Reza Farrahi Moghaddam
FSITM: A Feature Similarity Index For Tone-Mapped Images
Apr 19, 2017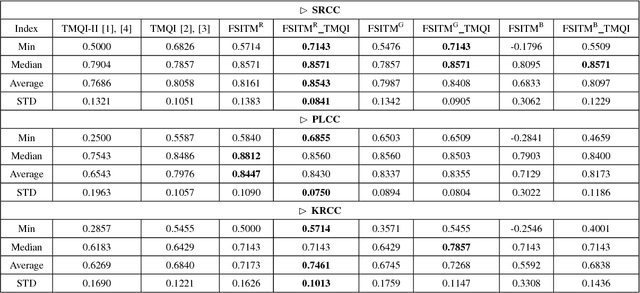

Abstract:In this work, based on the local phase information of images, an objective index, called the feature similarity index for tone-mapped images (FSITM), is proposed. To evaluate a tone mapping operator (TMO), the proposed index compares the locally weighted mean phase angle map of an original high dynamic range (HDR) to that of its associated tone-mapped image calculated using the output of the TMO method. In experiments on two standard databases, it is shown that the proposed FSITM method outperforms the state-of-the-art index, the tone mapped quality index (TMQI). In addition, a higher performance is obtained by combining the FSITM and TMQI indices. The MATLAB source code of the proposed metric(s) is available at https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/59814.
* 4 Pages, 1 Figure, 1 Table
A Multiple-Expert Binarization Framework for Multispectral Images
Aug 26, 2015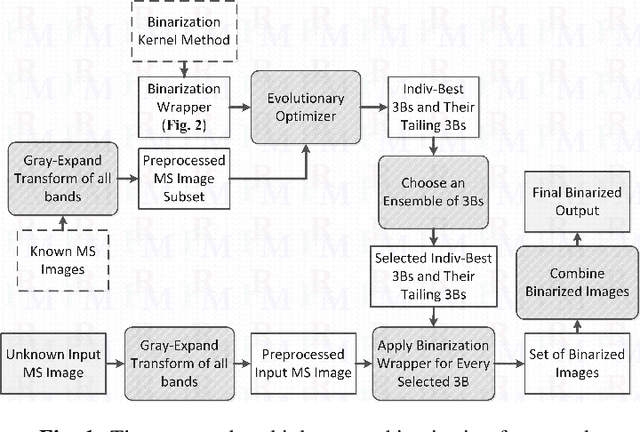
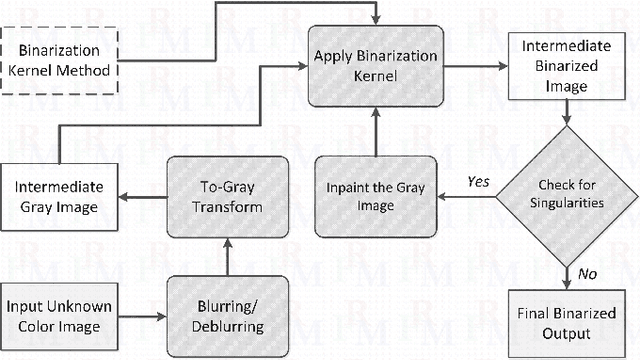

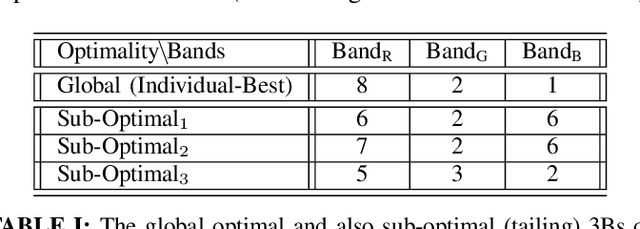
Abstract:In this work, a multiple-expert binarization framework for multispectral images is proposed. The framework is based on a constrained subspace selection limited to the spectral bands combined with state-of-the-art gray-level binarization methods. The framework uses a binarization wrapper to enhance the performance of the gray-level binarization. Nonlinear preprocessing of the individual spectral bands is used to enhance the textual information. An evolutionary optimizer is considered to obtain the optimal and some suboptimal 3-band subspaces from which an ensemble of experts is then formed. The framework is applied to a ground truth multispectral dataset with promising results. In addition, a generalization to the cross-validation approach is developed that not only evaluates generalizability of the framework, it also provides a practical instance of the selected experts that could be then applied to unseen inputs despite the small size of the given ground truth dataset.
Modified Hausdorff Fractal Dimension (MHFD)
May 14, 2015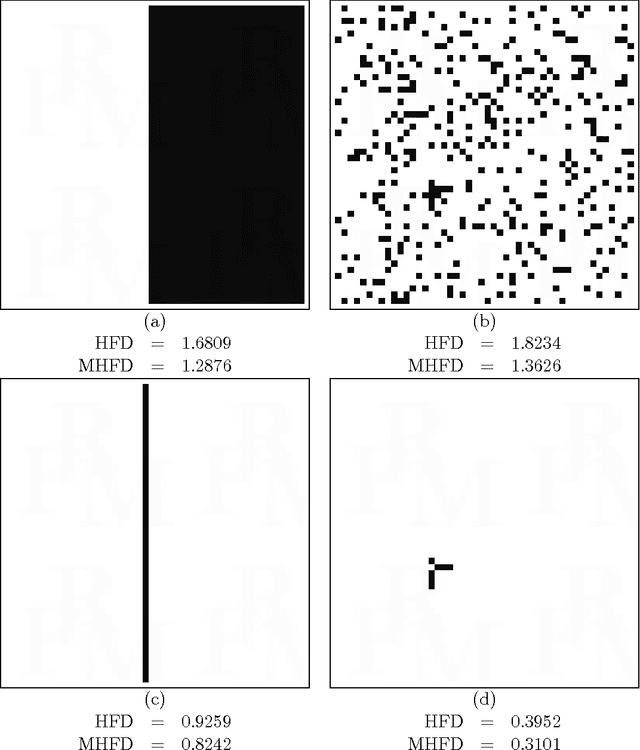
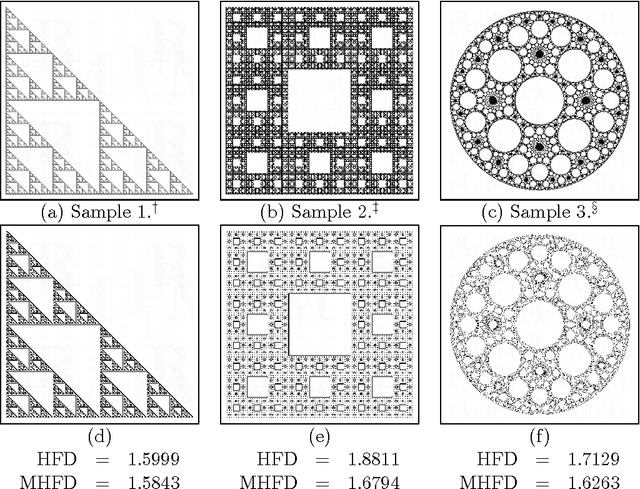
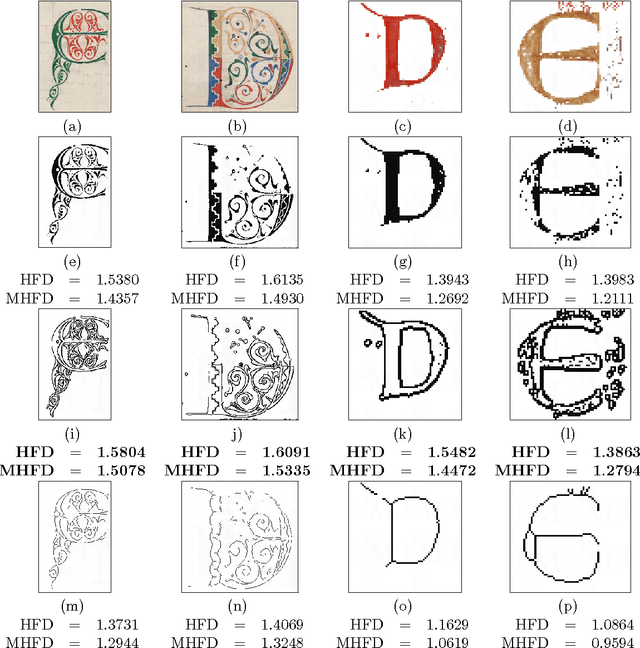

Abstract:The Hausdorff fractal dimension has been a fast-to-calculate method to estimate complexity of fractal shapes. In this work, a modified version of this fractal dimension is presented in order to make it more robust when applied in estimating complexity of non-fractal images. The modified Hausdorff fractal dimension stands on two features that weaken the requirement of presence of a shape and also reduce the impact of the noise possibly presented in the input image. The new algorithm has been evaluated on a set of images of different character with promising performance.
Spiralet Sparse Representation
Apr 15, 2014
Abstract:This is the first report on Working Paper WP-RFM-14-01. The potential and capability of sparse representations is well-known. However, their (multivariate variable) vectorial form, which is completely fine in many fields and disciplines, results in removal and filtering of important "spatial" relations that are implicitly carried by two-dimensional [or multi-dimensional] objects, such as images. In this paper, a new approach, called spiralet sparse representation, is proposed in order to develop an augmented representation and therefore a modified sparse representation and theory, which is capable to preserve the data associated to the spatial relations.
A maximal-information color to gray conversion method for document images: Toward an optimal grayscale representation for document image binarization
Jun 26, 2013



Abstract:A novel method to convert color/multi-spectral images to gray-level images is introduced to increase the performance of document binarization methods. The method uses the distribution of the pixel data of the input document image in a color space to find a transformation, called the dual transform, which balances the amount of information on all color channels. Furthermore, in order to reduce the intensity variations on the gray output, a color reduction preprocessing step is applied. Then, a channel is selected as the gray value representation of the document image based on the homogeneity criterion on the text regions. In this way, the proposed method can provide a luminance-independent contrast enhancement. The performance of the method is evaluated against various images from two databases, the ICDAR'03 Robust Reading, the KAIST and the DIBCO'09 datasets, subjectively and objectively with promising results. The ground truth images for the images from the ICDAR'03 Robust Reading dataset have been created manually by the authors.
Unsupervised ensemble of experts (EoE) framework for automatic binarization of document images
May 29, 2013



Abstract:In recent years, a large number of binarization methods have been developed, with varying performance generalization and strength against different benchmarks. In this work, to leverage on these methods, an ensemble of experts (EoE) framework is introduced, to efficiently combine the outputs of various methods. The proposed framework offers a new selection process of the binarization methods, which are actually the experts in the ensemble, by introducing three concepts: confidentness, endorsement and schools of experts. The framework, which is highly objective, is built based on two general principles: (i) consolidation of saturated opinions and (ii) identification of schools of experts. After building the endorsement graph of the ensemble for an input document image based on the confidentness of the experts, the saturated opinions are consolidated, and then the schools of experts are identified by thresholding the consolidated endorsement graph. A variation of the framework, in which no selection is made, is also introduced that combines the outputs of all experts using endorsement-dependent weights. The EoE framework is evaluated on the set of participating methods in the H-DIBCO'12 contest and also on an ensemble generated from various instances of grid-based Sauvola method with promising performance.
* 6-page version, Accepted to be presented in ICDAR'13
Curved Space Optimization: A Random Search based on General Relativity Theory
Aug 10, 2012
Abstract:Designing a fast and efficient optimization method with local optima avoidance capability on a variety of optimization problems is still an open problem for many researchers. In this work, the concept of a new global optimization method with an open implementation area is introduced as a Curved Space Optimization (CSO) method, which is a simple probabilistic optimization method enhanced by concepts of general relativity theory. To address global optimization challenges such as performance and convergence, this new method is designed based on transformation of a random search space into a new search space based on concepts of space-time curvature in general relativity theory. In order to evaluate the performance of our proposed method, an implementation of CSO is deployed and its results are compared on benchmark functions with state-of-the art optimization methods. The results show that the performance of CSO is promising on unimodal and multimodal benchmark functions with different search space dimension sizes.
A prototype system for handwritten sub-word recognition: Toward Arabic-manuscript transliteration
Nov 14, 2011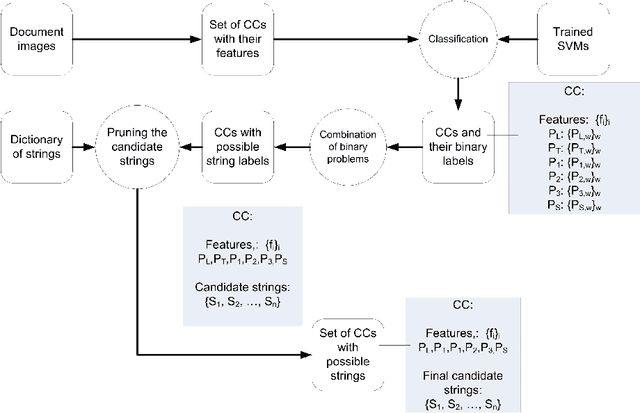


Abstract:A prototype system for the transliteration of diacritics-less Arabic manuscripts at the sub-word or part of Arabic word (PAW) level is developed. The system is able to read sub-words of the input manuscript using a set of skeleton-based features. A variation of the system is also developed which reads archigraphemic Arabic manuscripts, which are dot-less, into archigraphemes transliteration. In order to reduce the complexity of the original highly multiclass problem of sub-word recognition, it is redefined into a set of binary descriptor classifiers. The outputs of trained binary classifiers are combined to generate the sequence of sub-word letters. SVMs are used to learn the binary classifiers. Two specific Arabic databases have been developed to train and test the system. One of them is a database of the Naskh style. The initial results are promising. The systems could be trained on other scripts found in Arabic manuscripts.
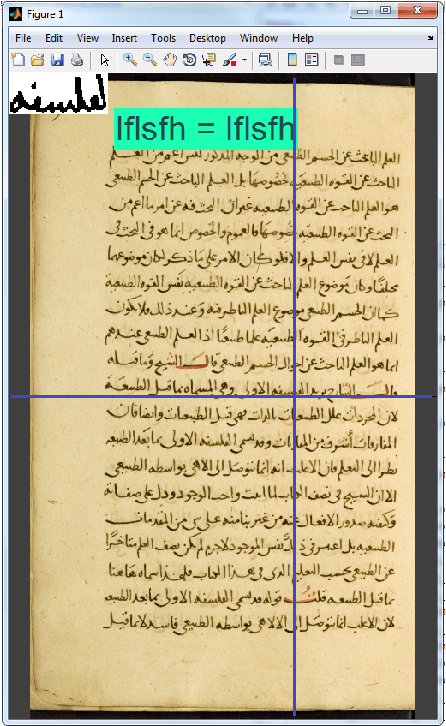
Beyond pixels and regions: A non local patch means method for content-level restoration, enhancement, and reconstruction of degraded document images
Nov 08, 2011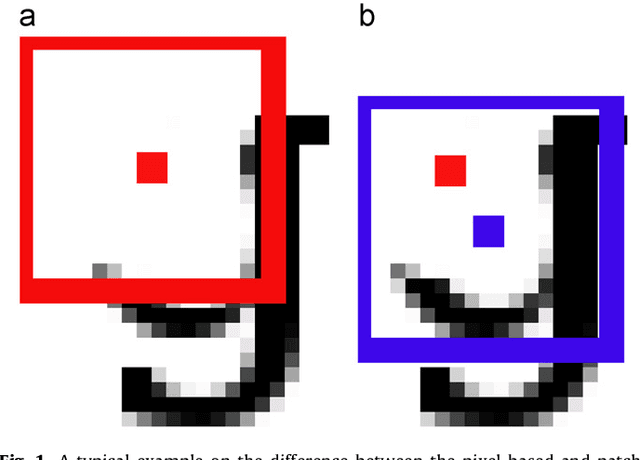
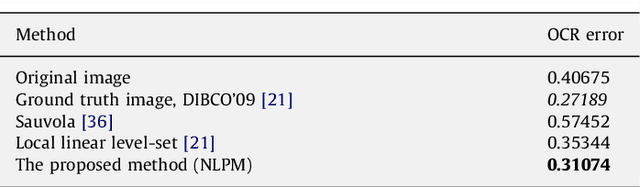
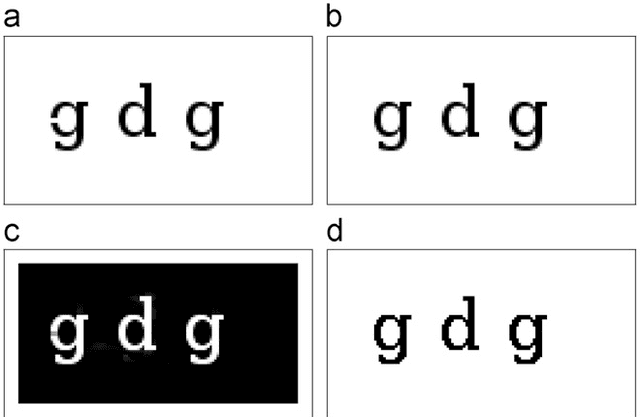
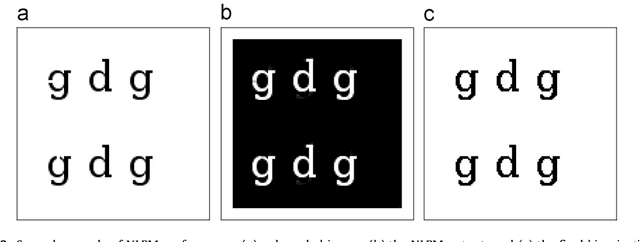
Abstract:A patch-based non-local restoration and reconstruction method for preprocessing degraded document images is introduced. The method collects relative data from the whole input image, while the image data are first represented by a content-level descriptor based on patches. This patch-equivalent representation of the input image is then corrected based on similar patches identified using a modified genetic algorithm (GA) resulting in a low computational load. The corrected patch-equivalent is then converted to the output restored image. The fact that the method uses the patches at the content level allows it to incorporate high-level restoration in an objective and self-sufficient way. The method has been applied to several degraded document images, including the DIBCO'09 contest dataset with promising results.
* This paper has been withdrawn by the author to avoid duplication on the DBLP bibliography
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge