Richard Nordsieck
XITASO GmbH
Masked Autoencoder Self Pre-Training for Defect Detection in Microelectronics
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Whereas in general computer vision, transformer-based architectures have quickly become the gold standard, microelectronics defect detection still heavily relies on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). We hypothesize that this is due to the fact that a) transformers have an increased need for data and b) labelled image generation procedures for microelectronics are costly, and labelled data is therefore sparse. Whereas in other domains, pre-training on large natural image datasets can mitigate this problem, in microelectronics transfer learning is hindered due to the dissimilarity of domain data and natural images. Therefore, we evaluate self pre-training, where models are pre-trained on the target dataset, rather than another dataset. We propose a vision transformer (ViT) pre-training framework for defect detection in microelectronics based on masked autoencoders (MAE). In MAE, a large share of image patches is masked and reconstructed by the model during pre-training. We perform pre-training and defect detection using a dataset of less than 10.000 scanning acoustic microscopy (SAM) images labelled using transient thermal analysis (TTA). Our experimental results show that our approach leads to substantial performance gains compared to a) supervised ViT, b) ViT pre-trained on natural image datasets, and c) state-of-the-art CNN-based defect detection models used in the literature. Additionally, interpretability analysis reveals that our self pre-trained models, in comparison to ViT baselines, correctly focus on defect-relevant features such as cracks in the solder material. This demonstrates that our approach yields fault-specific feature representations, making our self pre-trained models viable for real-world defect detection in microelectronics.
PDPK: A Framework to Synthesise Process Data and Corresponding Procedural Knowledge for Manufacturing
Aug 16, 2023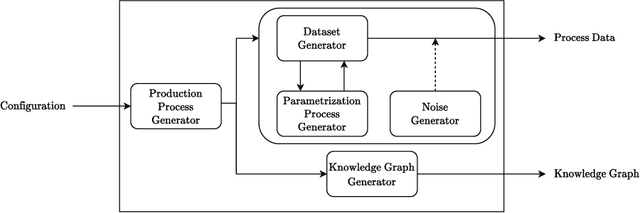
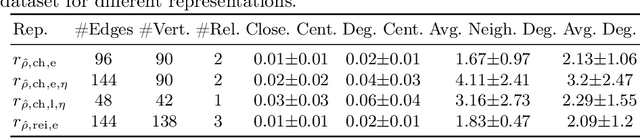
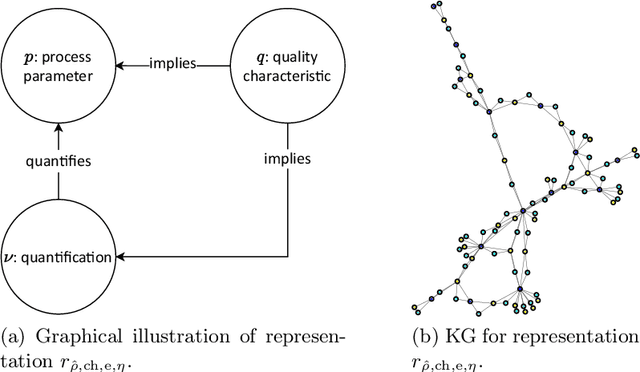
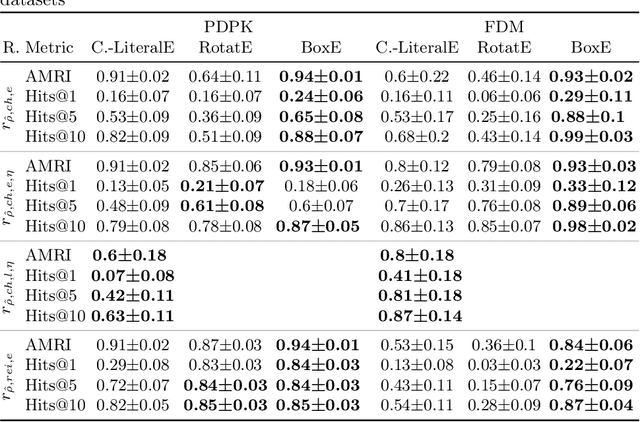
Abstract:Procedural knowledge describes how to accomplish tasks and mitigate problems. Such knowledge is commonly held by domain experts, e.g. operators in manufacturing who adjust parameters to achieve quality targets. To the best of our knowledge, no real-world datasets containing process data and corresponding procedural knowledge are publicly available, possibly due to corporate apprehensions regarding the loss of knowledge advances. Therefore, we provide a framework to generate synthetic datasets that can be adapted to different domains. The design choices are inspired by two real-world datasets of procedural knowledge we have access to. Apart from containing representations of procedural knowledge in Resource Description Framework (RDF)-compliant knowledge graphs, the framework simulates parametrisation processes and provides consistent process data. We compare established embedding methods on the resulting knowledge graphs, detailing which out-of-the-box methods have the potential to represent procedural knowledge. This provides a baseline which can be used to increase the comparability of future work. Furthermore, we validate the overall characteristics of a synthesised dataset by comparing the results to those achievable on a real-world dataset. The framework and evaluation code, as well as the dataset used in the evaluation, are available open source.
Learning Classifier Systems for Self-Explaining Socio-Technical-Systems
Jul 01, 2022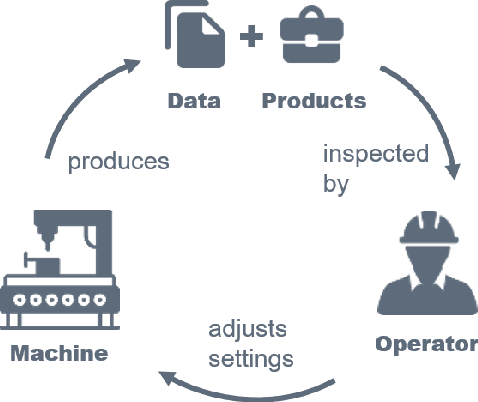
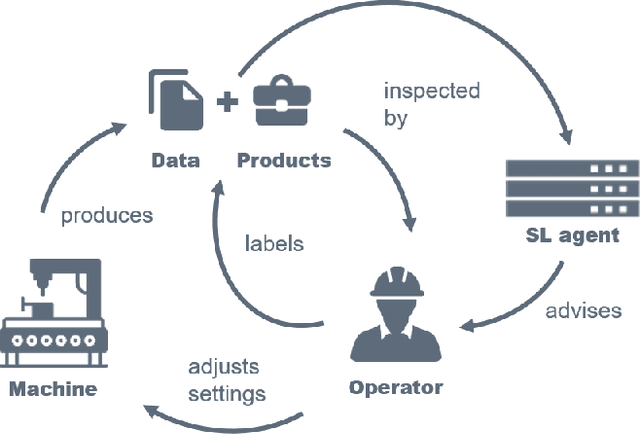
Abstract:In socio-technical settings, operators are increasingly assisted by decision support systems. By employing these, important properties of socio-technical systems such as self-adaptation and self-optimization are expected to improve further. To be accepted by and engage efficiently with operators, decision support systems need to be able to provide explanations regarding the reasoning behind specific decisions. In this paper, we propose the usage of Learning Classifier Systems, a family of rule-based machine learning methods, to facilitate transparent decision making and highlight some techniques to improve that. We then present a template of seven questions to assess application-specific explainability needs and demonstrate their usage in an interview-based case study for a manufacturing scenario. We find that the answers received did yield useful insights for a well-designed LCS model and requirements to have stakeholders actively engage with an intelligent agent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge