Rashindra Manniesing
Adversarial cycle-consistent synthesis of cerebral microbleeds for data augmentation
Jan 16, 2021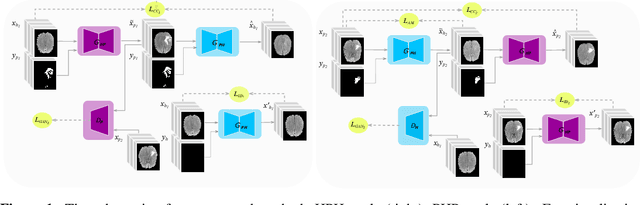
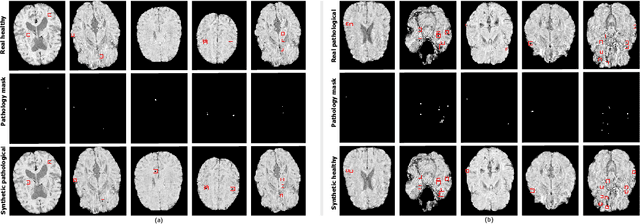
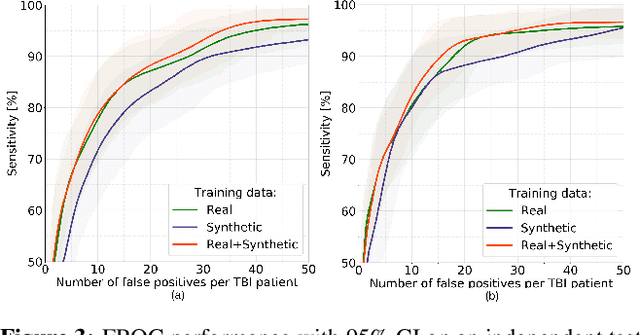
Abstract:We propose a novel framework for controllable pathological image synthesis for data augmentation. Inspired by CycleGAN, we perform cycle-consistent image-to-image translation between two domains: healthy and pathological. Guided by a semantic mask, an adversarially trained generator synthesizes pathology on a healthy image in the specified location. We demonstrate our approach on an institutional dataset of cerebral microbleeds in traumatic brain injury patients. We utilize synthetic images generated with our method for data augmentation in cerebral microbleeds detection. Enriching the training dataset with synthetic images exhibits the potential to increase detection performance for cerebral microbleeds in traumatic brain injury patients.
Student Beats the Teacher: Deep Neural Networks for Lateral Ventricles Segmentation in Brain MR
Mar 03, 2018Abstract:Ventricular volume and its progression are known to be linked to several brain diseases such as dementia and schizophrenia. Therefore accurate measurement of ventricle volume is vital for longitudinal studies on these disorders, making automated ventricle segmentation algorithms desirable. In the past few years, deep neural networks have shown to outperform the classical models in many imaging domains. However, the success of deep networks is dependent on manually labeled data sets, which are expensive to acquire especially for higher dimensional data in the medical domain. In this work, we show that deep neural networks can be trained on much-cheaper-to-acquire pseudo-labels (e.g., generated by other automated less accurate methods) and still produce more accurate segmentations compared to the quality of the labels. To show this, we use noisy segmentation labels generated by a conventional region growing algorithm to train a deep network for lateral ventricle segmentation. Then on a large manually annotated test set, we show that the network significantly outperforms the conventional region growing algorithm which was used to produce the training labels for the network. Our experiments report a Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of $0.874$ for the trained network compared to $0.754$ for the conventional region growing algorithm ($p < 0.001$).
* 7 pages, 4 figures, SPIE Medical Imaging 2018 Conference paper
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge