinformation tweets. Word2Vec+BiLSTM was the best model for misinformation classification, with an F1-score of 0.92. The US had the highest proportion of misinformation tweets (58.02%), followed by the UK (10.38%) and India (7.33%). Disgust, anticipation, and anger were associated with an increased prevalence of misinformation tweets. Disgust was the predominant emotion associated with misinformation tweets in the US, while anticipation was the predominant emotion in India. For India, the misinformation rate exhibited a lead relationship with vaccination, while in the US it lagged behind vaccination. Our study deciphered that emotions acted as differential carriers of misinformation across geography and time. These carriers can be monitored to develop strategic interventions for countering misinformation, leading to improved public health.
Mining Trends of COVID-19 Vaccine Beliefs on Twitter with Lexical Embeddings
Apr 02, 2021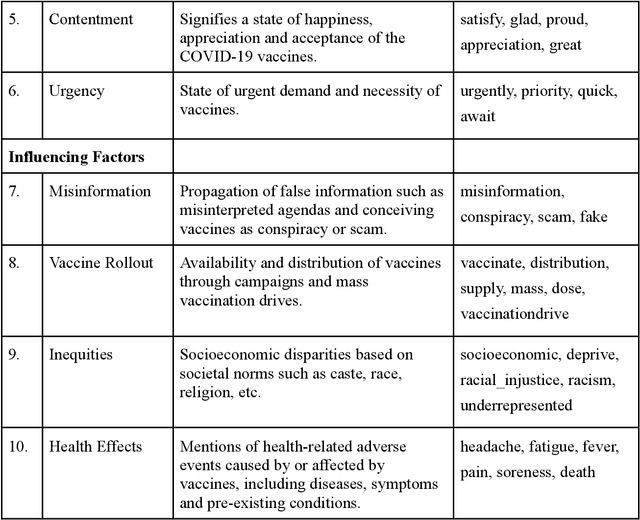

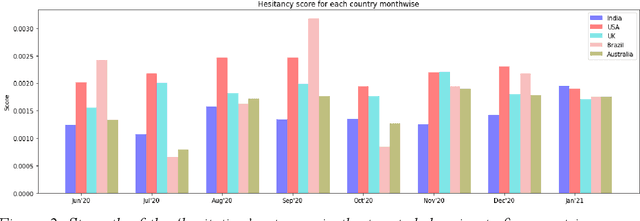
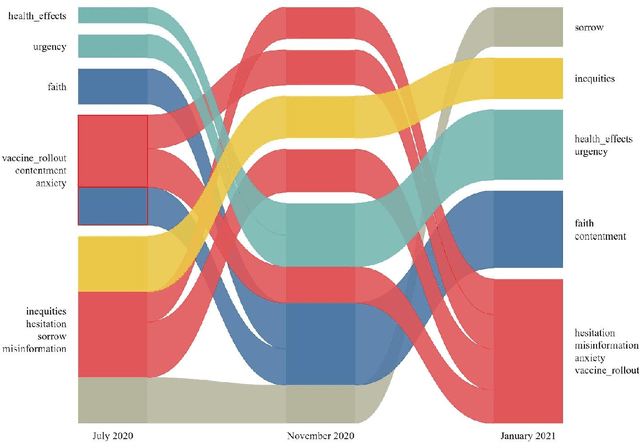
Abstract:Social media plays a pivotal role in disseminating news across the globe and acts as a platform for people to express their opinions on a variety of topics. COVID-19 vaccination drives across the globe are accompanied by a wide variety of expressed opinions, often colored by emotions. We extracted a corpus of Twitter posts related to COVID-19 vaccination and created two classes of lexical categories - Emotions and Influencing factors. Using unsupervised word embeddings, we tracked the longitudinal change in the latent space of the lexical categories in five countries with strong vaccine roll-out programs, i.e. India, USA, Brazil, UK, and Australia. Nearly 600 thousand vaccine-related tweets from the United States and India were analyzed for an overall understanding of the situation around the world for the time period of 8 months from June 2020 to January 2021. Cosine distance between lexical categories was used to create similarity networks and modules using community detection algorithms. We demonstrate that negative emotions like hesitancy towards vaccines have a high correlation with health-related effects and misinformation. These associations formed a major module with the highest importance in the network formed for January 2021, when millions of vaccines were administered. The relationship between emotions and influencing factors were found to be variable across the countries. By extracting and visualizing these, we propose that such a framework may be helpful in guiding the design of effective vaccine campaigns and can be used by policymakers for modeling vaccine uptake.
A Cross-lingual Natural Language Processing Framework for Infodemic Management
Oct 30, 2020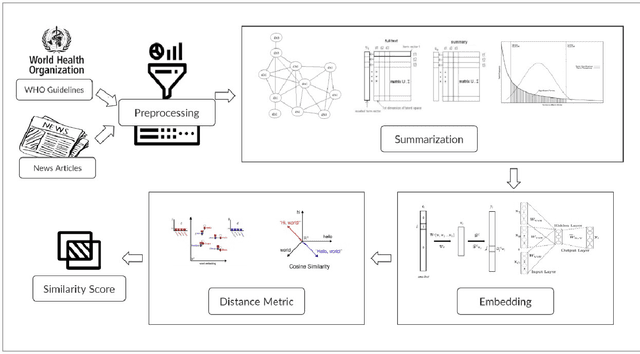

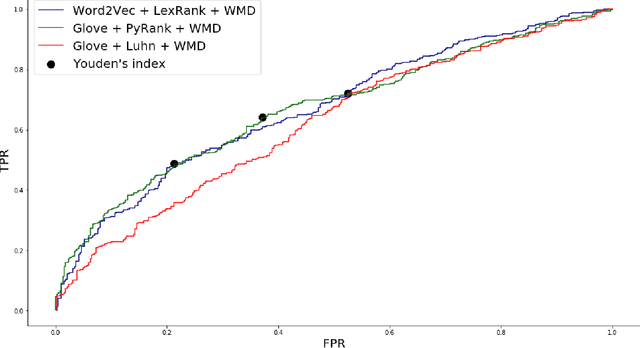
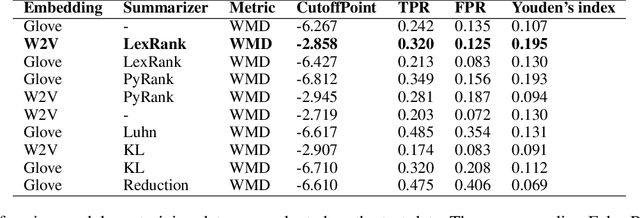
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has put immense pressure on health systems which are further strained due to the misinformation surrounding it. Under such a situation, providing the right information at the right time is crucial. There is a growing demand for the management of information spread using Artificial Intelligence. Hence, we have exploited the potential of Natural Language Processing for identifying relevant information that needs to be disseminated amongst the masses. In this work, we present a novel Cross-lingual Natural Language Processing framework to provide relevant information by matching daily news with trusted guidelines from the World Health Organization. The proposed pipeline deploys various techniques of NLP such as summarizers, word embeddings, and similarity metrics to provide users with news articles along with a corresponding healthcare guideline. A total of 36 models were evaluated and a combination of LexRank based summarizer on Word2Vec embedding with Word Mover distance metric outperformed all other models. This novel open-source approach can be used as a template for proactive dissemination of relevant healthcare information in the midst of misinformation spread associated with epidemics.
A Machine Learning Application for Raising WASH Awareness in the Times of COVID-19 Pandemic
Apr 18, 2020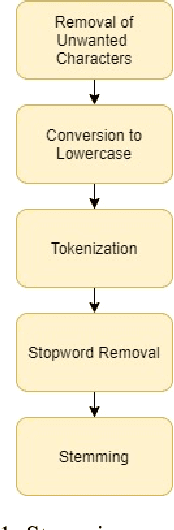
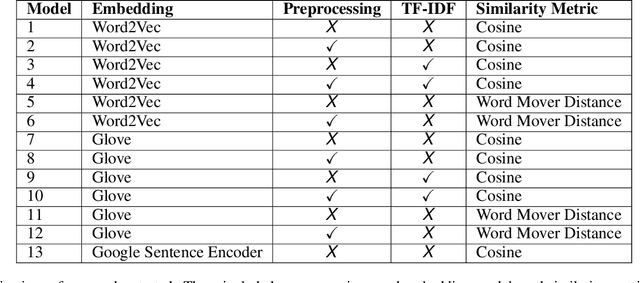
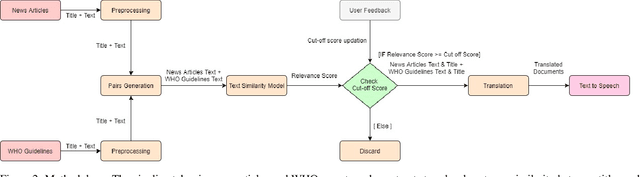
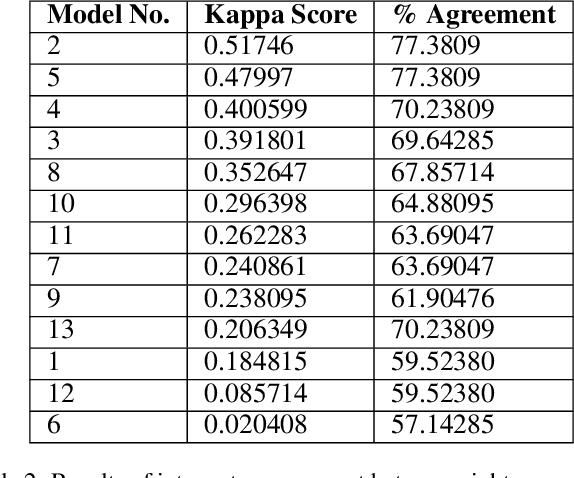
Abstract:Proactive management of an Infodemic that grows faster than the underlying epidemic is a modern-day challenge. This requires raising awareness and sensitization with the correct information in order to prevent and contain outbreaks such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, there is a fine balance between continuous awareness-raising by providing new information and the risk of misinformation. In this work, we address this gap by creating a life-long learning application that delivers authentic information to users in Hindi and English, the most widely used languages in India. It does this by matching sources of verified and authentic information such as the WHO reports against daily news by using machine learning and natural language processing. It delivers the narrated content in Hindi by using state-of-the-art text to speech engines. Finally, the approach allows user input for continuous improvement of news feed relevance daily. We demonstrate this approach for Water, Sanitation, Hygiene information for containment of the COVID-19 pandemic. Thirteen combinations of pre-processing strategies, word-embeddings, and similarity metrics were evaluated by eight human users via calculation of agreement statistics. The best performing combination achieved a Cohen's Kappa of 0.54 and was deployed as On AIr, WashKaro's AI-powered back-end. We introduced a novel way of contact tracing, deploying the Bluetooth sensors of an individual's smartphone and automatic recording of physical interactions with other users. Additionally, the application also features a symptom self-assessment tool based on WHO-approved guidelines, human-curated and vetted information to reach out to the community as audio-visual content in local languages. WashKaro - http://tiny.cc/WashKaro
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge