Randy Tan
Classification of Lung Pathologies in Neonates using Dual Tree Complex Wavelet Transform
Feb 17, 2023Abstract:Annually 8500 neonatal deaths are reported in the US due to respiratory failure. Recently, Lung Ultrasound (LUS), due to its radiation free nature, portability, and being cheaper is gaining wide acceptability as a diagnostic tool for lung conditions. However, lack of highly trained medical professionals has limited its use especially in remote areas. To address this, an automated screening system that captures characteristics of the LUS patterns can be of significant assistance to clinicians who are not experts in lung ultrasound (LUS) images. In this paper, we propose a feature extraction method designed to quantify the spatially-localized line patterns and texture patterns found in LUS images. Using the dual-tree complex wavelet transform (DTCWT) and four types of common image features we propose a method to classify the LUS images into 6 common neonatal lung conditions. These conditions are normal lung, pneumothorax (PTX), transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), chronic lung disease (CLD) and consolidation (CON) that could be pneumonia or atelectasis. The proposed method using DTCWT decomposition extracted global statistical, grey-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), grey-level run length matrix (GLRLM) and linear binary pattern (LBP) features to be fed to a linear discriminative analysis (LDA) based classifier. Using 15 best DTCWT features along with 3 clinical features the proposed approach achieved a per-image classification accuracy of 92.78% with a balanced dataset containing 720 images from 24 patients and 74.39% with the larger unbalanced dataset containing 1550 images from 42 patients. Likewise, the proposed method achieved a maximum per-subject classification accuracy of 81.53% with 43 DTCWT features and 3 clinical features using the balanced dataset and 64.97% with 13 DTCWT features and 3 clinical features using the unbalanced dataset.
Locality Guided Neural Networks for Explainable Artificial Intelligence
Jul 12, 2020
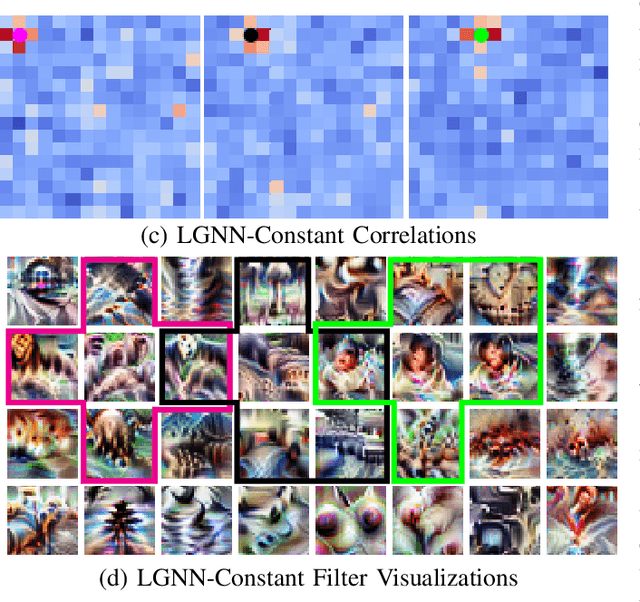
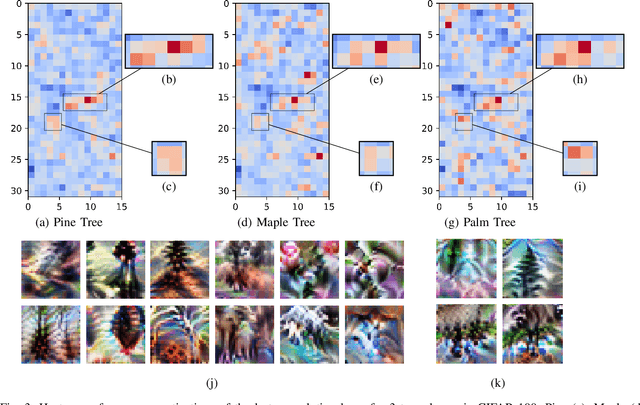
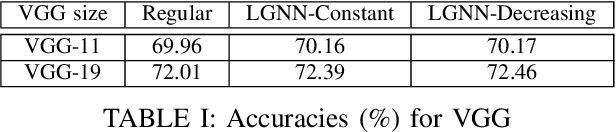
Abstract:In current deep network architectures, deeper layers in networks tend to contain hundreds of independent neurons which makes it hard for humans to understand how they interact with each other. By organizing the neurons by correlation, humans can observe how clusters of neighbouring neurons interact with each other. In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm for back propagation, called Locality Guided Neural Network(LGNN) for training networks that preserves locality between neighbouring neurons within each layer of a deep network. Heavily motivated by Self-Organizing Map (SOM), the goal is to enforce a local topology on each layer of a deep network such that neighbouring neurons are highly correlated with each other. This method contributes to the domain of Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI), which aims to alleviate the black-box nature of current AI methods and make them understandable by humans. Our method aims to achieve XAI in deep learning without changing the structure of current models nor requiring any post processing. This paper focuses on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), but can theoretically be applied to any type of deep learning architecture. In our experiments, we train various VGG and Wide ResNet (WRN) networks for image classification on CIFAR100. In depth analyses presenting both qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our method is capable of enforcing a topology on each layer while achieving a small increase in classification accuracy
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge