Renhao Cui
Towards Successful Social Media Advertising: Predicting the Influence of Commercial Tweets
Oct 28, 2019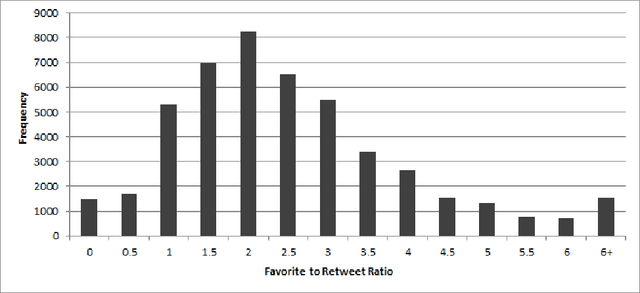
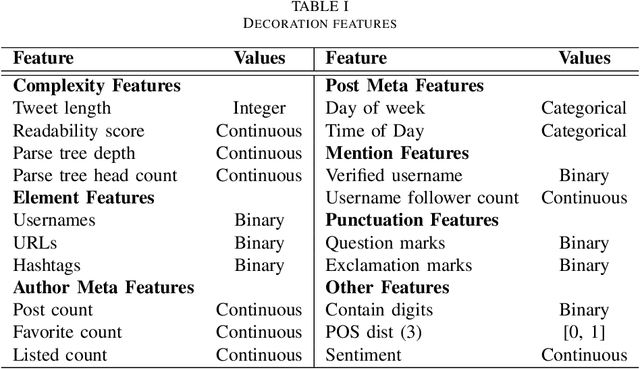
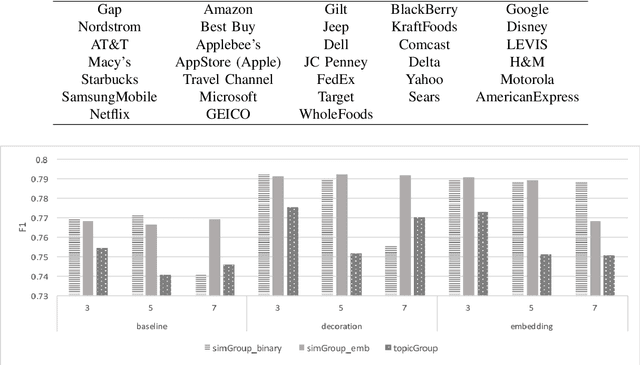
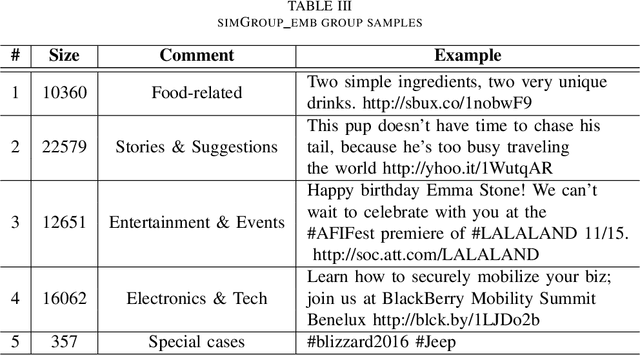
Abstract:Businesses communicate using Twitter for a variety of reasons -- to raise awareness of their brands, to market new products, to respond to community comments, and to connect with their customers and potential customers in a targeted manner. For businesses to do this effectively, they need to understand which content and structural elements about a tweet make it influential, that is, widely liked, followed, and retweeted. This paper presents a systematic methodology for analyzing commercial tweets, and predicting the influence on their readers. Our model, which use a combination of decoration and meta features, outperforms the prediction ability of the baseline model as well as the tweet embedding model. Further, in order to demonstrate a practical use of this work, we show how an unsuccessful tweet may be engineered (for example, reworded) to increase its potential for success.
Comparison of Quality Indicators in User-generated Content Using Social Media and Scholarly Text
Oct 24, 2019


Abstract:Predicting the quality of a text document is a critical task when presented with the problem of measuring the performance of a document before its release. In this work, we evaluate various features including those extracted from the text content (textual) and those describing higher-level characteristics of the text (meta) features that are not directly available from the text, and show how these features inform prediction of document quality in different ways. Moreover, we also compare our methods on both social user-generated data such as tweets, and scholarly user-generated data such as academic articles, showing how the same features differently influence prediction of quality across these disparate domains.
Tweets Can Tell: Activity Recognition using Hybrid Long Short-Term Memory Model
Jul 10, 2019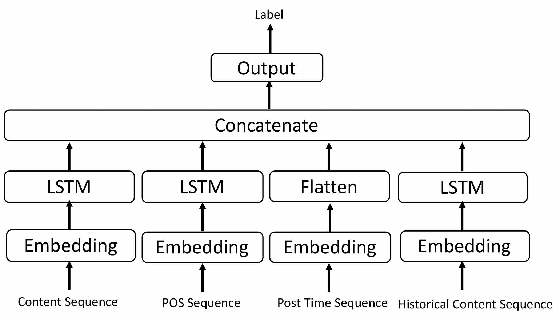
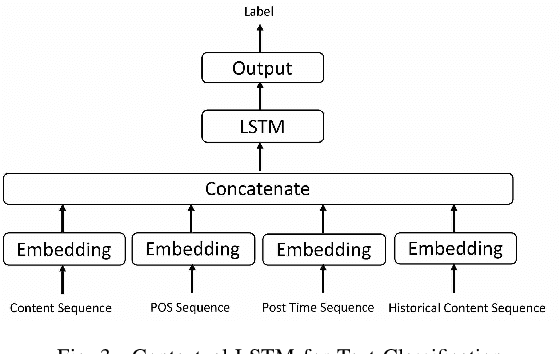
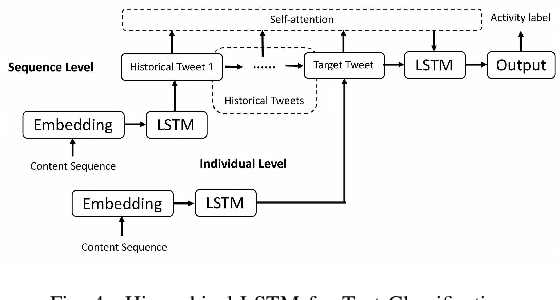
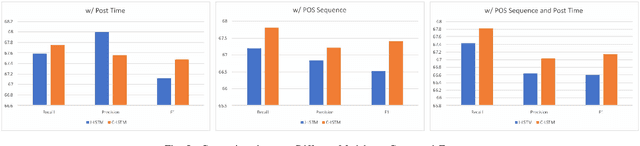
Abstract:This paper presents techniques to detect the "offline" activity a person is engaged in when she is tweeting (such as dining, shopping or entertainment), in order to create a dynamic profile of the user, for uses such as better targeting of advertisements. To this end, we propose a hybrid LSTM model for rich contextual learning, along with studies on the effects of applying and combining multiple LSTM based methods with different contextual features. The hybrid model is shown to outperform a set of baselines and state-of-the-art methods. Finally, this paper presents an orthogonal validation with a real-case application. Our model generates an offline activity analysis for the followers of several well-known accounts, which is quite representative of the expected characteristics of these accounts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge